LHS 4a: A Qing period manuscript illustration of the Yuanmen maijue neizhao tu 元門脈訣內罩圖

A B Travelling guts A A Qing period manuscript illustration of the Yuanmen maijue neizhao tu 元門脈訣內罩圖 (Internal Visualisation Charts from the ‘Primordial Portal’ Secret Art of the Pulse), attr. Hua Tuo, 3rd century CE. This chart shows the position of Qi Hai (the Sea of Qi, the diaphragm).Library of China Academy of Chinese Medical […]
SET 3a-f Kim Yemong et al. Ui’bang’ryuchui 醫方類聚, vol. 5, pp. 51-70

A D B E C F SET 3a-f Kim Yemong et al. Ui’bang’ryuchui 醫方類聚, vol. 5, pp. 51-70 (original edition in Kyoto Palace, Japan; microfilm copy in National Library, Korea) Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) – Chinese ideas about the images of the animal spirits, here of the lungs, the heart, the liver, the […]
SET 2a+b Huangting dunjia yuanshen jing 黃庭遁甲緣身經 (Book of the Hidden Period and the Causal [Karma] Body of the Yellow Court) DZ 0873
![SET 2a+b Huangting dunjia yuanshen jing (Buch der verborgenen Periode und der kausale [Karma] Körper des gelben Hofes) Die beiden Schwarz-Weiß-Bilder aus dem 15. Jahrhundert zeigen unter einem Text in chinesischen Schriftzeichen vogelähnliche Wesen. Auf dem mit „A“ gekennzeichneten hochformatigen Bild links nimmt die Darstellung des Wesens die unteren zwei Drittel ein. Das Wesen ist schreitend mit angelegten Flügeln im Profil dargestellt. Es hat lange, dünne und unbefiederte Füße mit Krallen. Die Unterseite des schlanken kleinen Körpers ist hell. Das Deckgefieder ist gebändert. Lange Schwanzfedern, die in ihrer Form an die eines Pfaus erinnern, ragen aus dem Hinterleib. Der Hals ist nach hinten gebogen, seine kurzen Federn biegen sich nach oben, ebenso das Gefieder am Hinterkopf. Der dunkle Schnabel des Vogelwesens ist kurz und spitz mit einem Höcker darüber. Auf dem Kopf sitzt eine Federkrone Über dem Vogelwesen befinden sich neun, etwa gleich lange Spalten mit Schriftzeichen. Sie erstrecken sich über die gesamte Breite des Bildes. In einer Art Titelzeile darüber befinden sich mit einem größeren Abstand zu einander drei einzelne Schriftzeichen. Das rechts daneben positionierte Hochformat ist mit dem Buchstaben „B“ bezeichnet. Die Aufteilung des Bildraumes zwischen Schriftzeichen und Illustration ist ähnlich wie bei Bild „A“. Unter einer Art Überschrift aus zwei einzelnen Schriftzeichen erstrecken sich die neun Spalten über die gesamte Breite. Auch in diesem Bild ist das Vogelwesen mit angelegten Flügeln im Profil gezeichnet. Es steht auf einem Bein, das andere hat es angehoben und die Krallen zusammengezogen. Die Füße sind unbefiedert. Der helle Brust- und Bauchbereich ist durch eine klare Linie markiert. An den kleinen gedrungenen Körper schließt ein buschig befiederter emporgereckter Hals an. Das Wesen hält seinen drachenähnlichen Kopf in Richtung seines Rückens gedreht. Federbüschel ragen zu beiden Seiten seines Hauptes wie Ohren in die Höhe. Daneben treten zwei dünne gewellte Hörner hervor, ein weiteres Horn sitzt auf der Schnauze. Das Vogelwesen hat lange dünne Schwanzfedern, die an die eines Fasans erinnern. Sie sind schräg nach oben gerichtet. — — SET 2a+b Huangting dunjia yuanshen jing (Book of the Hidden Period and the Causal [Karma] Body of the Yellow Court) The two black and white images from the 15th century show bird-like creatures under a text in Chinese characters. In the portrait format image marked "A" on the left, the depiction of the creature occupies the lower two-thirds. The creature is shown in profile, striding with its wings spread. It has long, thin, and featherless feet with claws. The underside of its slender and small body is pale. The cover plumage is banded. Long tail feathers, resembling those of a peacock in shape, protrude from the abdomen. The neck is bent backwards, and its short feathers curve upwards, as does the plumage on the back of the head. The bird's dark beak is short and pointed with a hump above it. A crown of feathers sits on top of the head. Above the bird-like creature are nine columns of characters of roughly equal length. They extend across the entire width of the image. In a kind of title line at the top of the page, there are three individual characters at a greater distance from each other. On the portrait format image marked “B” on the right, the division of the pictorial space between the characters and the illustration is similar to that in image "A". Under a kind of heading consisting of two individual characters, the nine columns extend across the entire width. In this image, too, the bird is drawn in profile with its wings spread. It is standing on one leg, the other raised and the claws drawn together. The feet are not feathered. The light breast and belly area is marked by a clear line. The small stocky body is joined by a bushy, feathered upturned neck. The creature holds its dragon-like head turned towards its back. Tufts of feathers rise up on either side of its head like ears. Two thin wavy horns protrude next to it, another horn sits on its snout. The creature has long thin tail feathers that resemble those of a pheasant. They are slanted upwards.](https://comparative-guts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/2a-copy-689x1024.jpg)
A B SET 2a+b Huangting dunjia yuanshen jing 黃庭遁甲緣身經 (Book of the Hidden Period and the Causal [Karma] Body of the Yellow Court) DZ 0873 A Shangqing huangting wuzang liufu zhenren yuzhou jing 上清黃庭五藏六腑真人玉軸經 (Precious Scroll of the Zhenren on the Six Receptacles and Five Viscera of the Yellow Court of Shangqing) DZ 1402Phoenix of […]
The Lower Cinnabar Field
The Lower Cinnabar Field Li Jiong’s Neijing tu 内景圖 (Chart of the Inner Landscape, (1269)) Huangdi bashiyi nanjing zuan tu jujie in Zhengtong Daozang 1436–49, Hanfen Lou, Shanghai (Ming edition of the Daoist Canon) Wellcome Library, London, L0034715. Cross-reference: Maps of the inner sceneries • from the right side, D | 16Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 […]
Reproduced artwork detailing small and large intestines with Tibetan and Latin labels
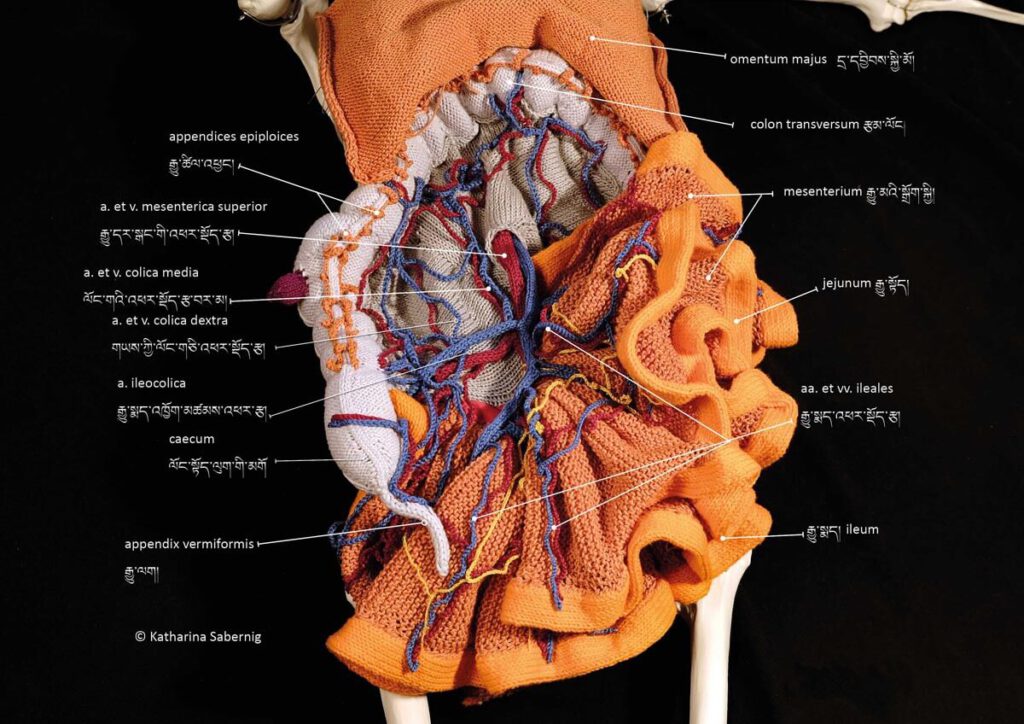
Reproduced artwork detailing small and large intestines with Tibetan and Latin labels Reproduced artwork detailing small and large intestines with Tibetan and Latin labels. Contemporary knitwork. © Katharina Sabernig – Tibetan classical medical vocabulary is already rich in anatomical terms. When encountering biomedical concepts, new terms were coined in the Tibetan language. Nevertheless, many historical […]
Knitted artwork of guts based on Tibetan medical painting at Atsagat Monastery, Republic of Buryatia, Russia.
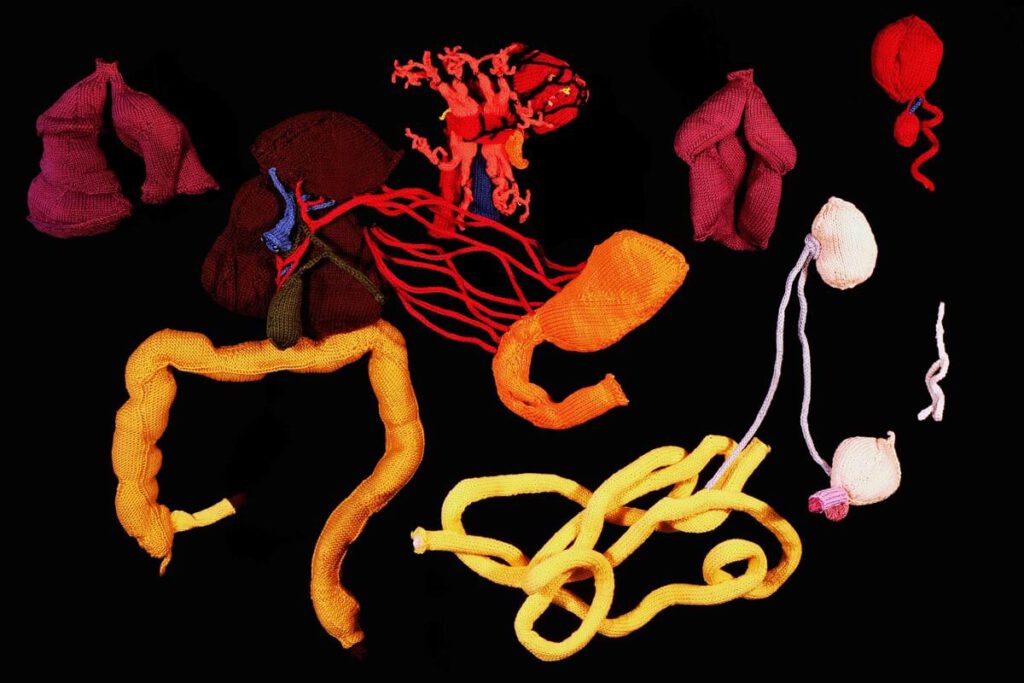
Knitted artwork of guts based on Tibetan medical painting at Atsagat Monastery, Republic of Buryatia, Russia Knitted artwork of guts based on Tibetan medical painting at Atsagat Monastery, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. © Katharina Sabernig – In Buryatia, an ethnically Mongolian region belonging to Russia, Tibetan medical knowledge encountered biomedical knowledge in the early twentieth […]
Moxibustion points according to Medical Arts of the Lunar King, Sowa Rigpa intersections with Chinese and Indian medical canons
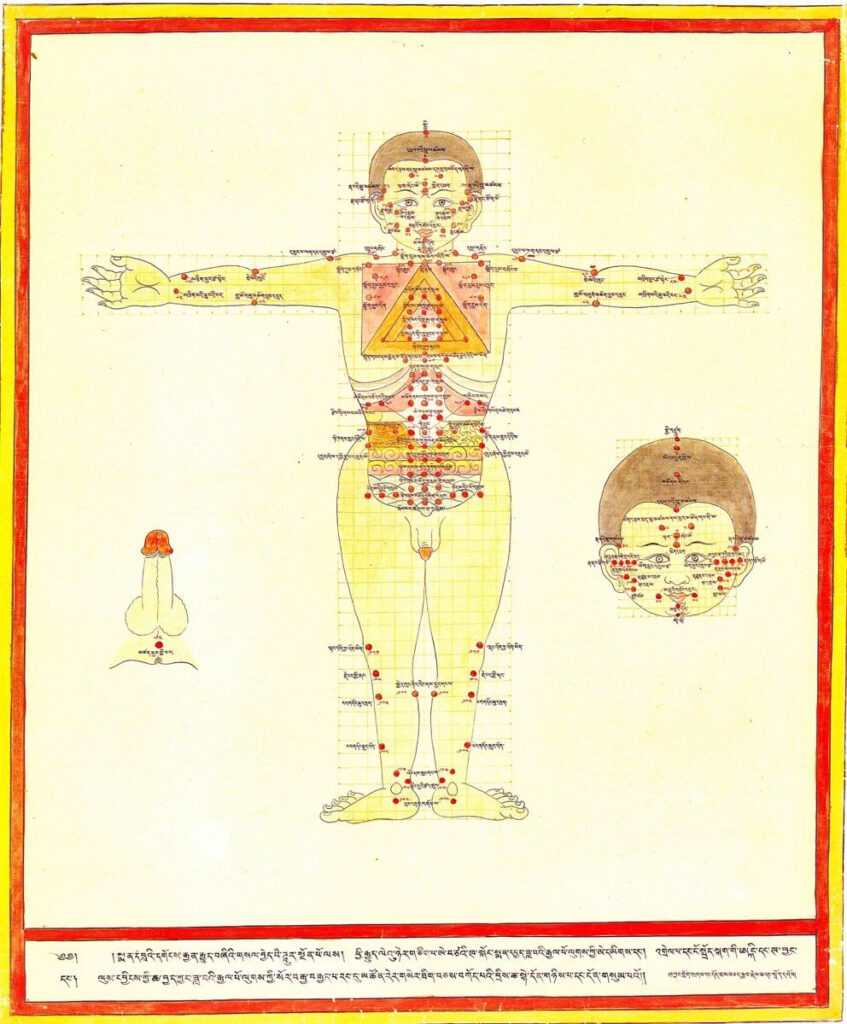
Moxibustion points according to Medical Arts of the Lunar King, Sowa Rigpa intersections with Chinese and Indian medical canons 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – Moxibustion is a treatment particularly indicated for metabolic conditions (ma zhu ba) and weak digestive fire (me drod nyams pa) […]
Treatment points for moxibustion, venesection, and surgery
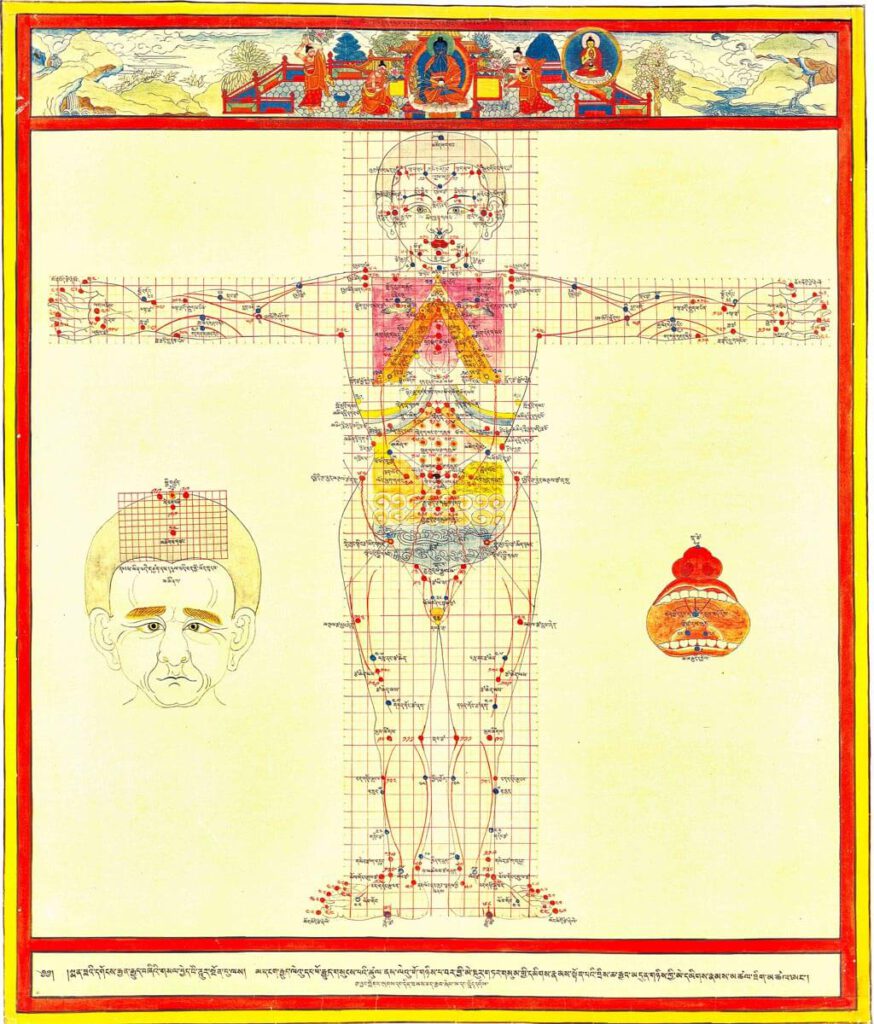
Treatment points for moxibustion, venesection, and surgery 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – This painting depicts the anterior view for the three types of external therapy treatment points: moxibustion, venesection, and surgical puncture. Moxibustion points are vermillion numbers and lines, venesection points are blue lines […]
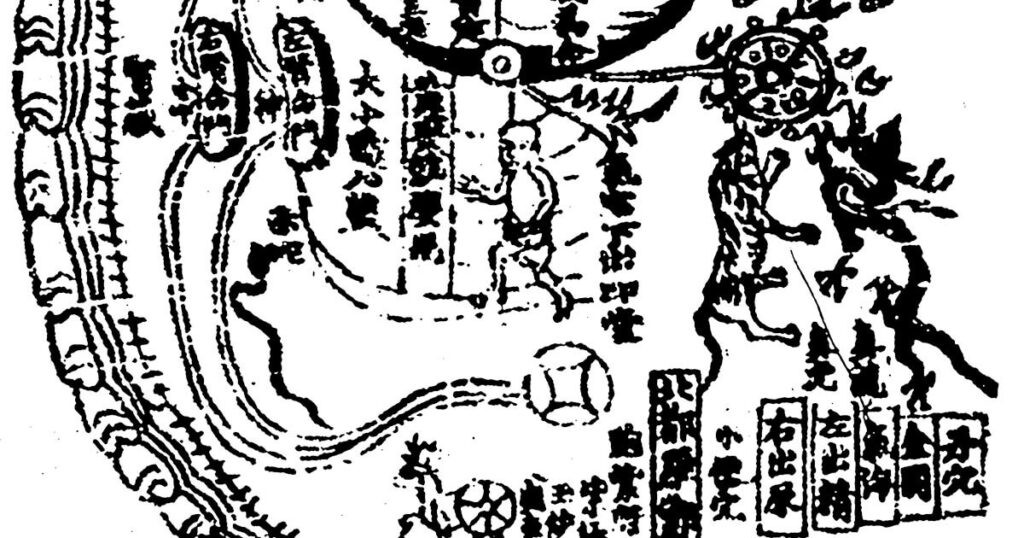
Major connecting blood vasculature of the body including gut with related vulnerable points
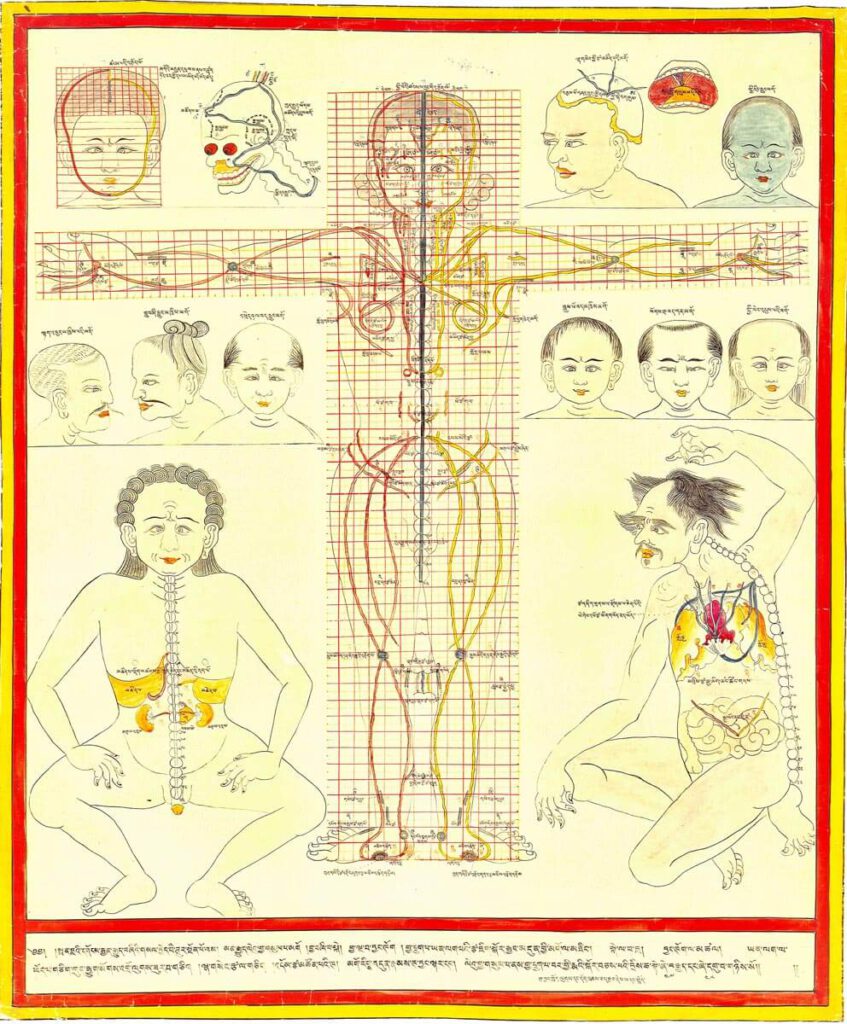
Major connecting blood vasculature of body including gut with related vulnerable points 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – Explicated in high detail in the traumatology section of the Four Tantras as developed from early military medical manuals, this painting depicts major blood vessels of the […]
Body metaphors including guts

Body metaphors including guts 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia – The musculoskeletal system is likened to the architecture of a Tibetan temple, while internal organs, differentiated as solid (vital) and hollow (vessel) types, use different illustrative metaphors. The group of solid viscera include the heart, […]
