Lehrbuch der urologischen Diagnostik
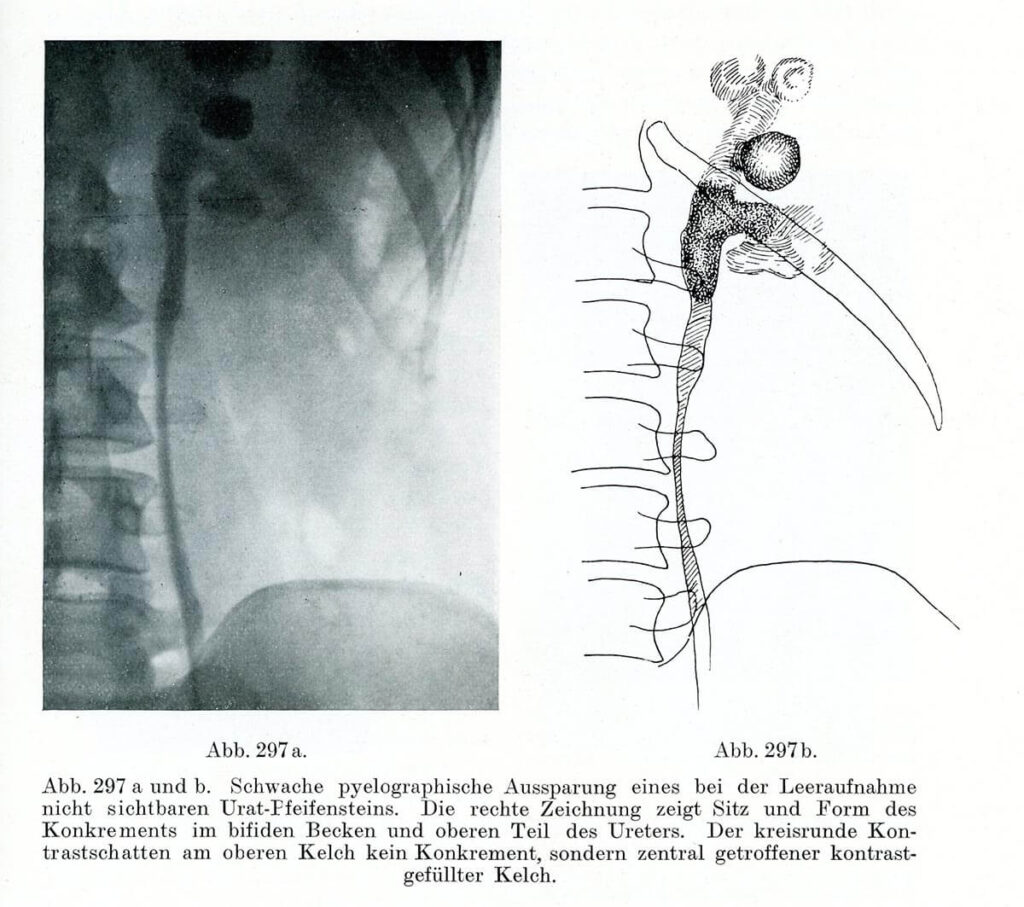
Pyeolographische Darstellung eines Konkrements im Ureter Leopold Casper und Edwin Picard (1930) Lehrbuch der urologischen Diagnostik. Thieme, Leipzig, S. 397 – Right after the discovery of X-rays, in the late 19th century, innumerable attempts were made to make this novel technique useful for medicine. While the radiological detection of bones quickly became a routine procedure, […]
Carcinoma colloides peritonei

Carcinoma colloides peritonei From: Emil Ponfick: Topographischer Atlas der Medizinisch-Chirurgischen Diagnostik / Topographic atlas of medico-surgical diagnosis, G. Fischer. Jena 1900-1905 Artist: Dr. Emil Löschmann, Breslau — The attempts of the German pathologist Emil Ponfick, who in 1901 attempted to reduce the gap between drawing and original object, show how objectives and implementation should be brought together […]
A fresco, Catacomba di Via Dino Compagni
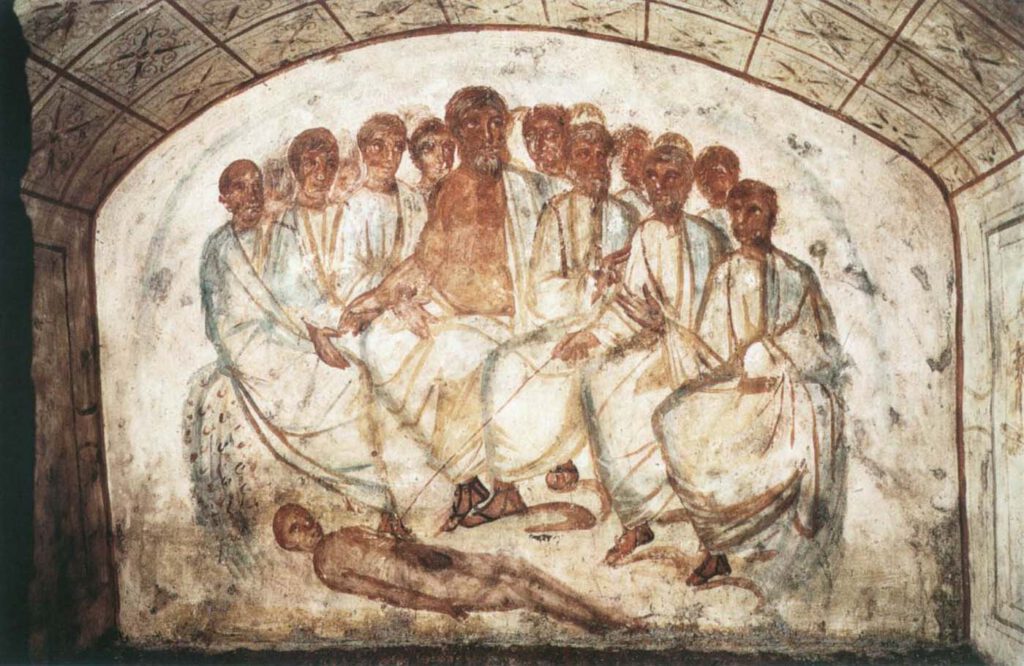

A fresco, Catacomba di Via Dino Compagni © foto Pontificia Commissione di Archeologia Sacra” or “© foto Archivio PCAS” [Kontakt zur PCAS in Arbeit] – This fresco from the hypogeum of Via Dino Compagni in the Via Latina Catacomb in Rome dates to the fourth century CE. It shows a large group of men looking […]
Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Douris
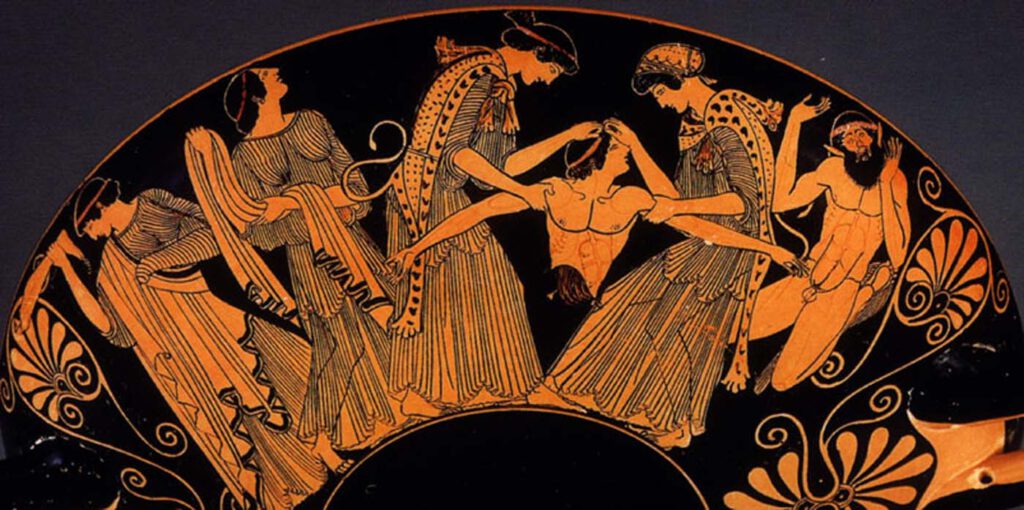

Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Douris death of Pentheus (detail), c.480 B.C. Cervetri, Museo Nazionale CeritePhoto: 2023@photo Scala, Florence, Kimbell Art Museum, Fort Worth, Texas /Art Resource, NY/Scala, Florence – The death of Pentheus is most familiar in the description given by Euripides in Bacchae. There a messenger speech describes how Pentheus’ mother, Agave, and […]
A female ‘open torso’ figurine

A female ‘open torso’ figurine Nottingham Castle Museum – This female figurine was discovered at the sanctuary of the Graeco-Roman goddess Artemis/Diana Nemorensis at Lake Nemi in Italy in 1885. It was excavated and recovered from a sacred pit where it had been ritually disposed of sometime in antiquity after it had ceased to be […]
A polyvisceral plaque
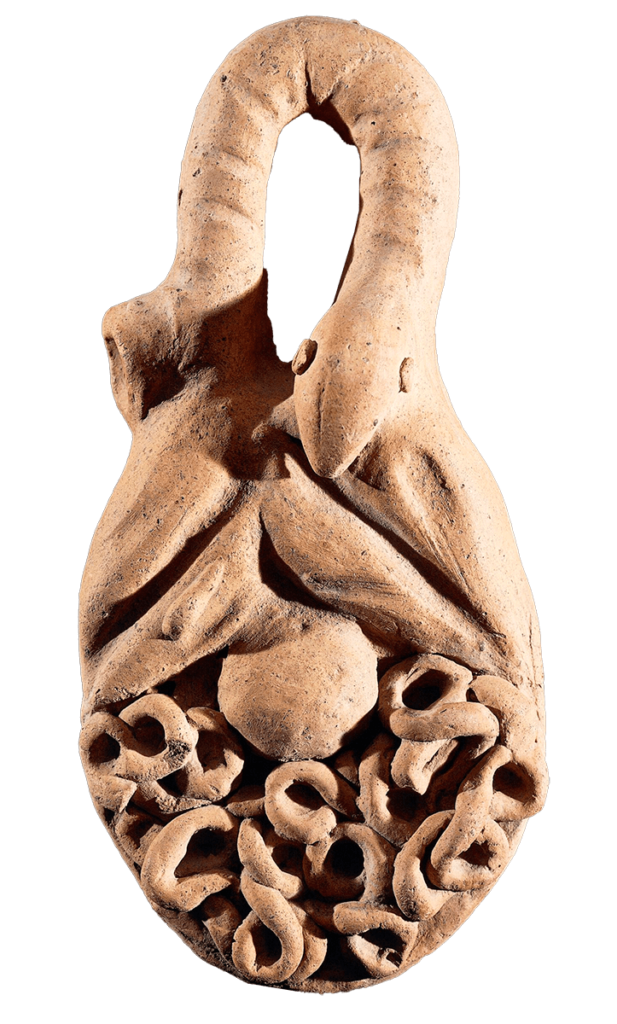

A polyvisceral plaque Museo Nazionale Etrusco Di Villa Giulia – This Etruscan polyvisceral plaque from Tessennano in Latium in Italy is thought to date from around 400 BCE. Anatomical votives like these were deposited in sanctuaries and temples as offerings to the gods, generally interpreted as a gesture of gratitude for some manner of divine […]
The ‘Piacenza Liver’
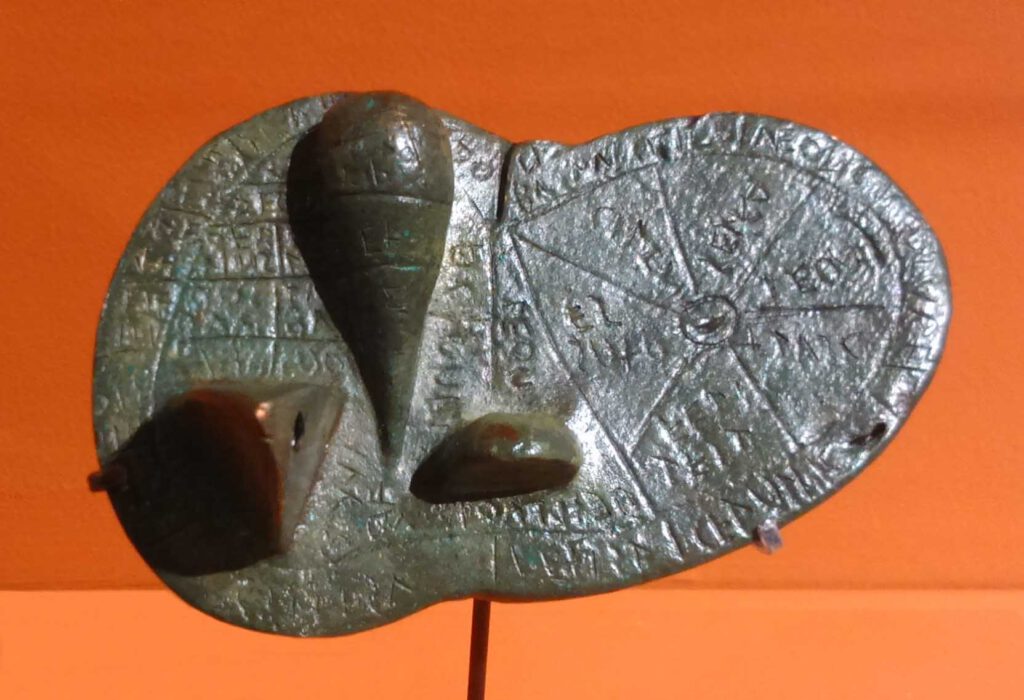

The ‘Piacenza Liver’ Municipale Museum of Piacenza CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) – This Etruscan bronze life-size model of a sheep’s liver was discovered in a field near Gossolengo in Piacenza in Italy in 1877 and is thought to date from the late second or early first century BCE. Although its precise purpose is not […]
Tupilak carving
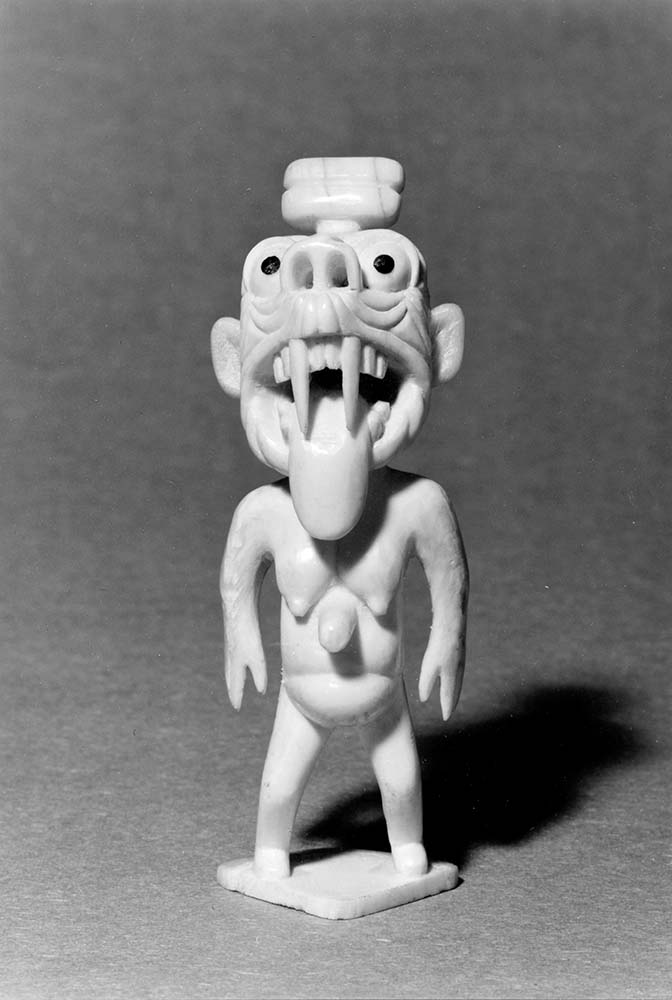

Tupilak carving Tupilak carving, ivory, Greenland. Before 1962.Photo: Ole Woldbye, Danish Arctic Institute – A tupilak, today a tourist object and awkwardly considered to have been an auspicious talisman, was an object meant to do nothing but harm. Most Tupilaks were put together by bones from various animals, stuffed with sod and wrapped up in skin, to be […]
Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Oltos, examination of the liver of a sacrificial victim
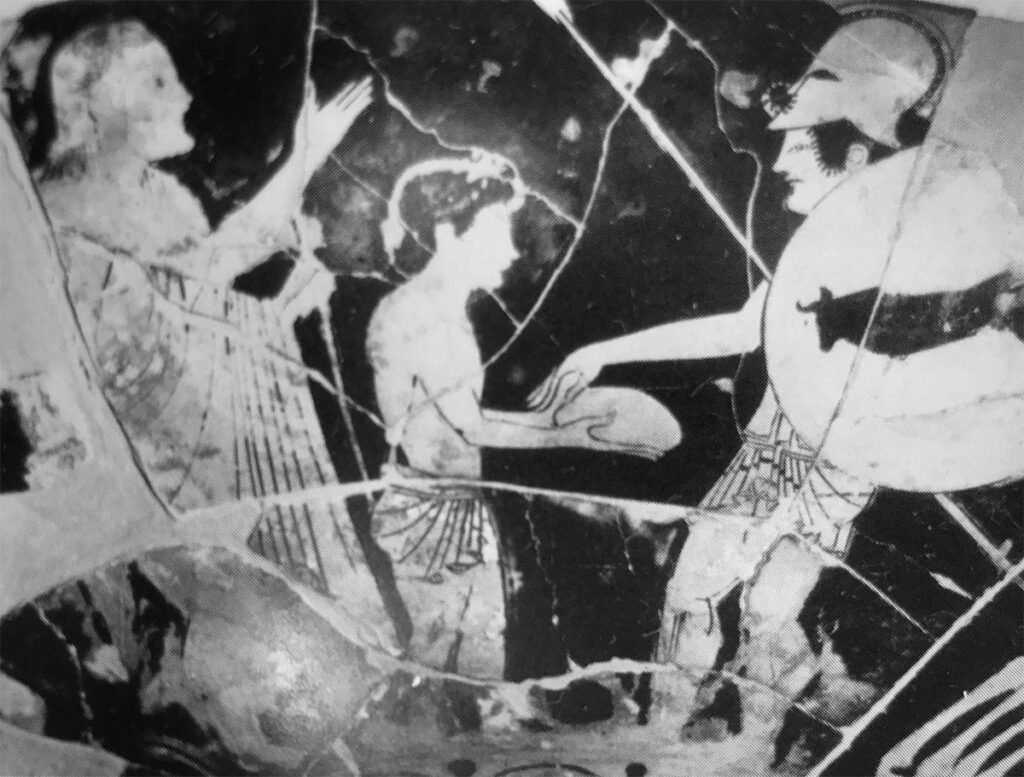

Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Oltos examination of the liver of a sacrificial victim (‘hieroscopy’), c.500 B.C.Cervetri, Museo Nazionale Cerite Photo: Jaime Ardiles-Arce – Representation of warfare is a feature of Greek painted pottery from the earliest figurative images from the eighth century BCE. In the second half of the sixth century and into the […]
Athenian red-figure krater signed by Euphronios
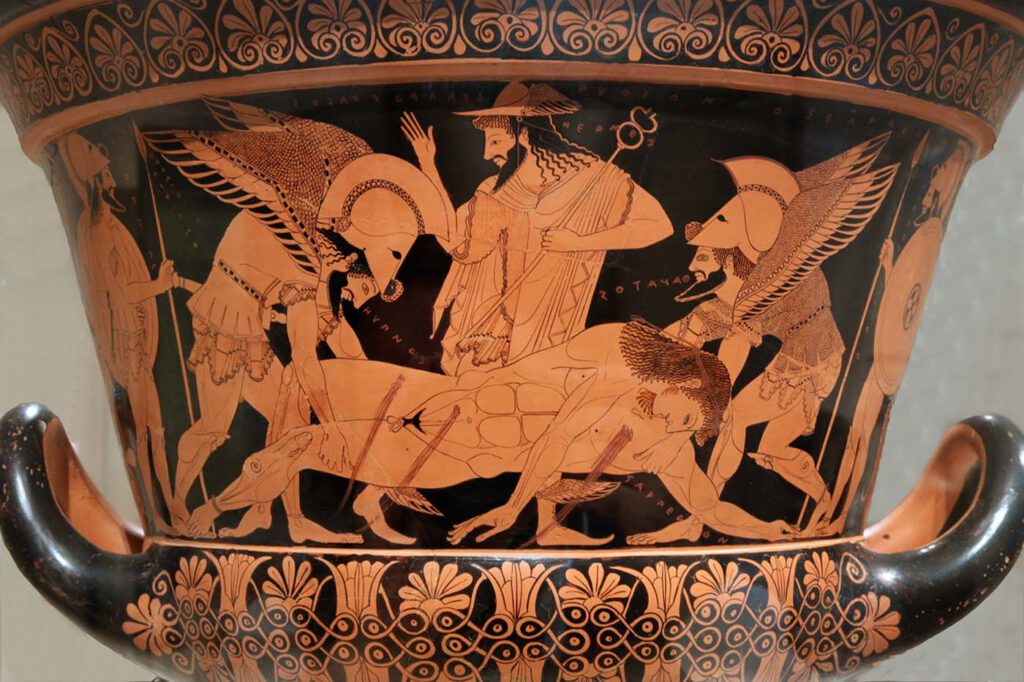

Athenian red-figure krater signed by Euphronios death of Sarpedon c.500 B.C. Cervetri, Museo Nazionale CeritePhoto: Jaime Ardiles-Arce, CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) – This pot has become particularly famous because it was illegally excavated and then acquired by the Metropolitan Museum in New York. The Met. subsequently agreed that its acquisition had been inappropriate and the […]
