Illustration accompanying De Arte Physicali et de Cirurgia
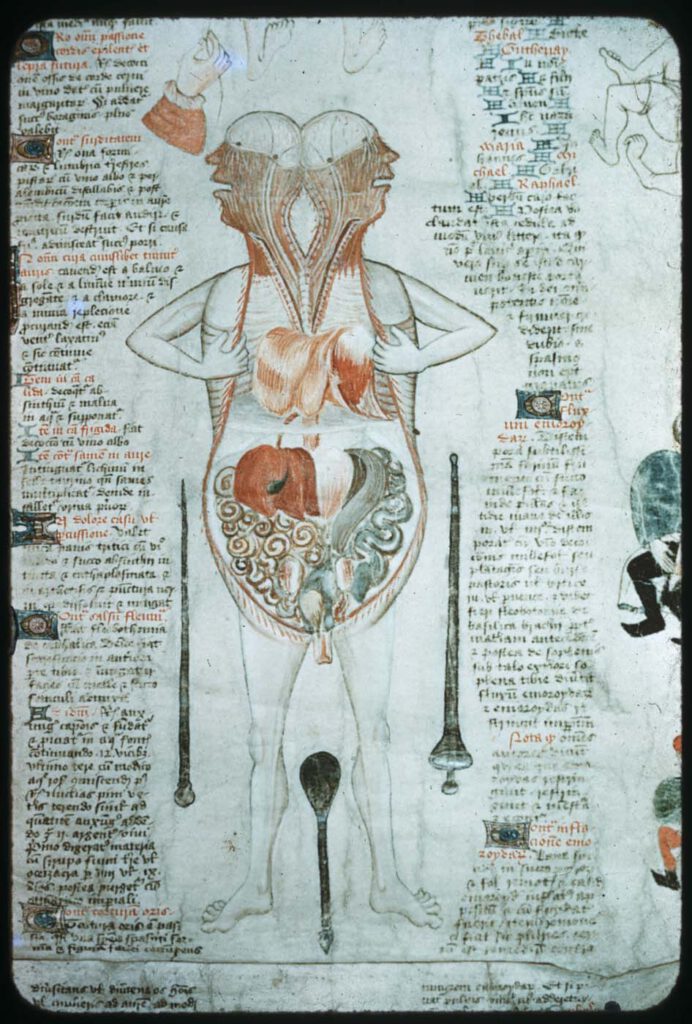
Illustration accompanying De Arte Physicali et de Cirurgia, attributed to John Arderne Stockholm, Kungliga Biblioteket X.118, fol. 6v/6r; c. 1430 – While the frontal approach to anatomical illustration exhibited in the Five/Nine-Figure Series and Guido da Vigevano’s work is most dominant, an alternative, sagittal approach emerged in the medieval period and survives in a few […]
Guido da Vigevano’s Anathomia, Figure 8
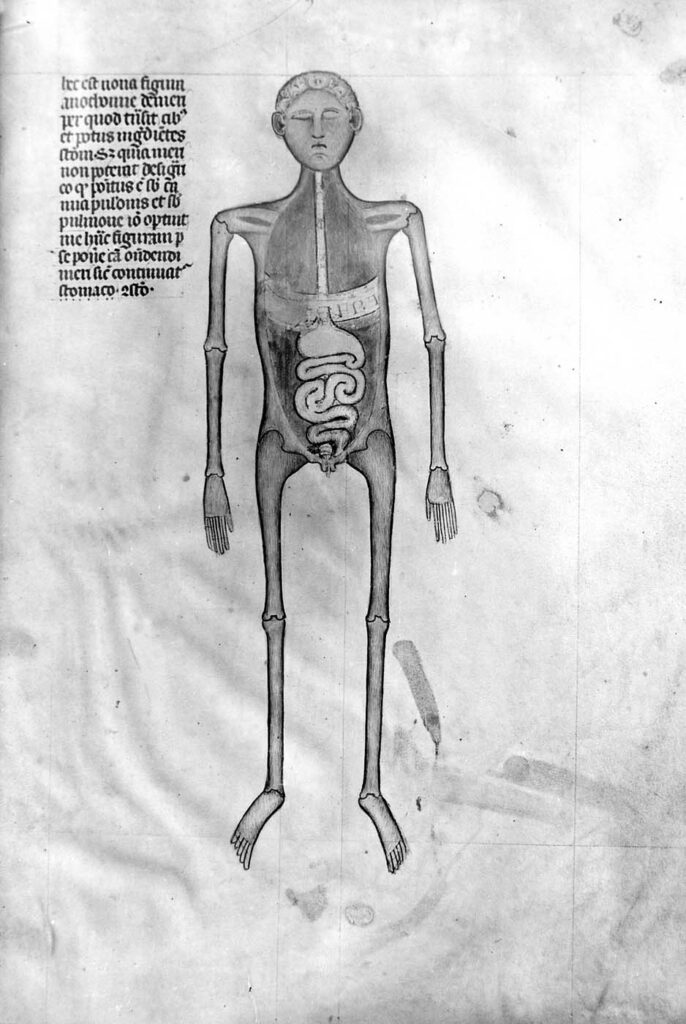
Guido da Vigevano’s Anathomia, Figure 9 (1345) Guido da Vigevano, Anathomia, 1345CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – Although human dissection began to be systematically practiced in Italy in the early 14th century, it was not immediately embraced across Europe. This prompted Guido da Vigevano to produce a series of seventeen illustrations included in his Book of Notable […]
Organs of the abdomen
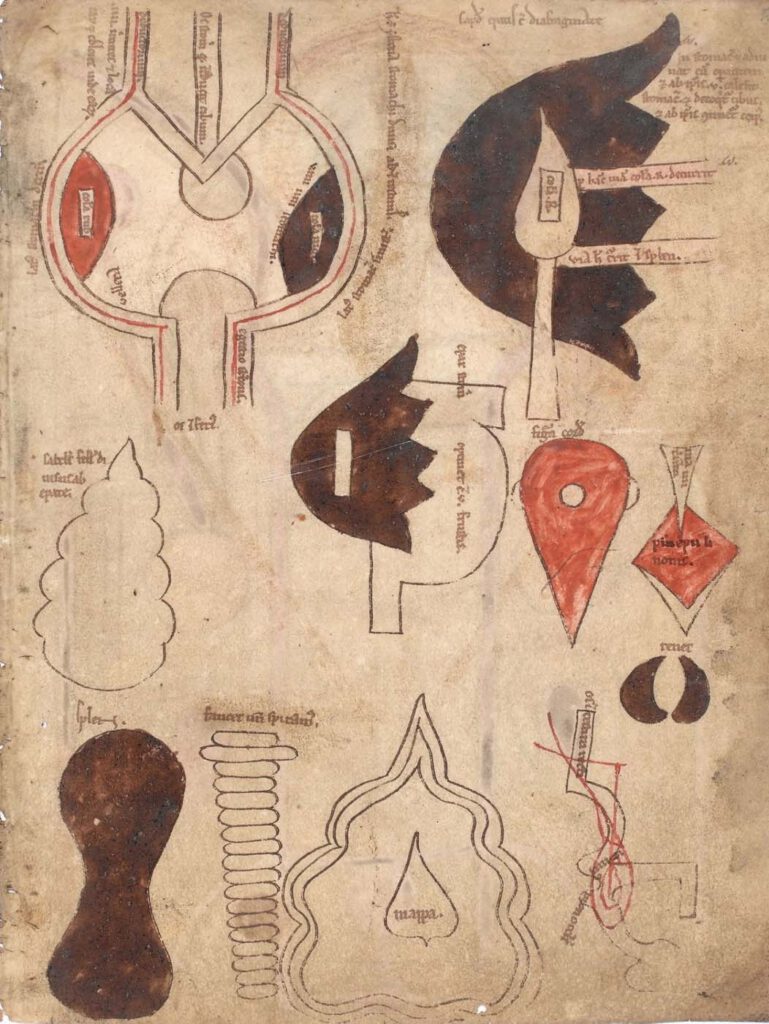
Organs of the abdomen Cambridge, Gonville and Caius College, MS 190/223, fol. 5r; 12th cent. CE Photo: By Permission of the Master and Fellows of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge. – While the five figures representing the five bodily systems are the core of the Five-Figure Series, several iterations include nine figures rather than five, […]
Manchu face, Universal body
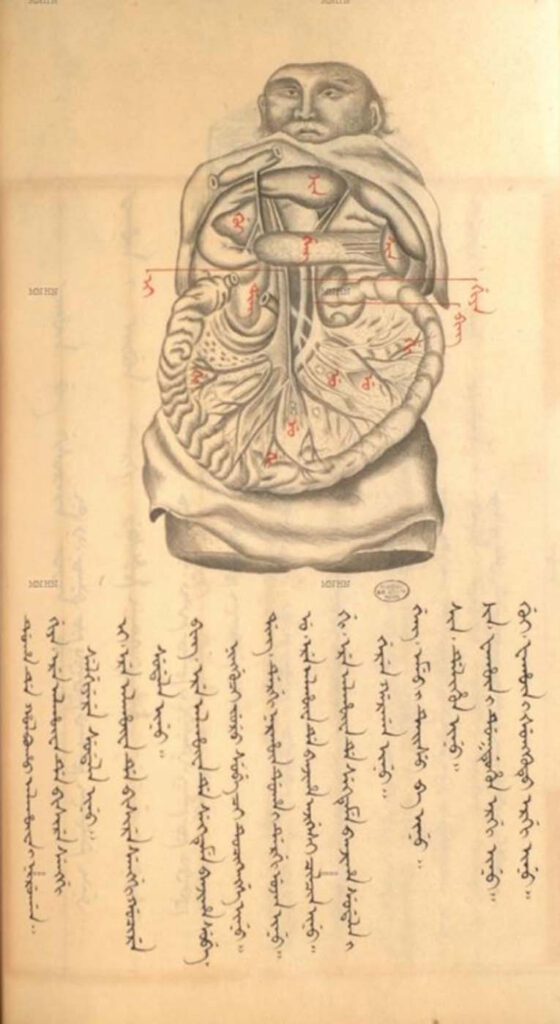
Manchu face, Universal body (Early 18th century) Ge ti ciowan lu bithe, or Manchu Anatomy (based on Thomas Bartholin, Anatomia, 1684), Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, Paris – The Jesuits actively persuaded the Kangxi Emperor to study anatomy. They hoped that he would convert to Christianity while marveling at the wonders of the various parts of […]
The Buddha’s Guts
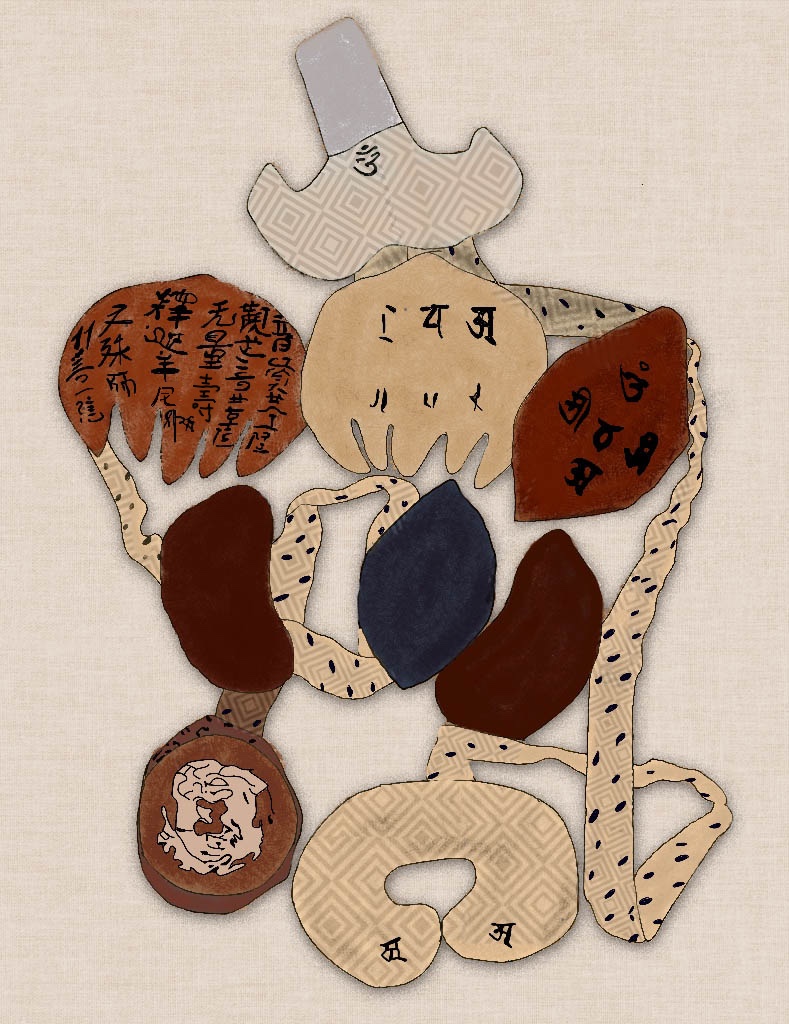

The Buddha’s Guts Digital rendition by Stella Thumiger after ‘ The viscera models in the statue of Sakyamuni’, Seiryōji Monestary, Kyoto (985) – In Medieval China, it was customary to put viscera models in Buddha statues. Some of them are still extent today. This one is the representative, which was brought to Japan from Taizhou, […]
ŠÀ, libbu
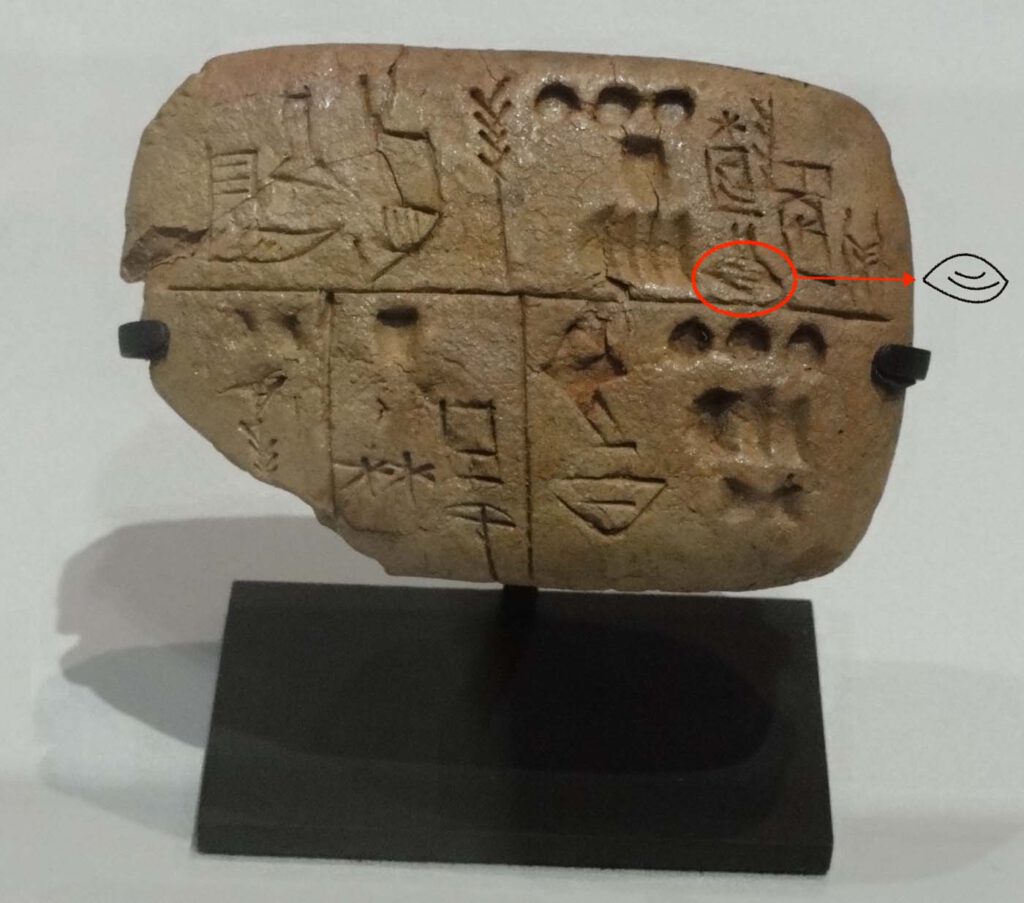

ŠÀ, libbu Detail of sign ŠÀ from AO 29561 (CDLI P005337) Photo: Louvre Museum, Paris, France.CC BY-SA 3.0 DE – The cuneiform sign ŠÀ, libbu in Akkadian, is a general term used to refer to the internal organs of the body, both animal and human. It is translated with “heart” (the original pictogram from which […]
Mask of Huwawa
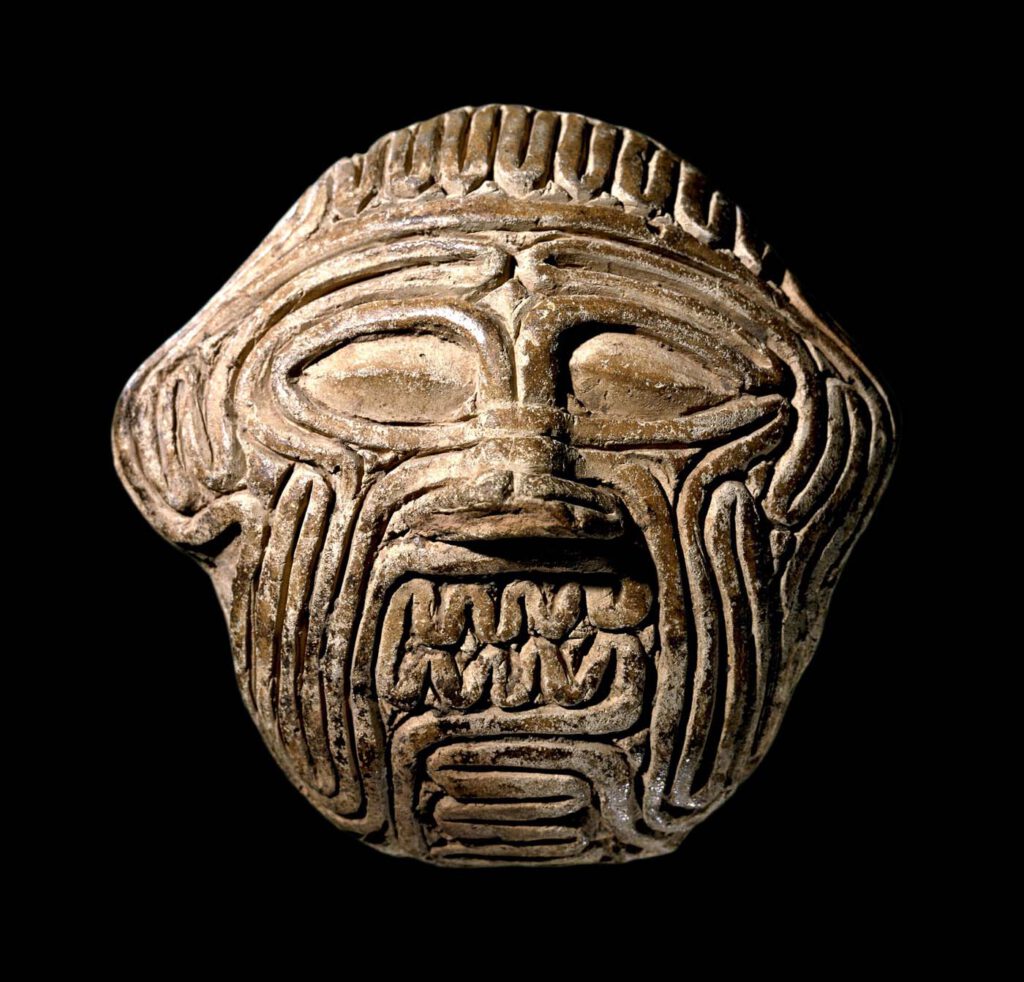

Previous slide Next slide Mask of Huwawa Clay tablet depicting the face of the demon Huwawa (Humbaba), also rendering the intestines of a sheep inspected for divination. British Museum, London (Museum Number: BM 116624), obverse and reverse. Photos: © The Trustees of the British Museum.CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – The coils of intestines reproduced on tīrānū-models […]
Diagrams of the internal organs
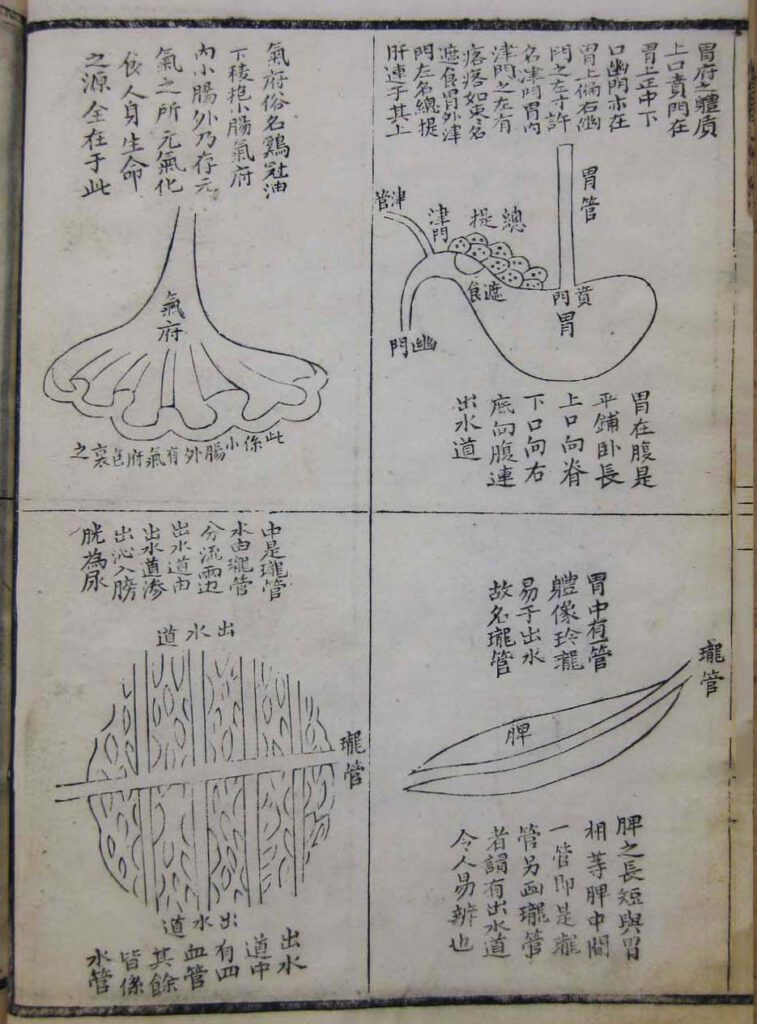
Diagrams of the internal organs from Wang Qingren (1768-1831), Correcting the Errors of Doctors (Yilin gaicuo), first printed in 1830. Jinqi shuye deji woodblock edition, 1847. In the library collection of the Needham Research Institute – Besides revising older depictions of the organs, Wang focused attention on structures that had not been previously discussed in medical […]
Diagram of the heart
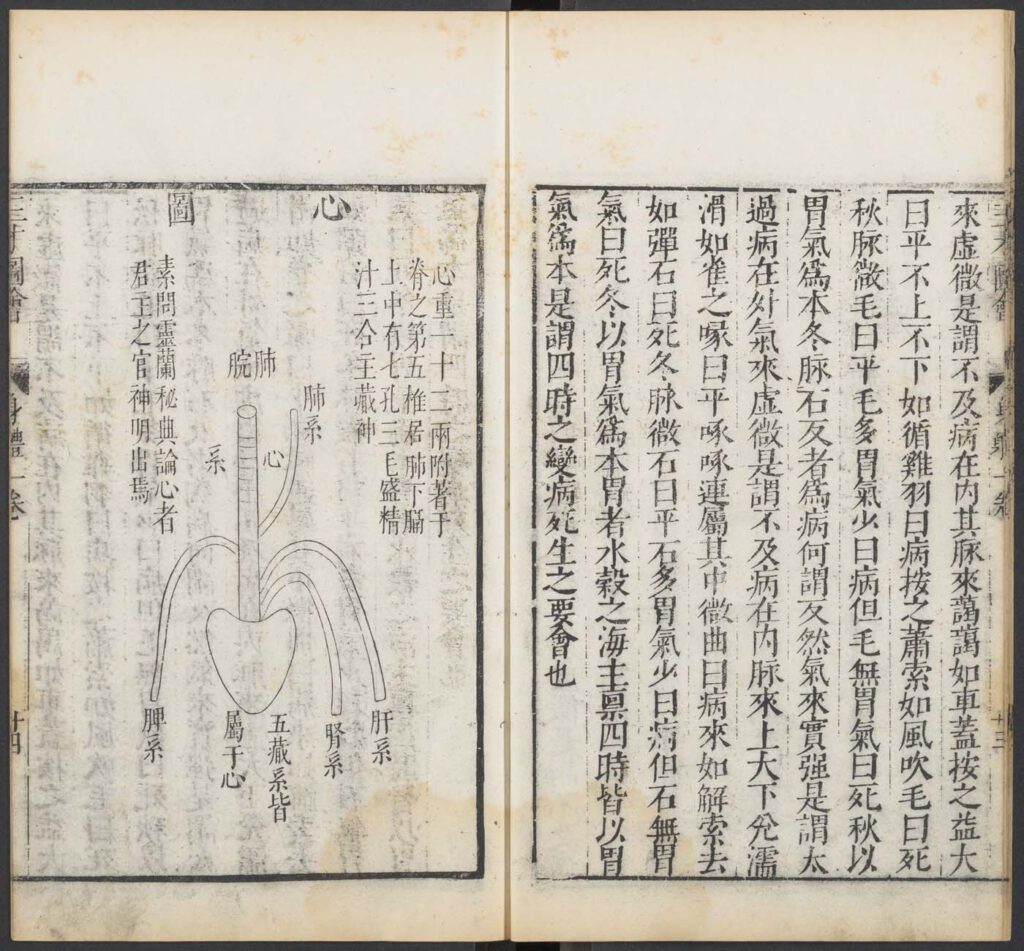
Diagram of the heart from Wang Qi (jinshi degree holder of 1565), Collected Diagrams of Heaven, Earth, and Man (Sancai tuhui), Chongzhen reign (1628-44) reprint of 1609 edition. In the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – This famous encyclopedia was a collection of illustrations of myriad aspects of the “three realms” of Heaven, […]
The diagram of the stomach

The diagram of the stomach from Zhang Jiebin (1563-1640), Illustrated Wing of the “Classified Canon” (Leijing tuyi), woodblock edition, preface dated 1624 From the collection of the Harvard-Yenching Library, Harvard University – This image of the stomach accompanies Zhang’s illustration of the pathway of the Foot Yang Brightness Stomach Channel. The upper text begins with […]
