The Dissected Horse

The Dissected Horse (15th century?) Pictorial Scroll of Hippiatry, Azabu University, Tokyo – Buddhist monks introduced veterinary medicine to Japan, and they also infiltrated animal medicine with religious connotations. There are several different schools of hippiatry painting scrolls in Japan, with slightly different contents, but they all include anatomical diagrams of the internal organs of […]
Diagrams of the internal organs
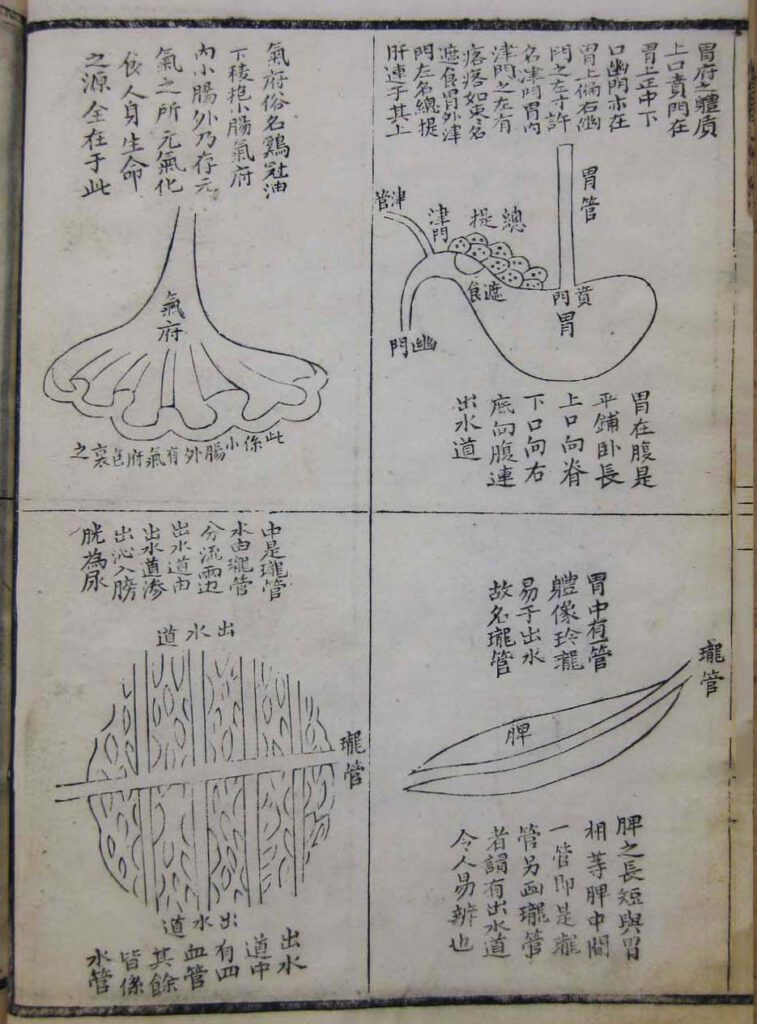
Diagrams of the internal organs from Wang Qingren (1768-1831), Correcting the Errors of Doctors (Yilin gaicuo), first printed in 1830. Jinqi shuye deji woodblock edition, 1847. In the library collection of the Needham Research Institute – Besides revising older depictions of the organs, Wang focused attention on structures that had not been previously discussed in medical […]
Diagram of the heart
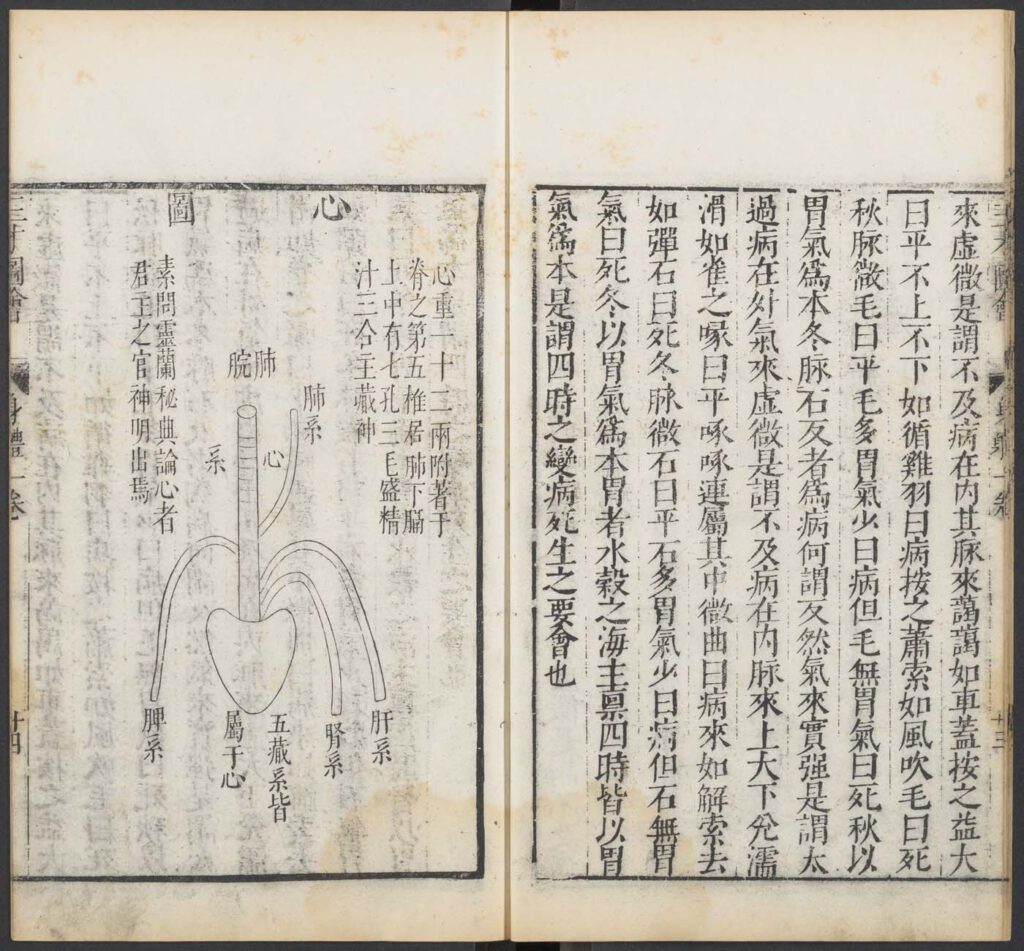
Diagram of the heart from Wang Qi (jinshi degree holder of 1565), Collected Diagrams of Heaven, Earth, and Man (Sancai tuhui), Chongzhen reign (1628-44) reprint of 1609 edition. In the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – This famous encyclopedia was a collection of illustrations of myriad aspects of the “three realms” of Heaven, […]
The diagram of the stomach

The diagram of the stomach from Zhang Jiebin (1563-1640), Illustrated Wing of the “Classified Canon” (Leijing tuyi), woodblock edition, preface dated 1624 From the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – This image of the stomach accompanies Zhang’s illustration of the pathway of the Foot Yang Brightness Stomach Channel. The upper text begins with […]
The hand lesser yin heart channel

The hand lesser yin heart channel (two facing pages) from Zhang Jiebin (1563-1640), Illustrated Wing of the “Classified Canon” (Leijing tuyi), woodblock edition, preface dated 1624. From the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – In writings on acupuncture, it became common to pair an image of an internal organ with an image of […]
Diagram of the Inner Landscape
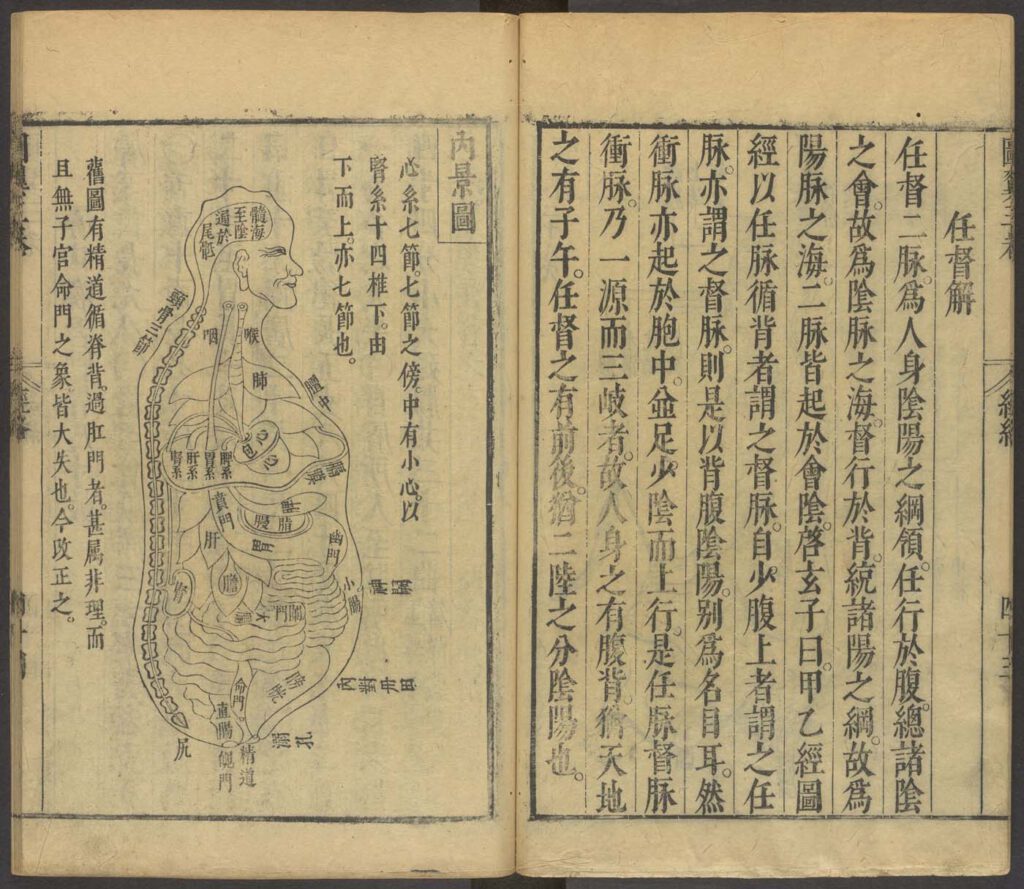
Diagram of the inner landscape from Zhang Jiebin (1563-1640), Illustrated Wing of the “Classified Canon” (Leijing tuyi), woodblock edition, preface dated 1624. From the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – In his magnum opus, The Classified Canon (Leijing), the physician Zhang Jiebin reorganized the contents of the Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon by topic. […]
Master Yan Luo’s head maps • frontal view and southwards looking
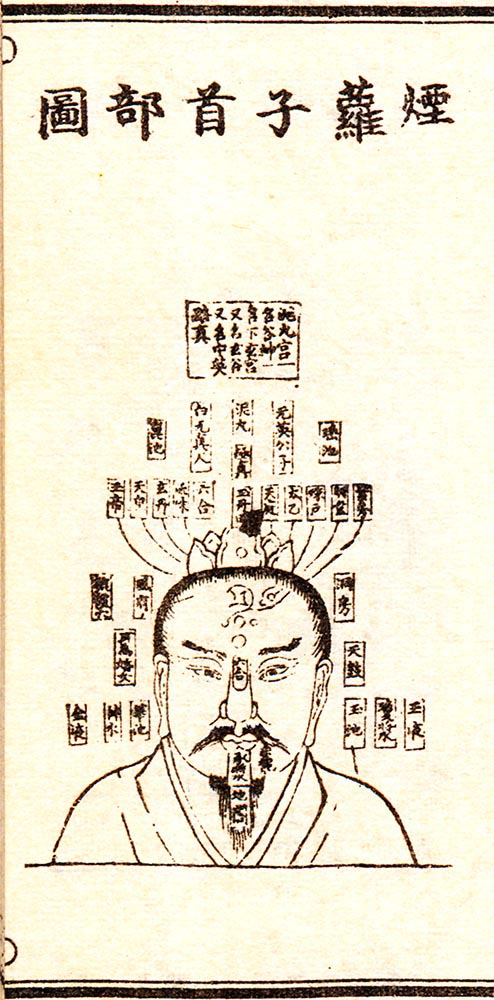
This page is viewed best with a large screen. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 B ‘Master Yan Luo’s map of courting the perfected’ (Ti ke ge, 2b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 […]
