Kotsanas’ wooden reproduction of the stomachion

Kotsanas’ wooden reproduction of the stomachion A modern reproduction of Archimedes’ stomachion Copyright: Collection and Archive of Kotsanas Museum of Ancient Greek Technology (www.kotsanas.com) – The image shows a reproduction of the stomachion game located in the K. Kotsanas Museum of Ancient Greek Technology in Heraklion, Crete. This wooden artefact consists of a square geometric […]
The geometric design of the stomachion diagram
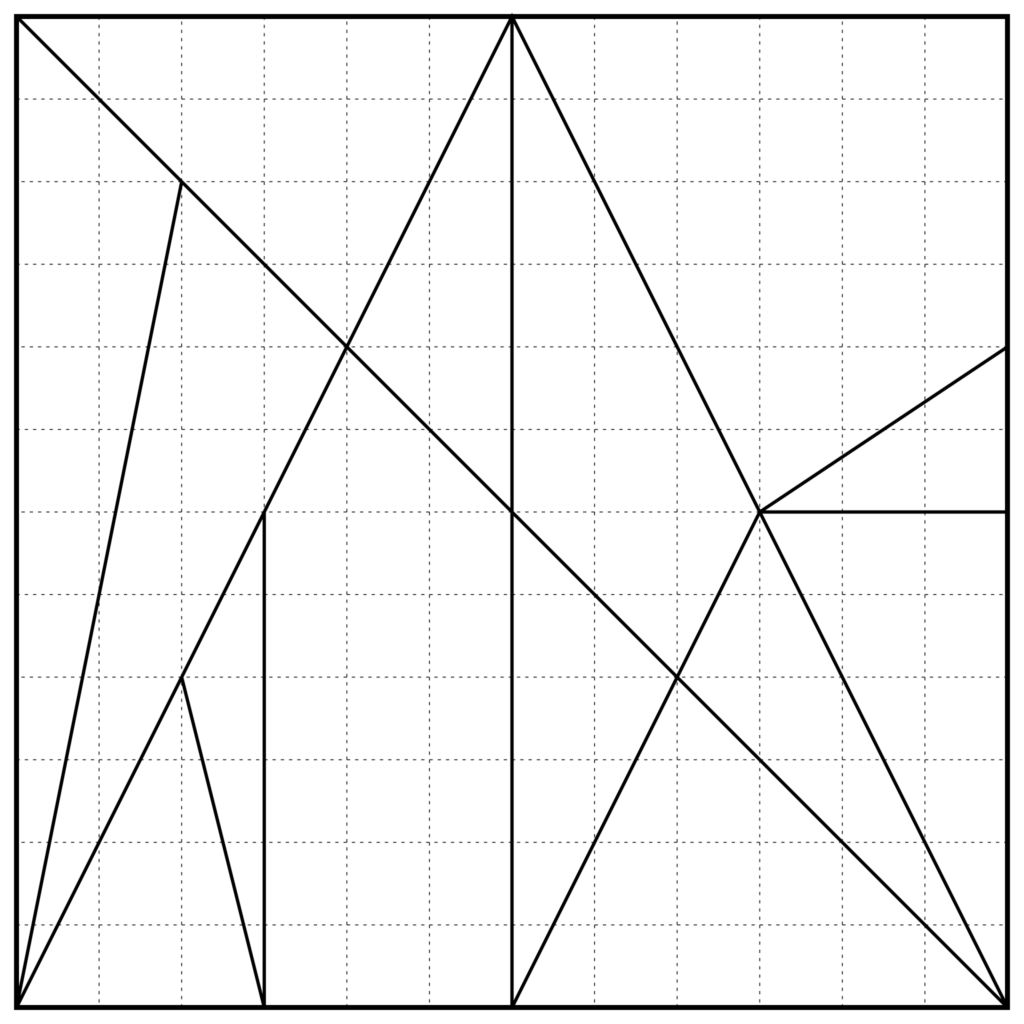
The geometric design of the stomachion diagram The division of the square according to the indications of an Arabic manuscript description: stomachion of Archimedes, with a 1/12 grid, author: Hagen von Eitzen, copyright: public domain – This image reproduces the Graeco-Roman stomachion square according to the proportions provided by a 17th c. manuscript in the […]
Roman marble version of a dying Gaul

Roman marble version of a dying Gaul the original was part of a major sculptural display on the Athenian Acropolis of Attalid Greeks fighting Gauls in Asia Minor, Gods fighting Giants, Greeks fighting Amazons, and Greeks fighting Persians in the Persian Wars, c.200 B.C. Naples Dying GaulPhoto: Mary Harrsch, CC-BY-NC-SA-2.0 – In c. 200 BCE Attalos […]
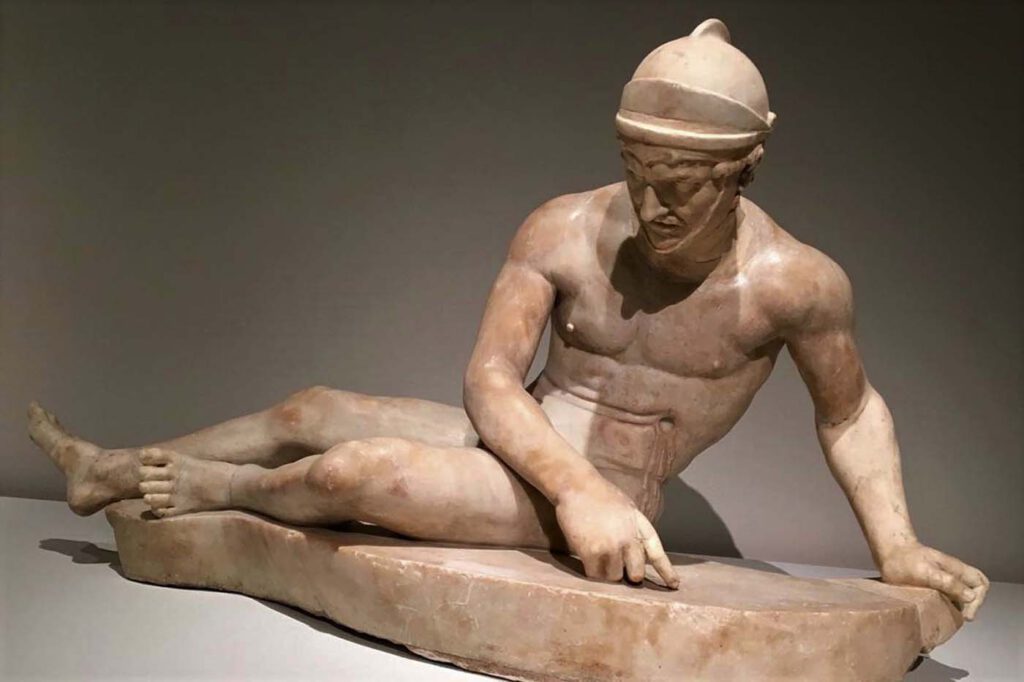
Marble votive relief

Marble votive relief showing votive body-parts c.480 B.C., fourth-century B.C. from Asklepieion at Athens Notwendige Votive Relief – Acr. 7232 © Acropolis MuseumPhoto: Constantinos Vasiliadis – A number of Greek sanctuaries, and in particular sanctuaries of healing god Asklepios, have yielded dedications of votive body-parts. These include arms and hands, legs and feet, eyes, ears, […]
A fresco, Catacomba di Via Dino Compagni
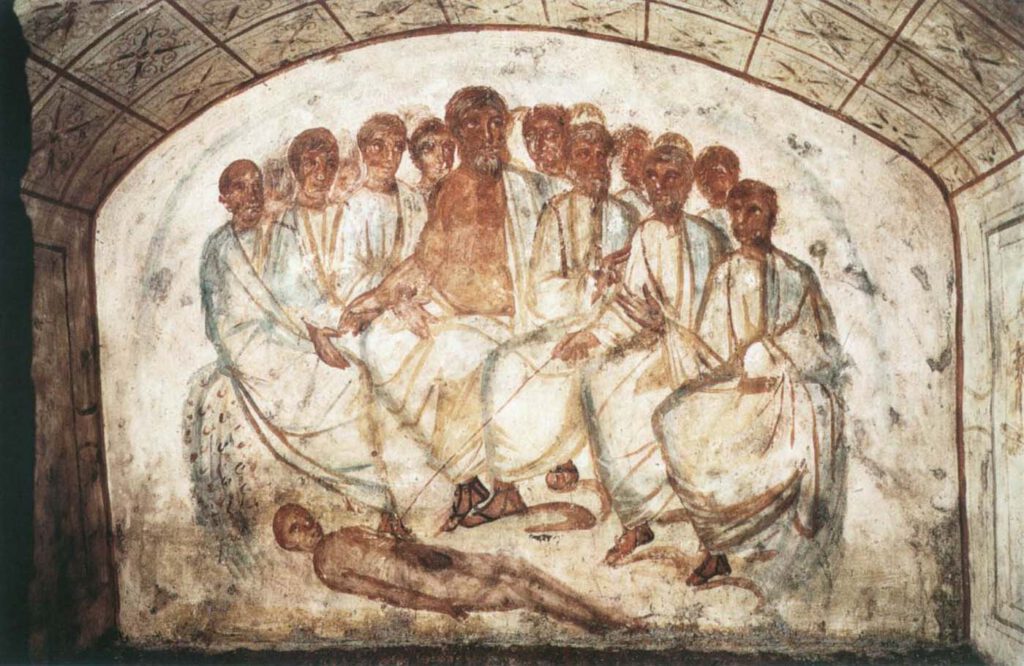

A fresco, Catacomba di Via Dino Compagni © foto Pontificia Commissione di Archeologia Sacra” or “© foto Archivio PCAS” [Kontakt zur PCAS in Arbeit] – This fresco from the hypogeum of Via Dino Compagni in the Via Latina Catacomb in Rome dates to the fourth century CE. It shows a large group of men looking […]
Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Douris
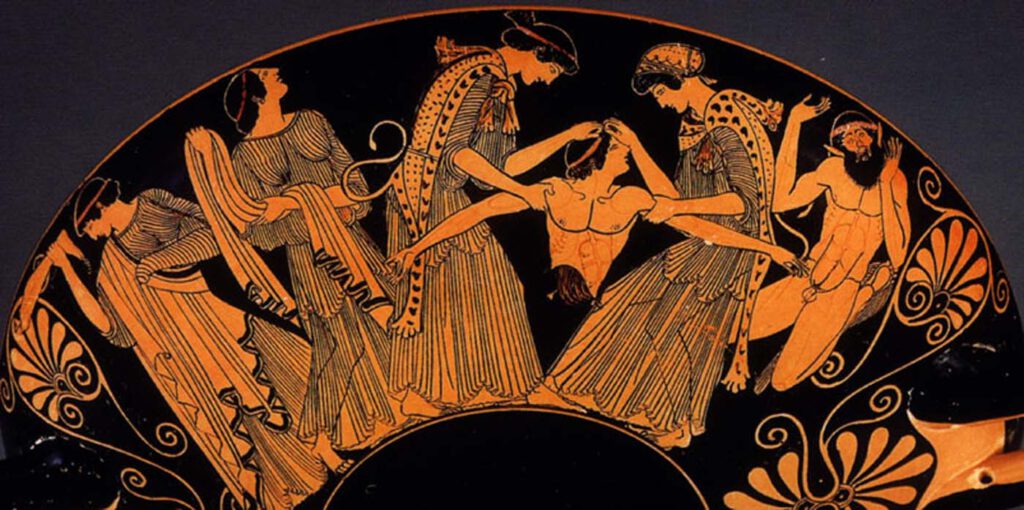

Athenian red-figure cup attributed to Douris death of Pentheus (detail), c.480 B.C. Cervetri, Museo Nazionale CeritePhoto: 2023@photo Scala, Florence, Kimbell Art Museum, Fort Worth, Texas /Art Resource, NY/Scala, Florence – The death of Pentheus is most familiar in the description given by Euripides in Bacchae. There a messenger speech describes how Pentheus’ mother, Agave, and […]
A female ‘open torso’ figurine

A female ‘open torso’ figurine Nottingham Castle Museum – This female figurine was discovered at the sanctuary of the Graeco-Roman goddess Artemis/Diana Nemorensis at Lake Nemi in Italy in 1885. It was excavated and recovered from a sacred pit where it had been ritually disposed of sometime in antiquity after it had ceased to be […]
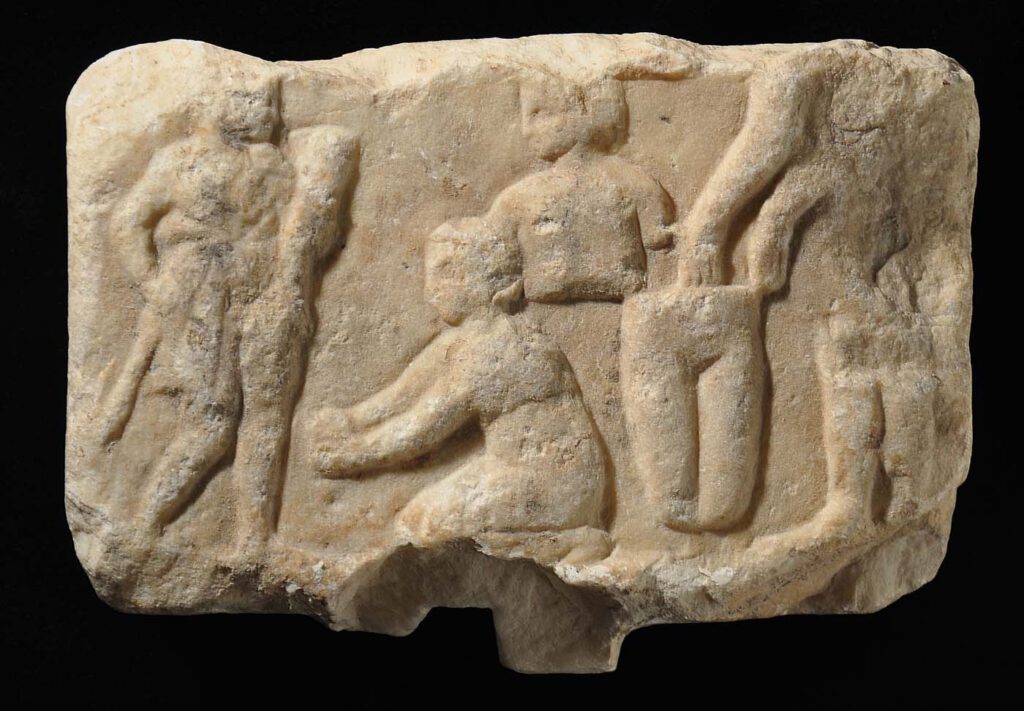
A polyvisceral plaque
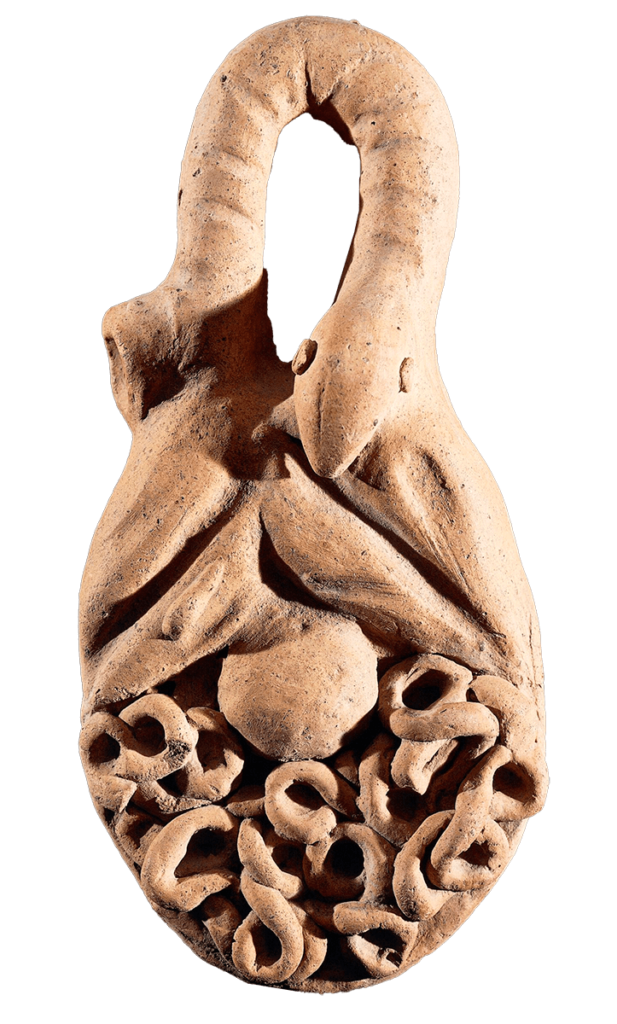

A polyvisceral plaque Museo Nazionale Etrusco Di Villa Giulia – This Etruscan polyvisceral plaque from Tessennano in Latium in Italy is thought to date from around 400 BCE. Anatomical votives like these were deposited in sanctuaries and temples as offerings to the gods, generally interpreted as a gesture of gratitude for some manner of divine […]
Athenian red-figure krater signed by Euphronios
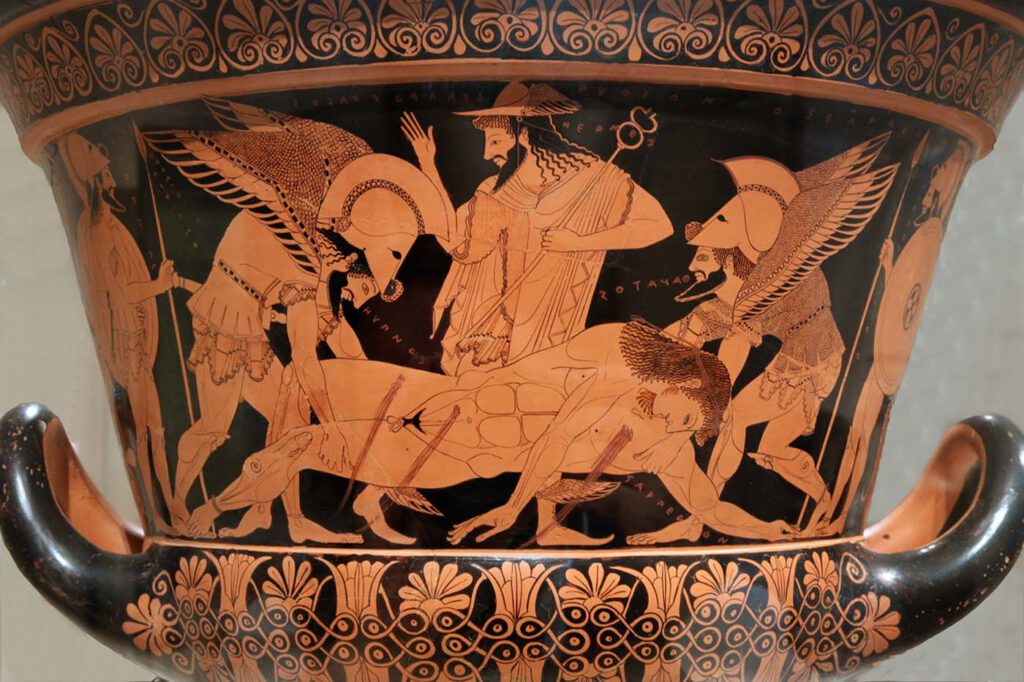

Athenian red-figure krater signed by Euphronios death of Sarpedon c.500 B.C. Cervetri, Museo Nazionale CeritePhoto: Jaime Ardiles-Arce, CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) – This pot has become particularly famous because it was illegally excavated and then acquired by the Metropolitan Museum in New York. The Met. subsequently agreed that its acquisition had been inappropriate and the […]
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra
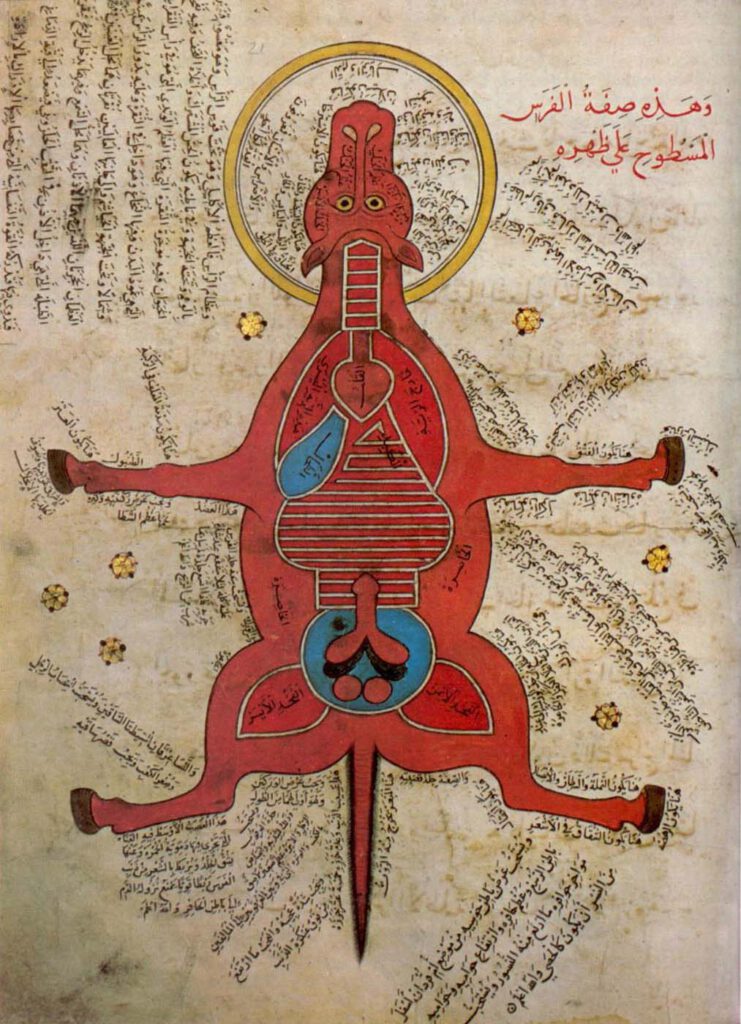
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra (Commentary on the Maqāma Ṣalāḥiyya on Horses and Venterinary) Istanbul University Library MS 4689 – Egypt, 15th c. – Hyppiatry has a long tradition in Islamic literature. Works dealing with horses may adopt different literary genres and cover a wide range of disciplines, from veterinary sciences to […]
