Grotesque figurine
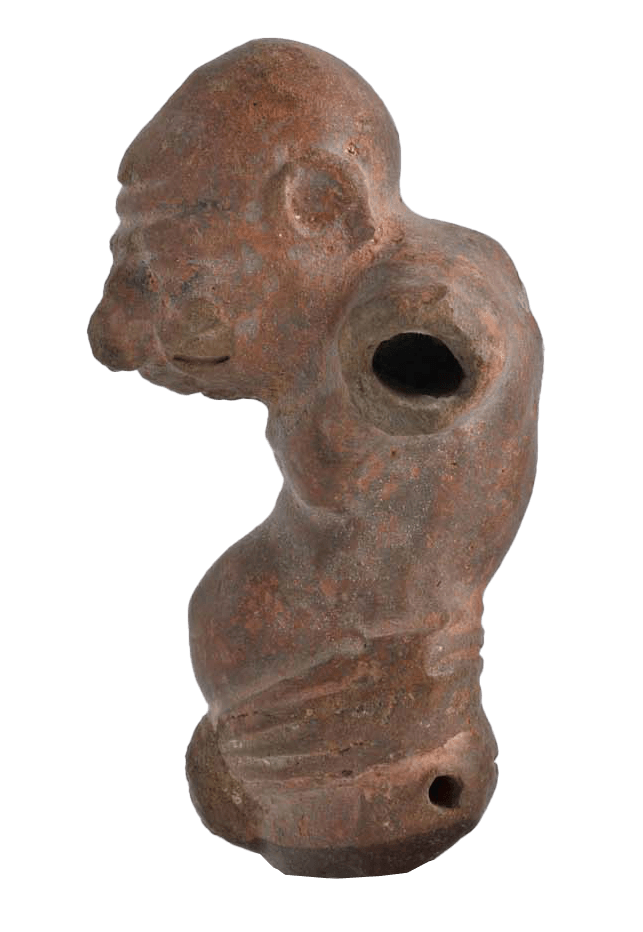
Grotesque terracotta figurine 3rd century BCE–3rd century CE (?) © 2023, Benaki Museum, Athens. Benaki Museum inv. No 12793 – This Hellenistic terracotta, part of the Benaki Museum collection in Athens, depicts with hyper-realistic traits an old, and/or ‘disabled’ man with a protruding pot belly, achieving a grotesque effect and signalling a pathology while offering […]
Marble tombstone of an Athenian physician
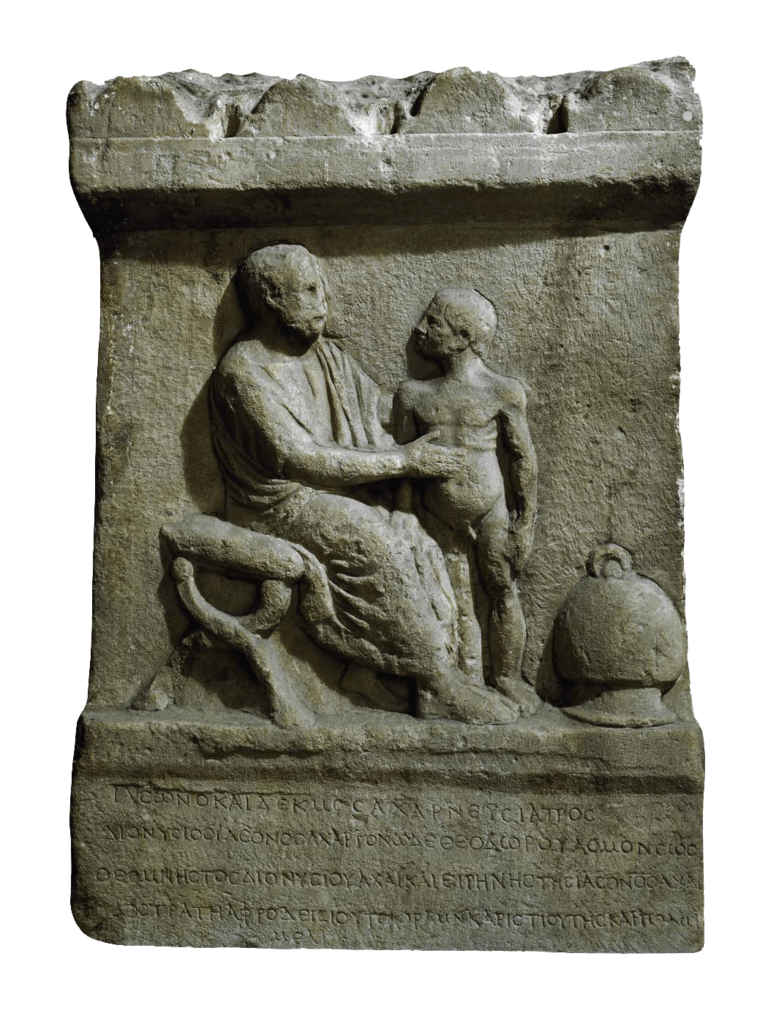

Athens, 2nd century CE
Maps of the inner sceneries • ventral and dorsal view
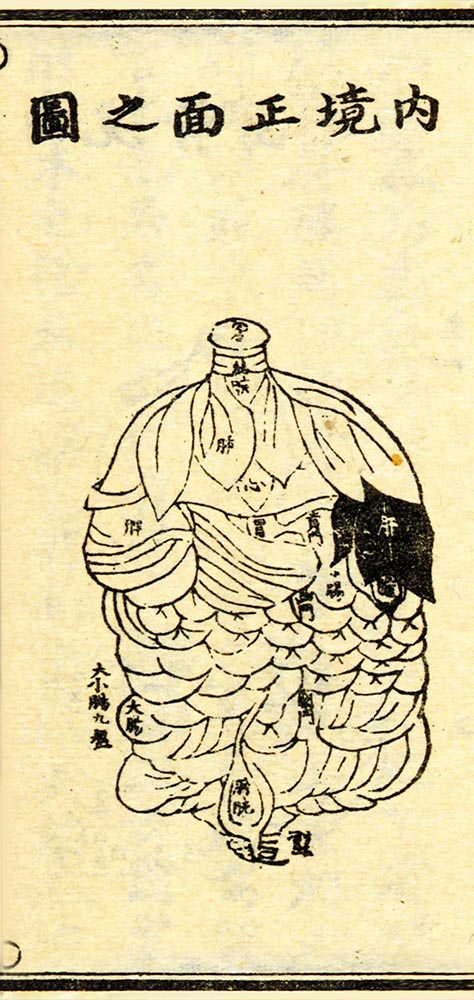

This page is viewed best with a large screen. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F ‘Map of the inner sceneries in dorsal view’ (Ti ke ge, 3b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 E ‘Map of the inner sceneries in ventral […]
The spleen-stomach system
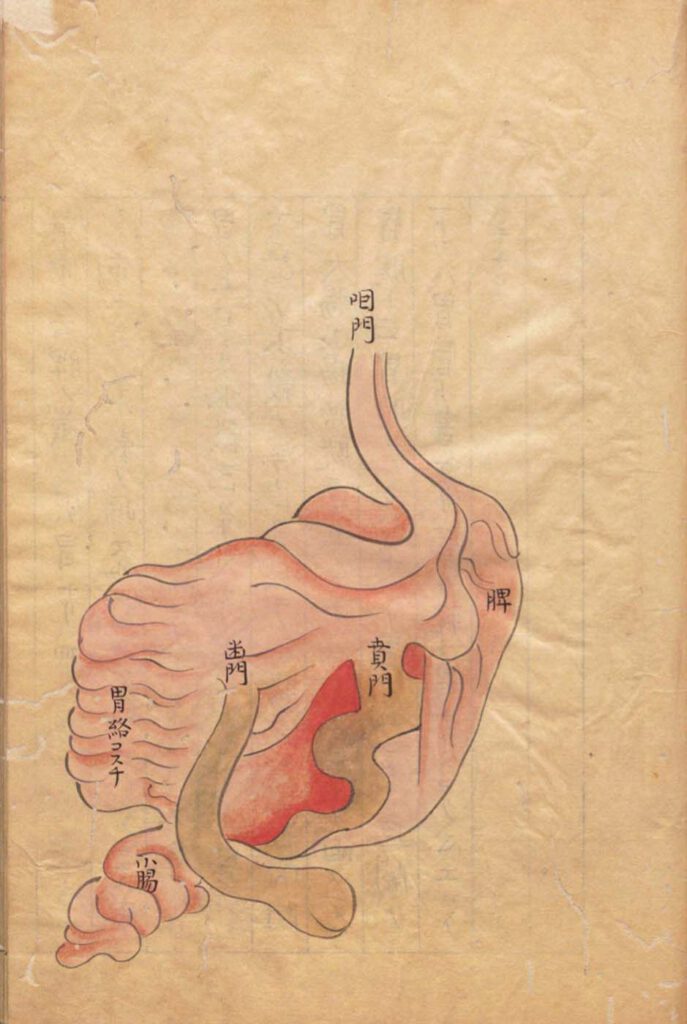
A B The spleen–stomach system A No title. The spleen-stomach system. Kajiwara Shōzen 梶原性全 (1265–1337) Man’anpo 万安方, 1315–27, scroll 54. Edo 江戸 period (1603–1868) manuscript. National Archives of Japan. B ‘Illustration of the spleen-stomach system’, Piweibao xi tu 脾胃胞系圖. Wang Haogu 王好古 (1200–64?) The Great Teaching of Yi Yin’s Decoction Classic Propagated by [Zhang] Zhongjing, Yi […]
The sea of qi and the diaphragm
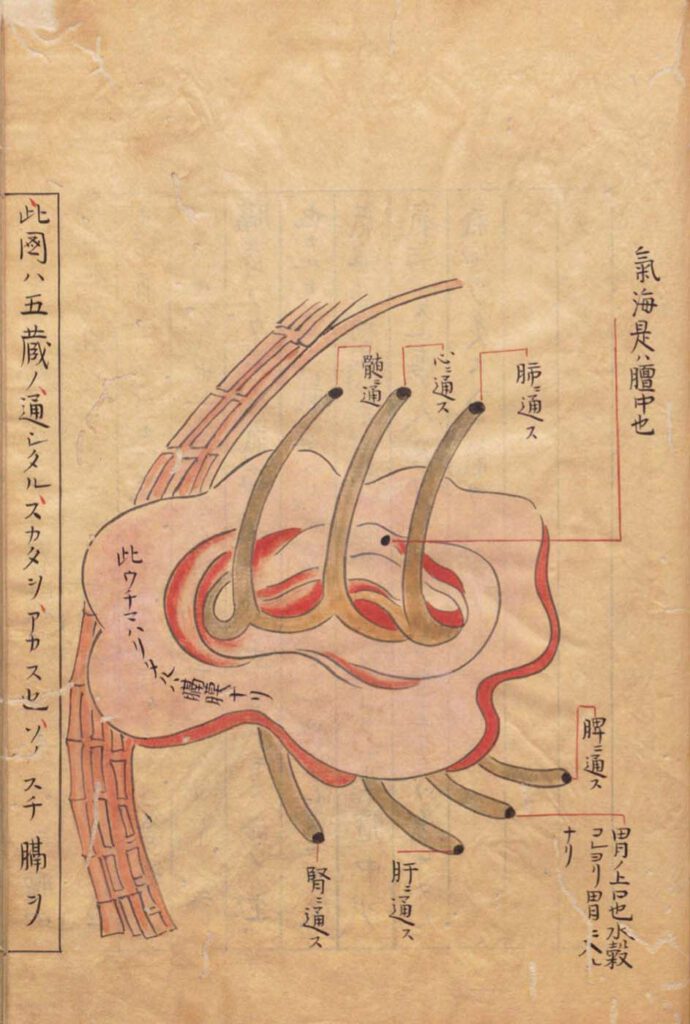
A B The sea of qi and the diaphragm A No title. The sea of qi and the diaphragm. Kajiwara Shōzen 梶原性全 (1265–1337) Man’anpo 万安方, 1315–27, scroll 54. Edo 江戸 period (1603–1868) manuscript. National Archives of Japan. B ‘Illustration of the sea of qi and the diaphragm’, Qihai gemo tu 氣海隔膜圖. Wang Haogu 王好古 (1200–64?) […]
Communication of the connectors of the five solid vessels with the heart.
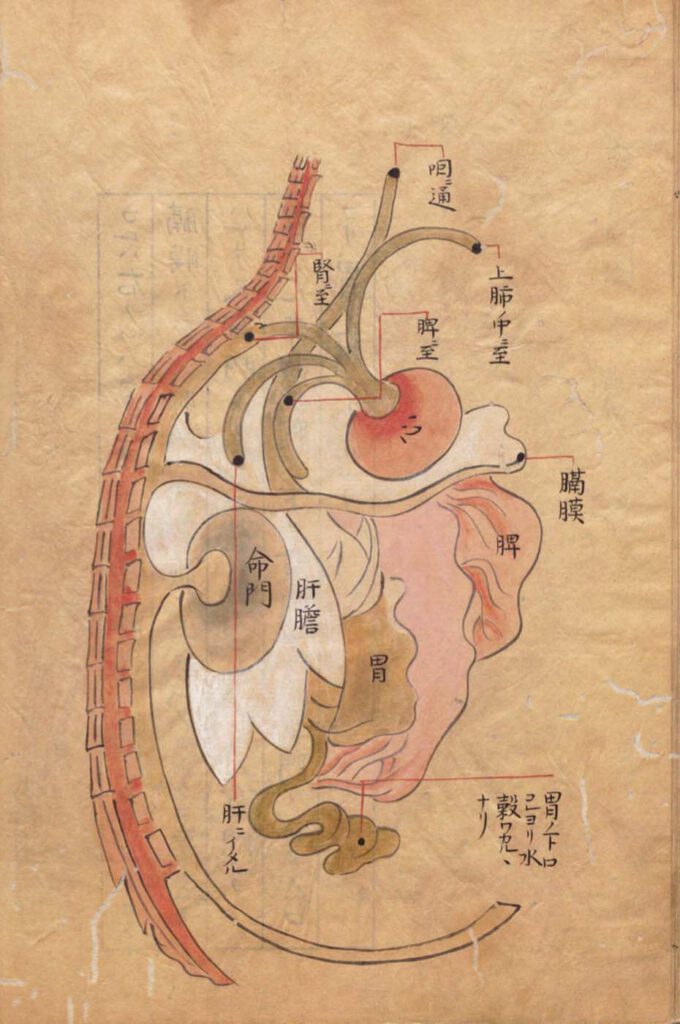
A B Communication of the connectors of the five solid vessels (wu zang) with the heart. A No title. Communication of the connectors of the five solid vessels with the heart. Kajiwara Shōzen 梶原性全 (1265–1337) Man’anpo 万安方, 1315–27, scroll 54. Edo 江戸 period (1603–1868) manuscript. National Archives of Japan. B ‘Illustration of the communication of […]
Canopic Jar Representing the Deity Qebehsenuef
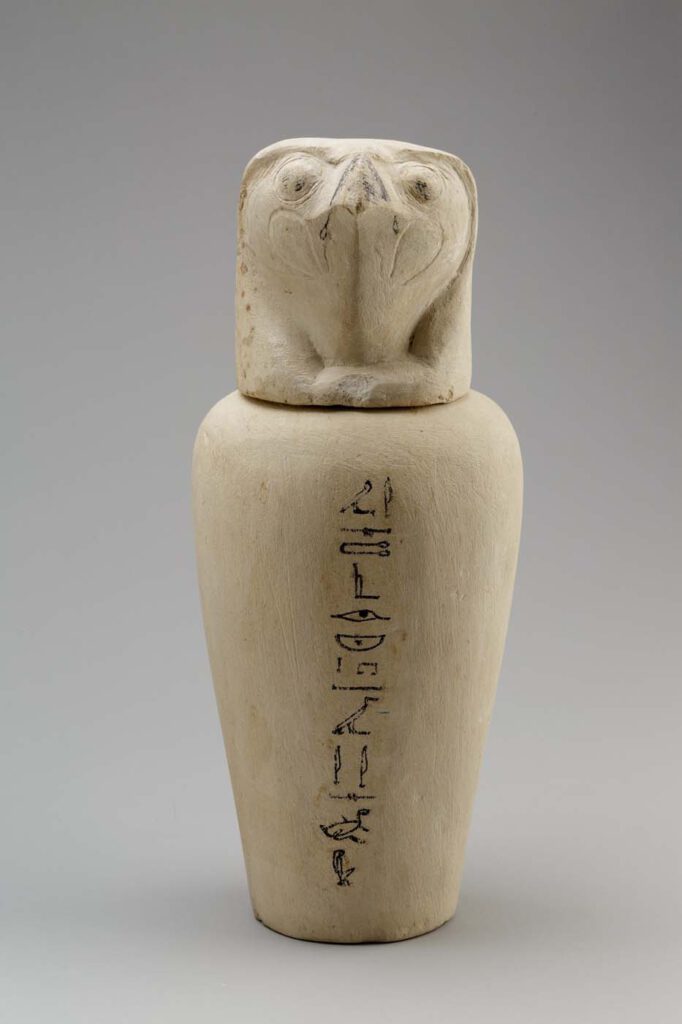

Canopic Jar Representing the Deity Qebehsenuef Photo: Metropolitan Museum of Art – During mummification, the internal organs (excluding the heart, which was generally left in place) were taken out of the body and placed in special containers known in Egyptology as canopic jars. Traditionally, the four canopic jars were connected to four mythological figures known […]
The Spleen and Stomach
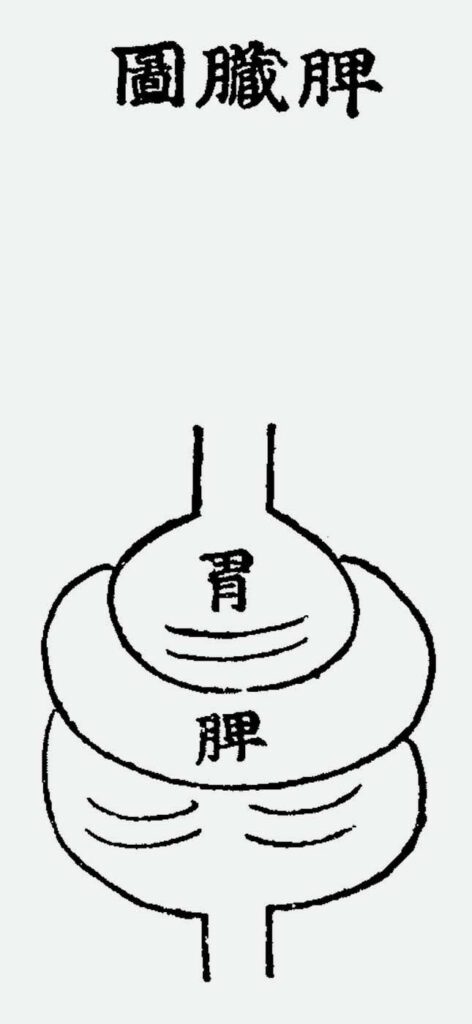
The Spleen and Stomach (from Hǒ Chun, Treasured Mirror of Eastern Medicine). – The spleen helps stomach ki 氣in digesting food and water. The stomach receives food while the spleen is responsible for digesting food. The five viscera and six bowels all receive ki from the stomach. Food passes through the stomach to the intestines. […]
The Spleen
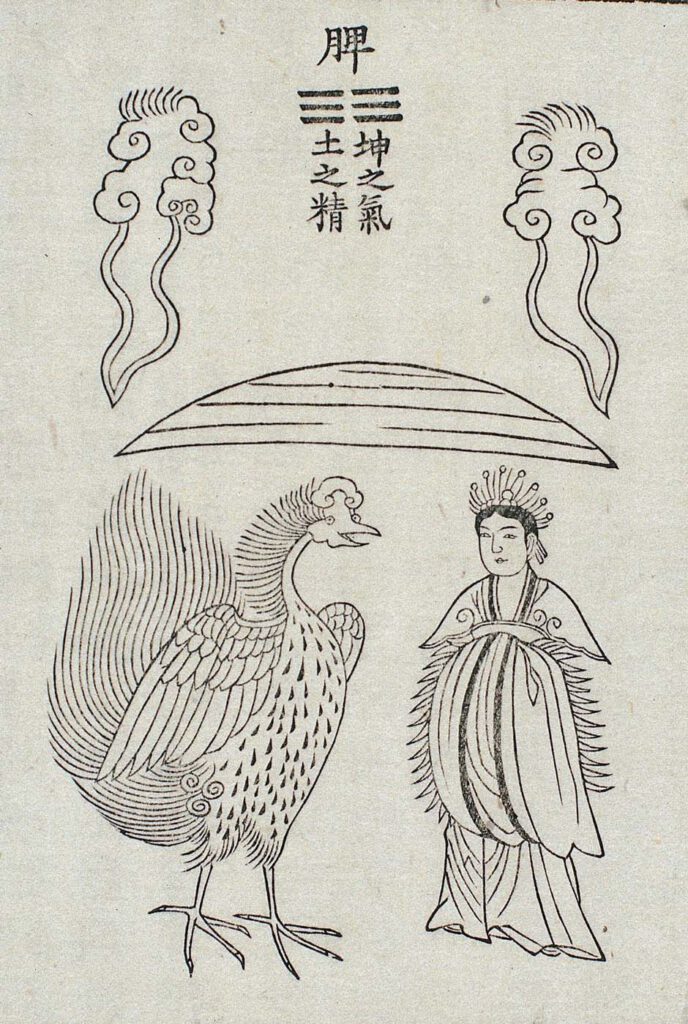

The Spleen organ responsible for digestion (from the Compilation of Medical Prescriptions). – This image appears in the Uibang Yuchwi 醫方類聚 (Compilation of Medical Prescriptions 1445). It draws inspiration from the Chinese physician Hu Yin’s (fl. 848) Huangting Neijing Wuzang Liufu Buxie Tu 黃庭內景五臟六腑補瀉圖(Diagram of the inner landscape of supplementing and reducing the five zang […]
Rock carving of reindeer with intestines
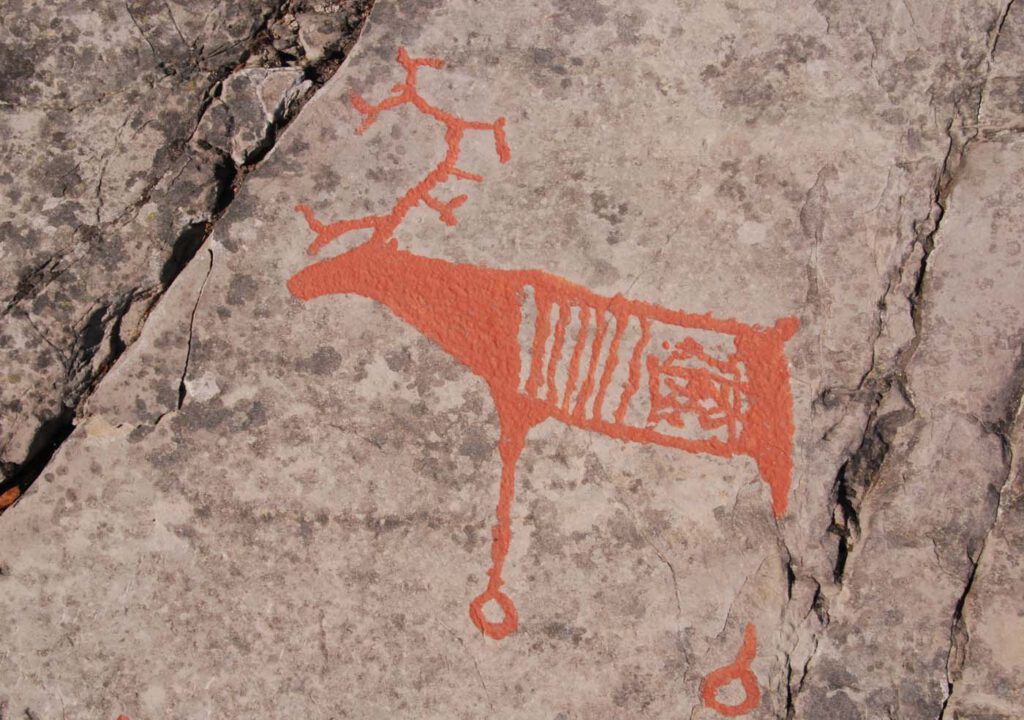

Rock carving of reindeer with intestines. Alta, northern Norway. Photo: Karin Tansem, VAM, Copyright © World Heritage Rock Art Centre – Alta Museum (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) – The large antlers indicate that this is a reindeer bull. The vertical lines in the front part of the torso may represent the ribs and the complex set of lines […]
