LHS 4a: A Qing period manuscript illustration of the Yuanmen maijue neizhao tu 元門脈訣內罩圖

A B Travelling guts A A Qing period manuscript illustration of the Yuanmen maijue neizhao tu 元門脈訣內罩圖 (Internal Visualisation Charts from the ‘Primordial Portal’ Secret Art of the Pulse), attr. Hua Tuo, 3rd century CE. This chart shows the position of Qi Hai (the Sea of Qi, the diaphragm).Library of China Academy of Chinese Medical […]
SET 3a-f Kim Yemong et al. Ui’bang’ryuchui 醫方類聚, vol. 5, pp. 51-70

A D B E C F SET 3a-f Kim Yemong et al. Ui’bang’ryuchui 醫方類聚, vol. 5, pp. 51-70 (original edition in Kyoto Palace, Japan; microfilm copy in National Library, Korea) Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) – Chinese ideas about the images of the animal spirits, here of the lungs, the heart, the liver, the […]
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist
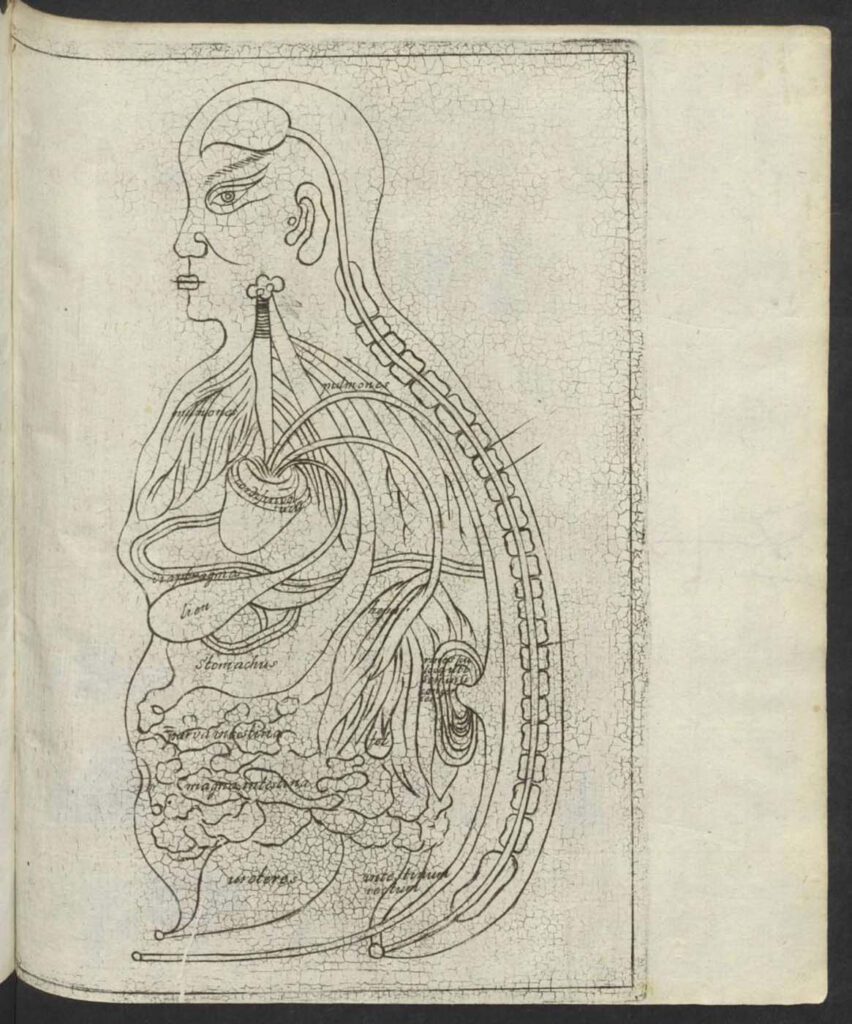
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist This “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (Image 1) but was printed in the 1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. The anonymous artist retained the Chinese original’s flat rendering (Image 1) rather than the three-dimensional rendering of Christian Mentzel’s sketch (Image 3) and the sketch (Image 4) in […]
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist
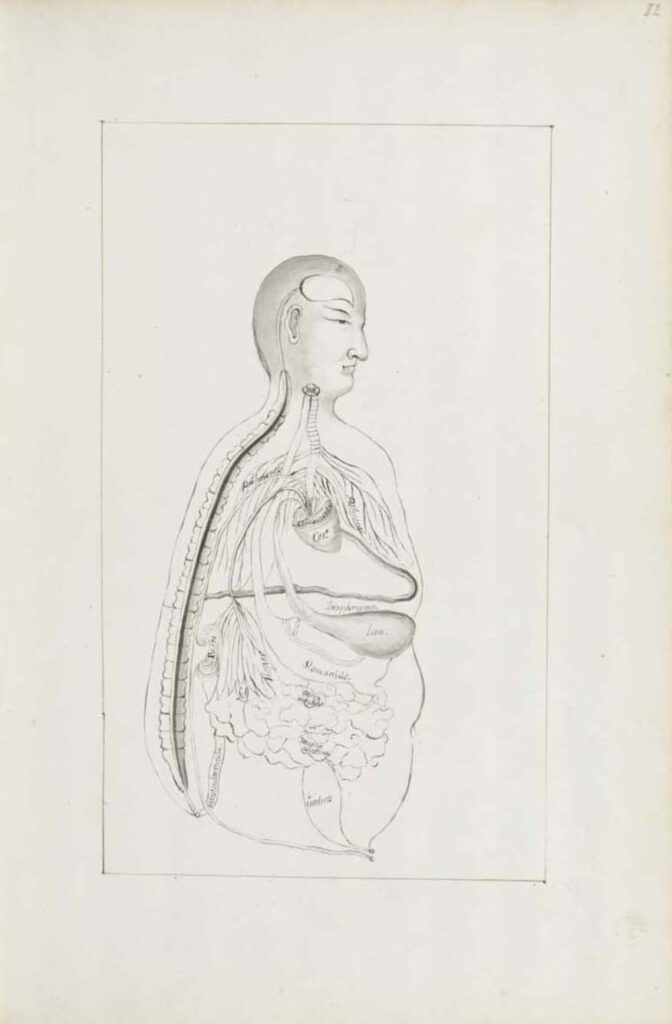
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist This sketch of the “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (image 1), however, the artist remains anonymous. It was included in the only known extant manuscript (Ms. Lat. Fol. 95 preserved in the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin) of the 1682 printed Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. It illustrates […]
Ca. 1681 Ms sin. 11, part 3 by Christian Mentzel
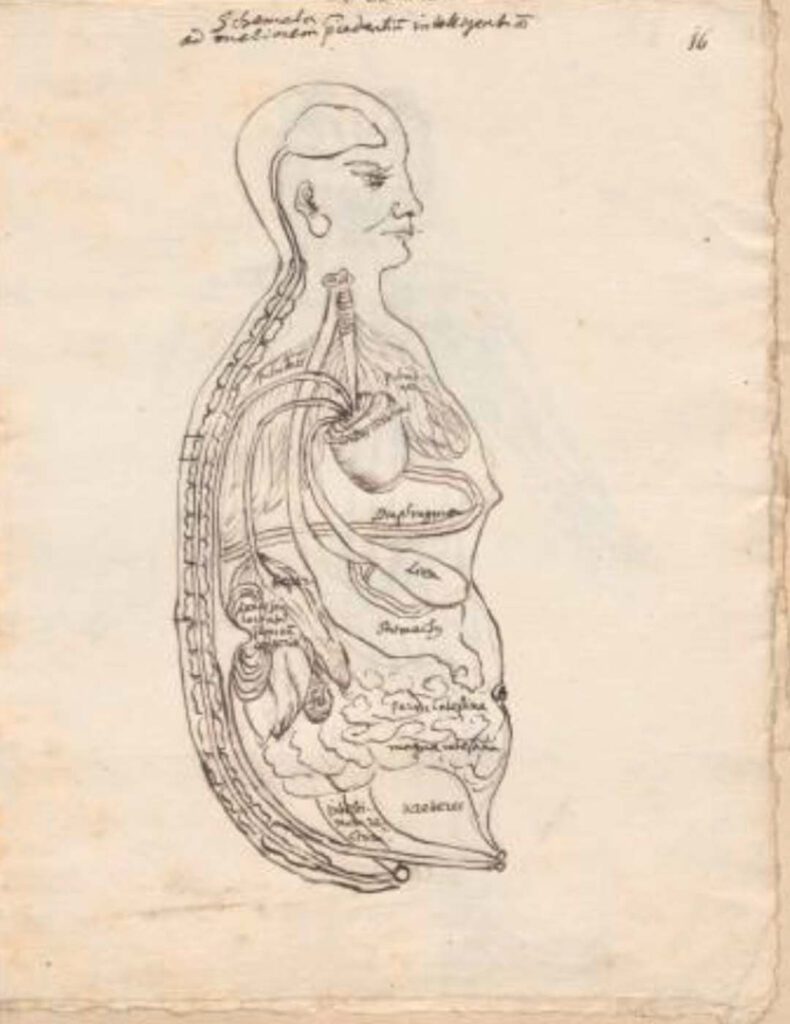
Ca. 1681 Ms sin. 11, part 3 by Christian Mentzel The personal physician to the Great Elector Friedrich Wilhelm of Brandenberg and curator of his library, Christian Mentzel (1622-1701), sketched this “Viscera Man” based on a Chinese source (Image 1). Both Mentzel’s sketch (Image 3) and the printed 1597 original (Image 1) are included in […]
1597 reprint of Wanbing huichun “Diagram of Man’s Side-Body”
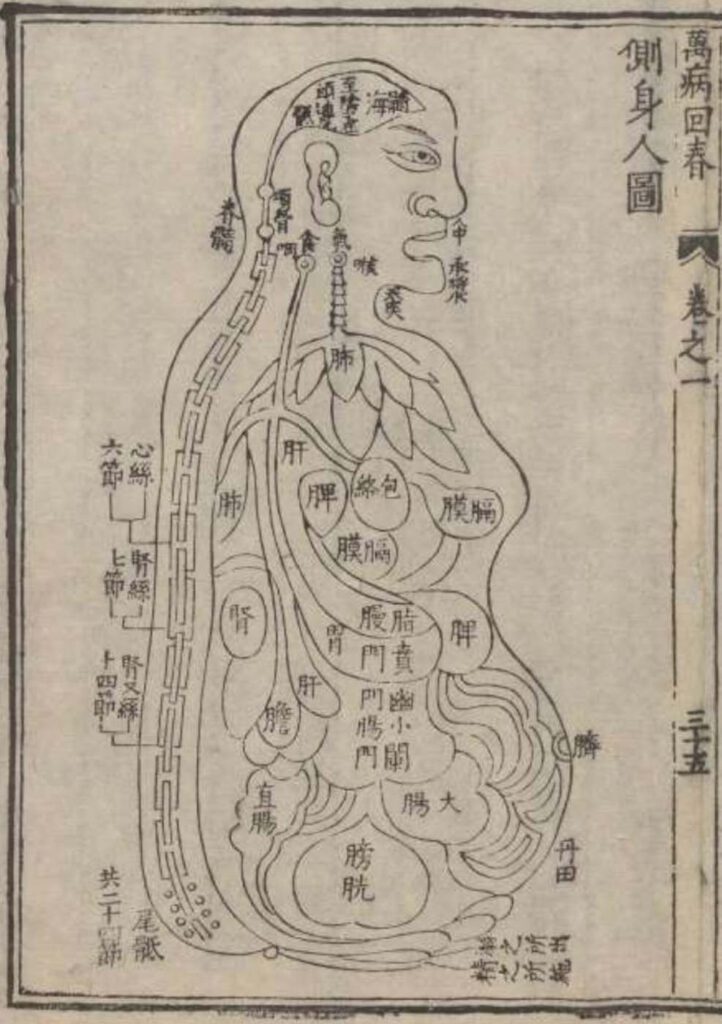
‘Diagram of Man’s Side-Body’ in 1597 reprint of Wanbing huichun (Ceshen ren tu 側身人圖). This version of the “Viscera Man” was printed in a 1597 reprint of the Chinese medical text Myriad diseases ‘Spring Returned’ (i.e., ‘cured’) (Wanbing huichun 萬病回春) that is preserved in the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin. – This 1597 reprint of a “viscera […]
Published in 1597 reprint of a 1565 Yixue gangmu, preserved in Ms sin. 11, part 1, “Enlightened-Hall Diagram of the Viscera”
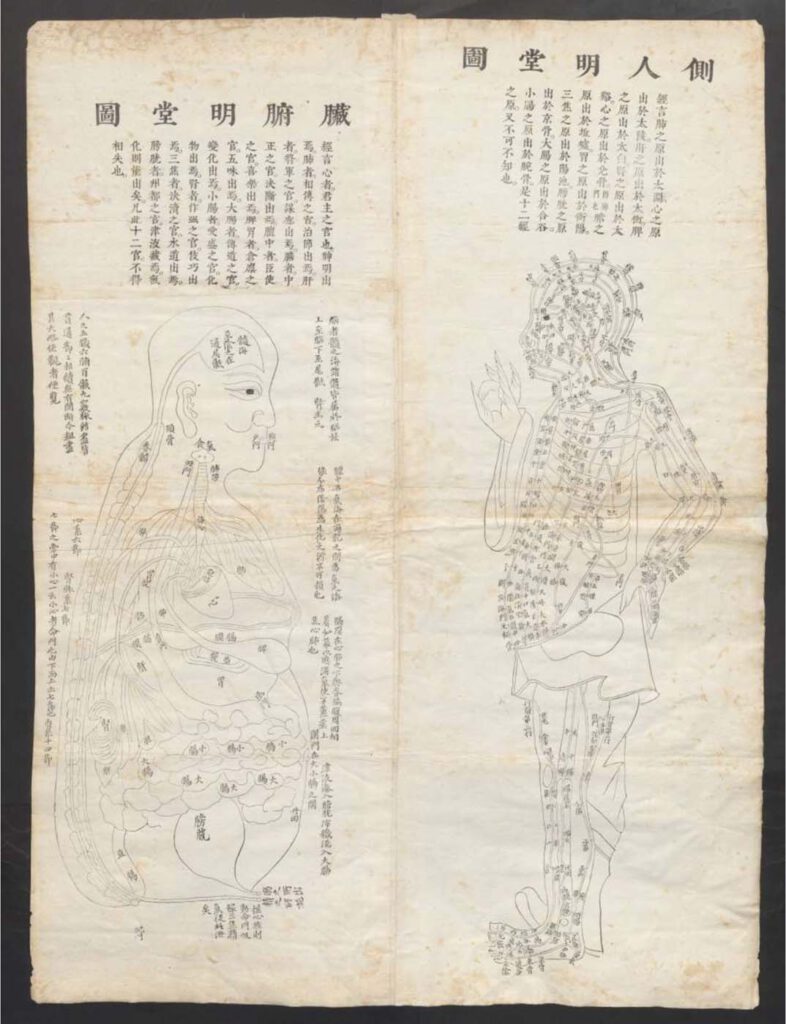
‘Enlightened-Hall Diagram of the Viscera’, in 1597 reprint of a 1565 Yixue gangmu, preserved in Ms sin. 11, part 1 (Zangfu Mingtang tu 臟腑明堂圖). This fold-out plate (ca. 79cm x 58cm) of a “Viscera Man” has been inserted into a manuscript (ms. sin. 11) preserved in Biblioteka Jagiellońska Kraków, Poland, digitalized by the Staatsbibliothek in […]
Manase Dōsan 曲直瀬道三, Hyakufuku zusetsu
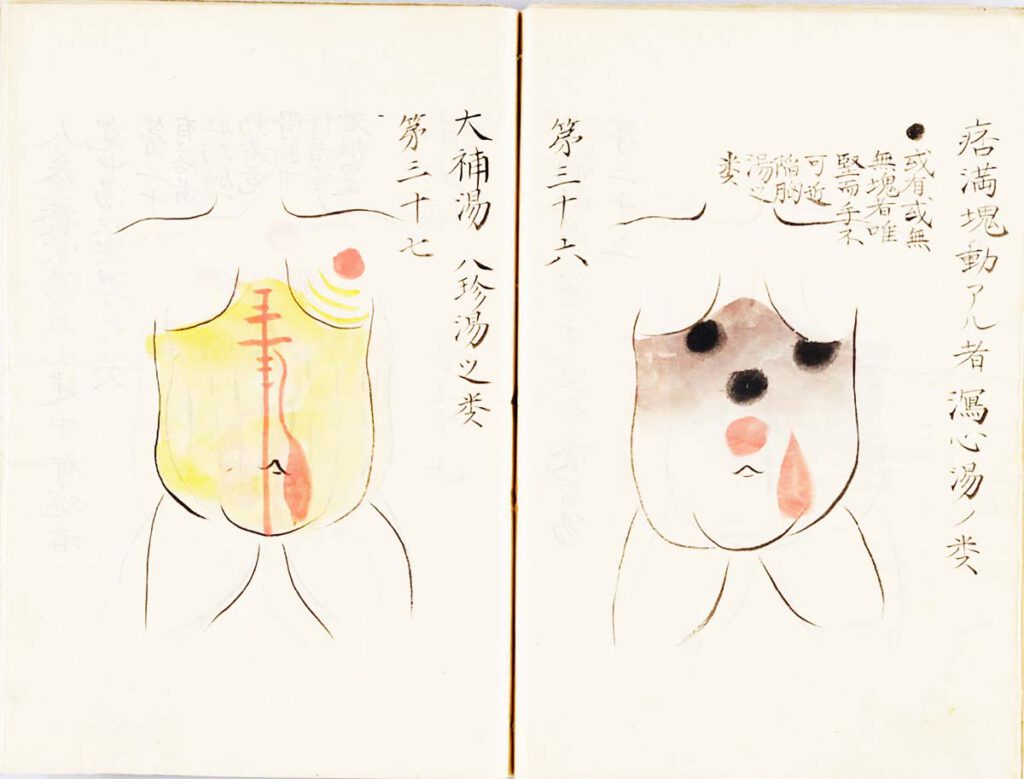
Manase Dōsan 曲直瀬道三, Hyakufuku zusetsu (百腹図説, “Illustrated Explanations of a Hundred Bellies”; n.d.) – Nothing more directly translated the early modern stress on practical, tangible realities than the Japanese innovation known as fukushin 腹診 (abdominal inspection). Whereas Chinese doctors had relied chiefly on feeling the pulse at the wrist to diagnose diseases, Japanese advocates of […]
Sugita Gempaku’s Kaitai shinsho
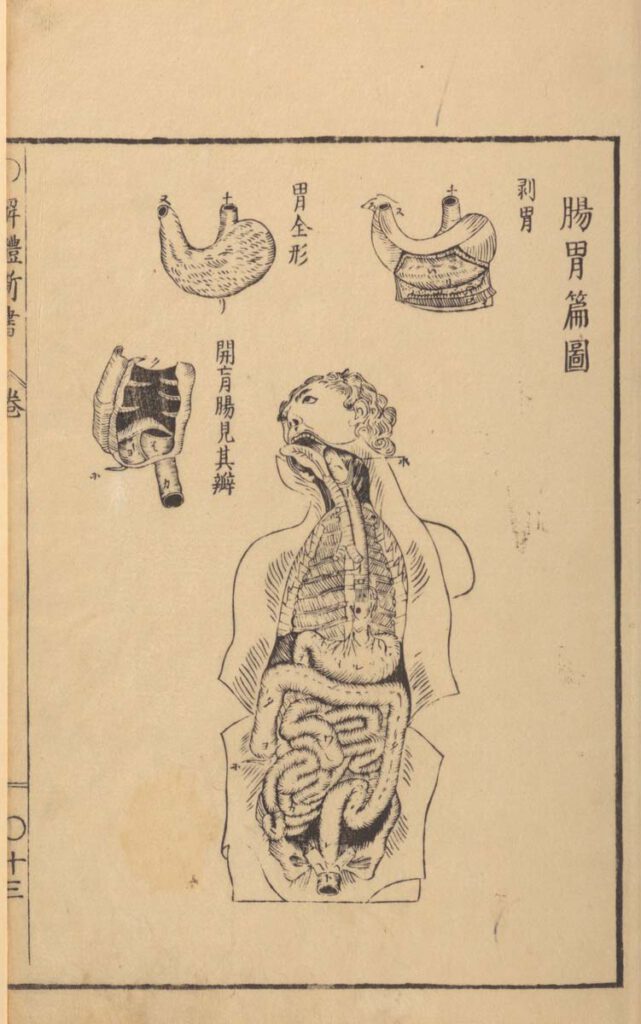
Sugita Gempaku’s Kaitai shinsho (解体新書, “New Book of Anatomy”; 1774) – Sugita Gempaku undertook his epoch-making translation of a Dutch anatomical manual before he could read Dutch. This point is key: What persuaded him of the manual’s truth was not its text, which he initially couldn’t comprehend, but rather, its images, and more specifically their […]
Minor connecting blood vasculature of the body including gut
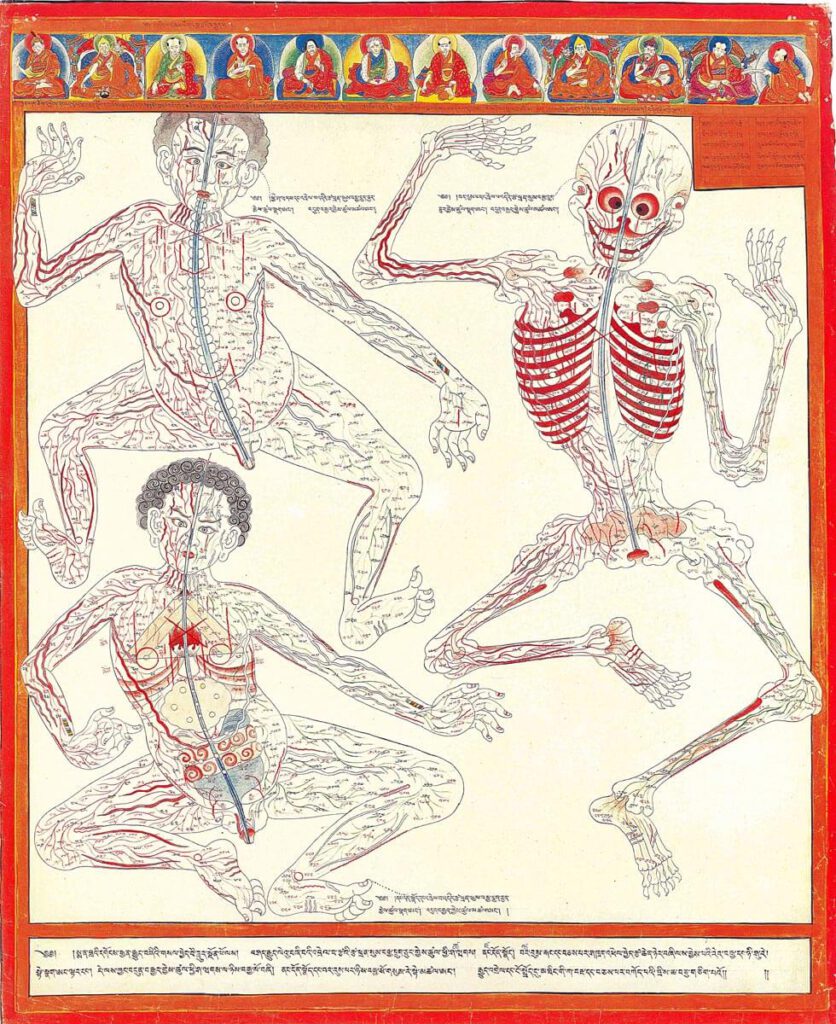
Minor connecting blood vasculature of body including gut 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia – The Four Tantras details specific enumerations of minor channels illustrated here in anatomical layout with important physiological functions. There are 360 interconnecting channels as they relate to skin and muscle tissue, […]
