The Gut / Der Darm
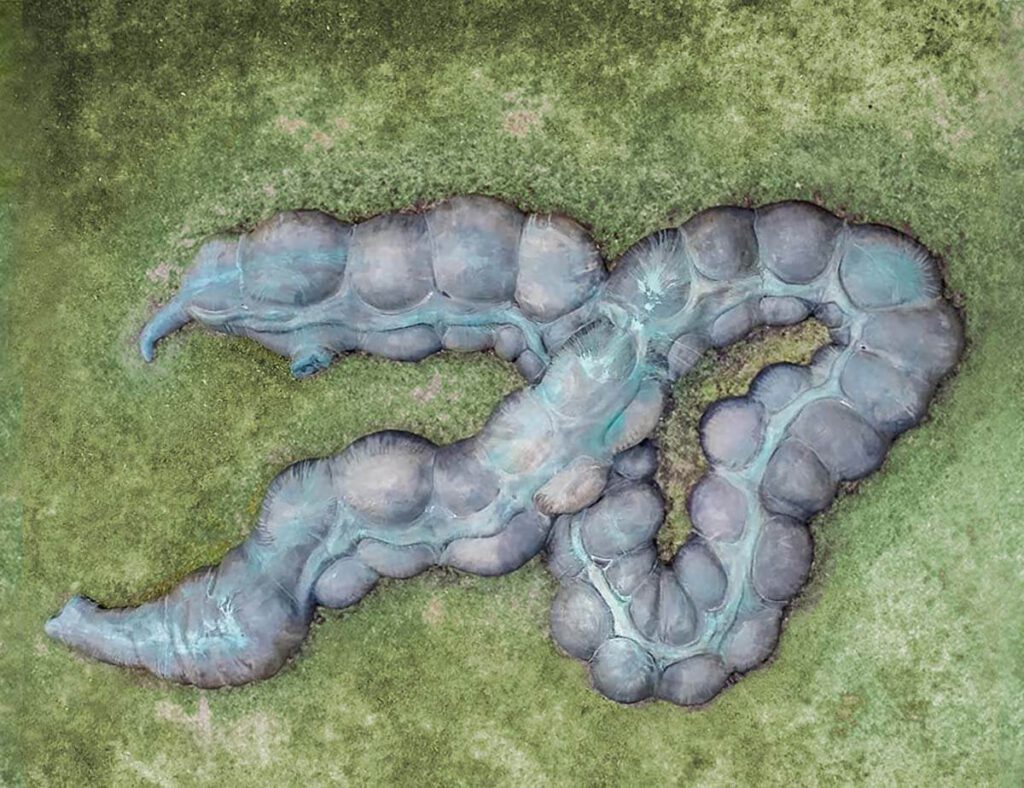
The Gut / Der Darm Anetta Mona Chisa & Lucia Tkacova public sculpture, Schillerplatz, Chemnitz (part of the project Gegenwarten | Presences), photographed by the artist – The Gut is the organ that renders Marx’s body in the city that holds the largest sculpture of Marx’s head in the world – Karl-Marx-Monument. The actual head […]
Henry Gray (anatomist) and Henry Vandyke Carter (artist), Fig. 1005, Superior and inferior duodenal fossæ.
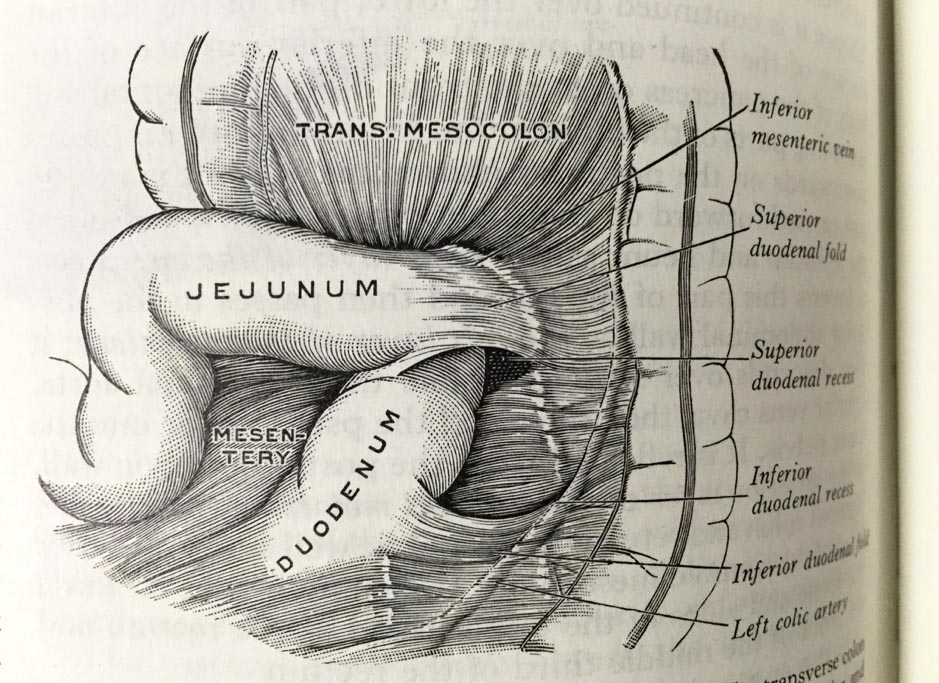
Henry Gray (anatomist) and Henry Vandyke Carter (artist), Fig. 1005, Superior and inferior duodenal fossæ. Gray’s Anatomy Descriptive and Applied. A New American Edition (1913), p. 1265.Private collection: Nina Sellars. Photographer: Nina Sellars. – Giving thoughtful attention to the physical qualities of the classical anatomical atlases brings our awareness not only to their content and […]
“Von Lebensadern umgeben, von Energie umgeben”
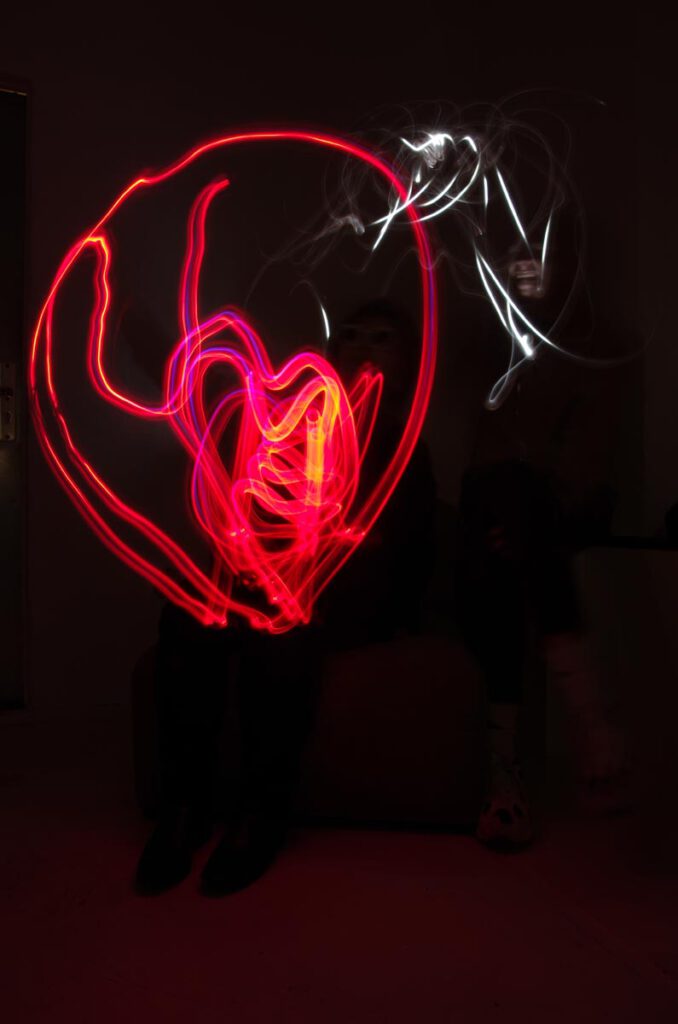

“Kopf mit Torso Im Licht verborgen” “Head with torso hidden in the light” – Lightpainting im Querformat mit schwarzem Hintergrund. Es schwebt ein sich leicht nach unten rechts neigend, ein rohrartiger, ein klein wenig nach oben gewölbter Gegenstand mit sehr unregelmäßigem, schattierten bläulich-weissem Wellencharakter. Es ist weiträumig umgeben von dünnen, kraftvollen roten, willkürlich geschwungenen Linien. […]
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist
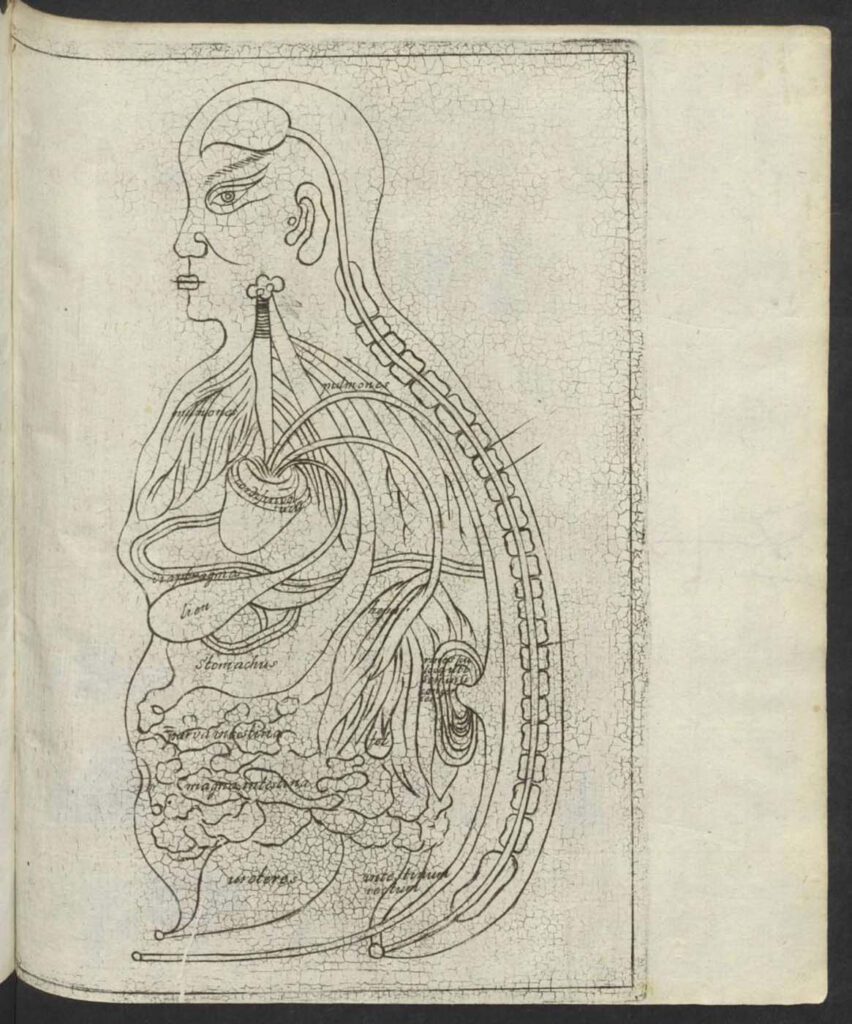
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist This “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (Image 1) but was printed in the 1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. The anonymous artist retained the Chinese original’s flat rendering (Image 1) rather than the three-dimensional rendering of Christian Mentzel’s sketch (Image 3) and the sketch (Image 4) in […]
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist
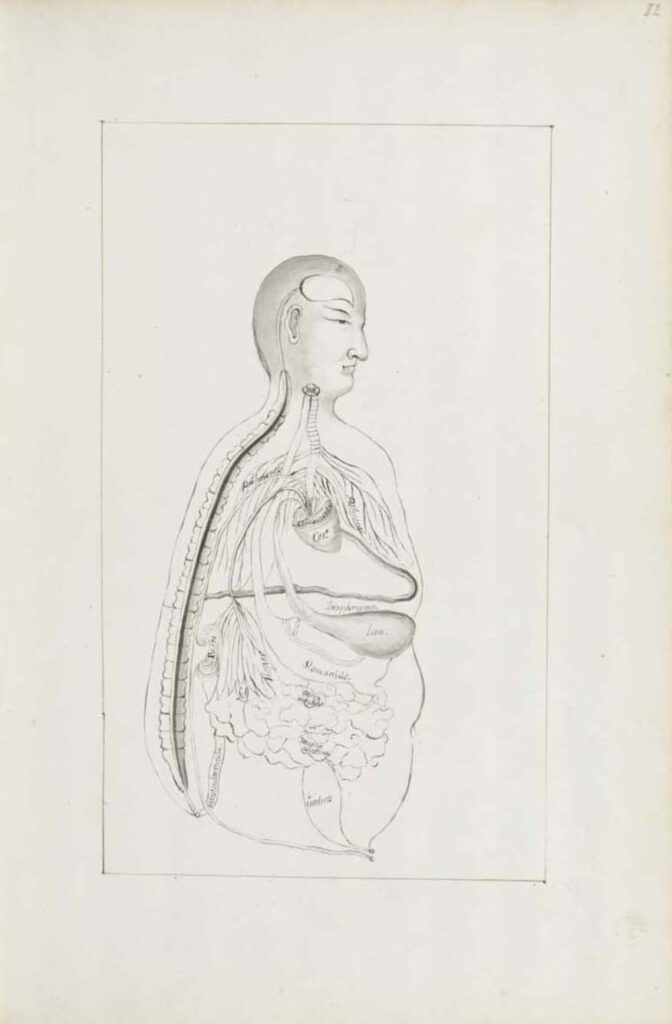
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist This sketch of the “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (image 1), however, the artist remains anonymous. It was included in the only known extant manuscript (Ms. Lat. Fol. 95 preserved in the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin) of the 1682 printed Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. It illustrates […]
Ca. 1681 Ms sin. 11, part 3 by Christian Mentzel
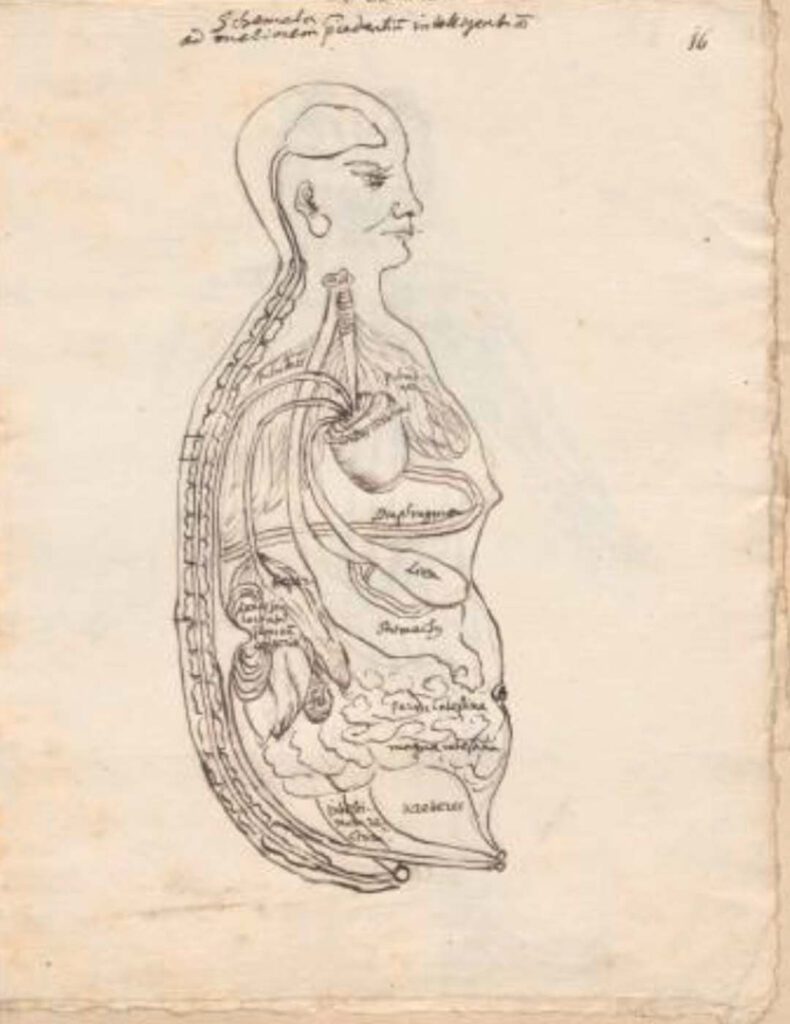
Ca. 1681 Ms sin. 11, part 3 by Christian Mentzel The personal physician to the Great Elector Friedrich Wilhelm of Brandenberg and curator of his library, Christian Mentzel (1622-1701), sketched this “Viscera Man” based on a Chinese source (Image 1). Both Mentzel’s sketch (Image 3) and the printed 1597 original (Image 1) are included in […]
1597 reprint of Wanbing huichun “Diagram of Man’s Side-Body”
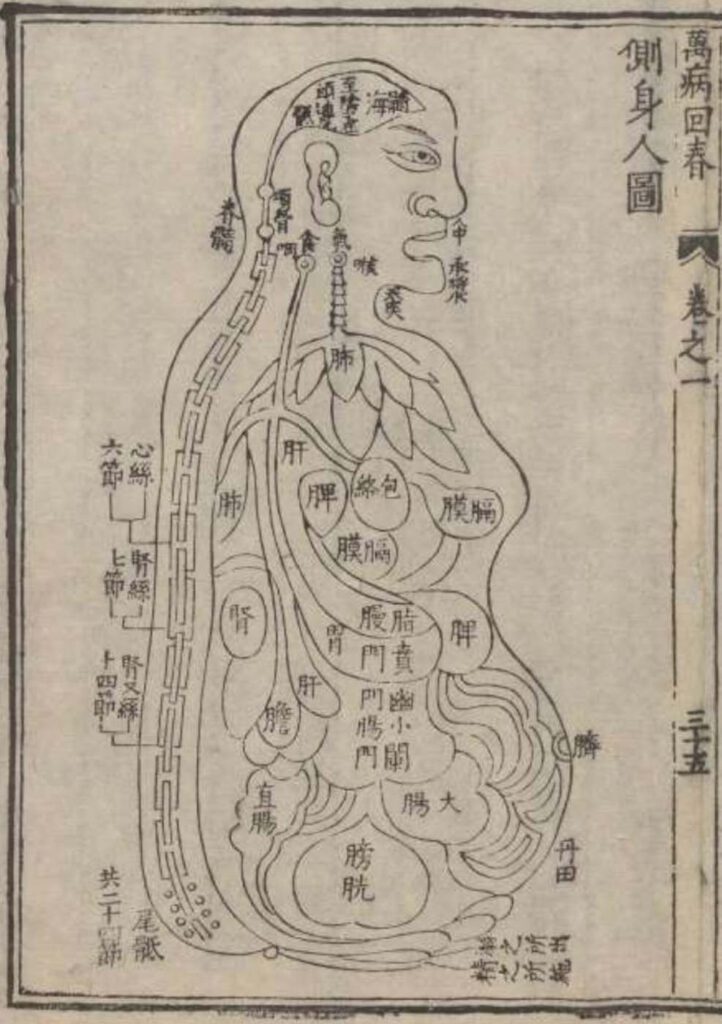
‘Diagram of Man’s Side-Body’ in 1597 reprint of Wanbing huichun (Ceshen ren tu 側身人圖). This version of the “Viscera Man” was printed in a 1597 reprint of the Chinese medical text Myriad diseases ‘Spring Returned’ (i.e., ‘cured’) (Wanbing huichun 萬病回春) that is preserved in the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin. – This 1597 reprint of a “viscera […]
Published in 1597 reprint of a 1565 Yixue gangmu, preserved in Ms sin. 11, part 1, “Enlightened-Hall Diagram of the Viscera”
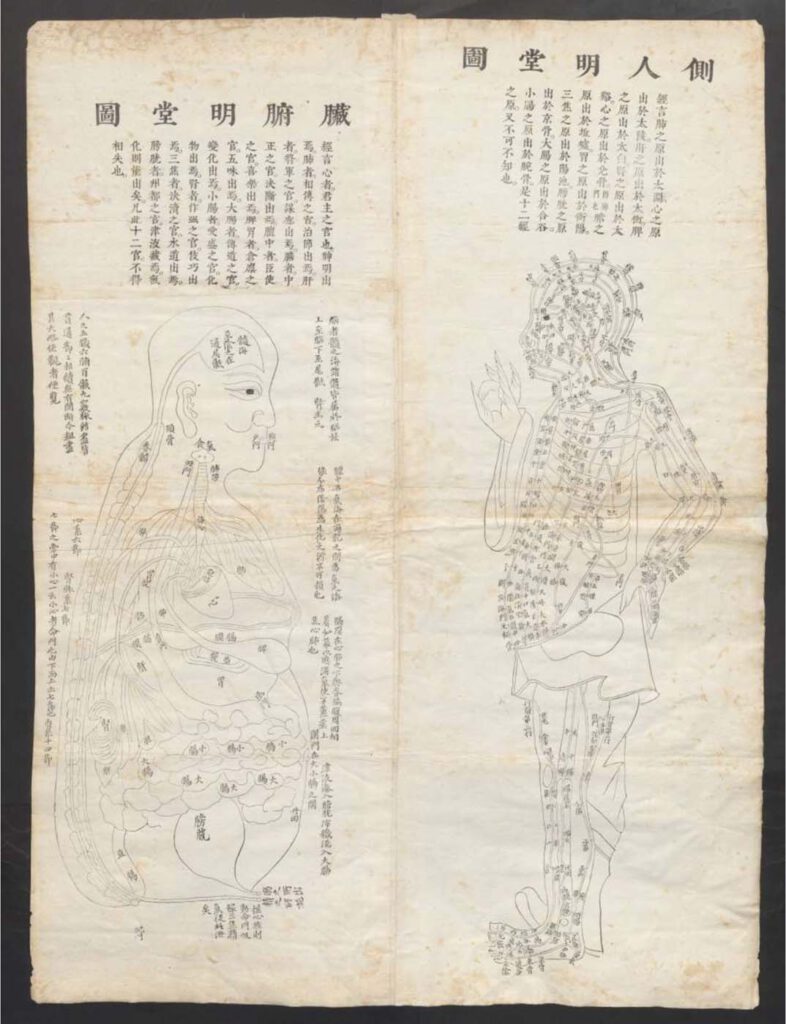
‘Enlightened-Hall Diagram of the Viscera’, in 1597 reprint of a 1565 Yixue gangmu, preserved in Ms sin. 11, part 1 (Zangfu Mingtang tu 臟腑明堂圖). This fold-out plate (ca. 79cm x 58cm) of a “Viscera Man” has been inserted into a manuscript (ms. sin. 11) preserved in Biblioteka Jagiellońska Kraków, Poland, digitalized by the Staatsbibliothek in […]
John Banister Delivering an Anatomical Lecture on the Viscera
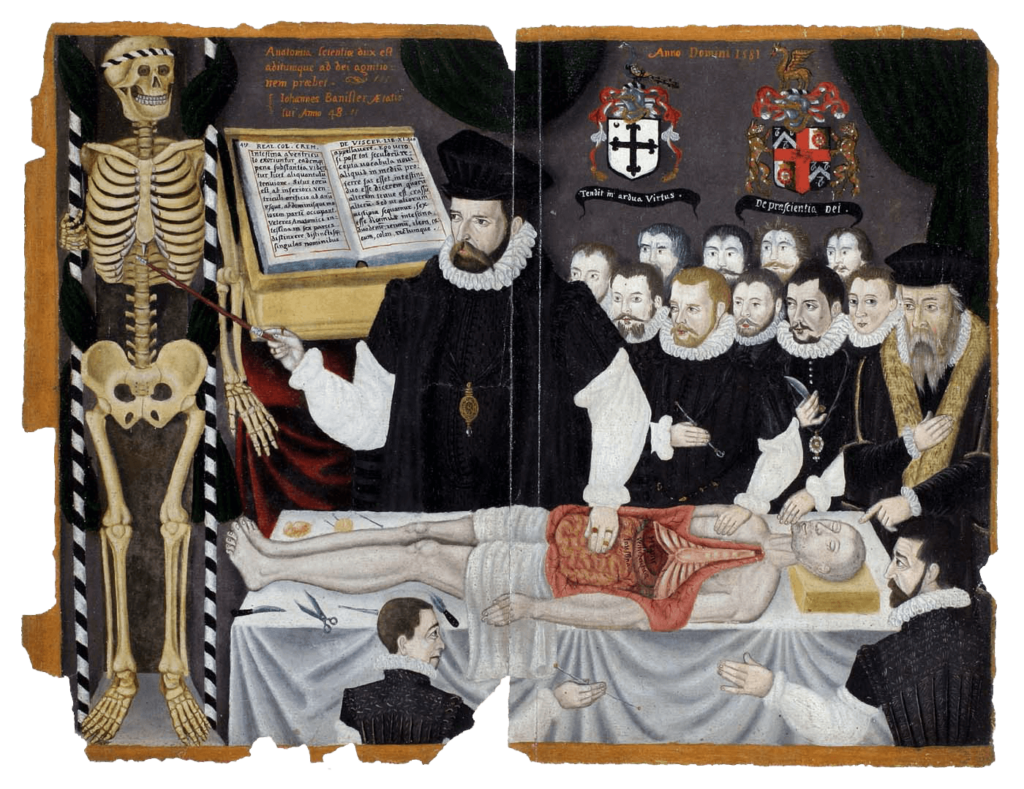
John Banister Delivering an Anatomical Lecture on the Viscera 1581, painting, 33.8 x 43.2 cm. University of Glasgow Library, Glasgow, GB 247 MS Hunter 364 (V.1.1), frontispieceUniversity of Glasgow Archives & Special Collections, MS Hunter 364. – The English surgeon and physician John Banister (1532/3–1599?) lectures on the viscera, placing his hand on the open abdomen […]
Abdominal Dissection
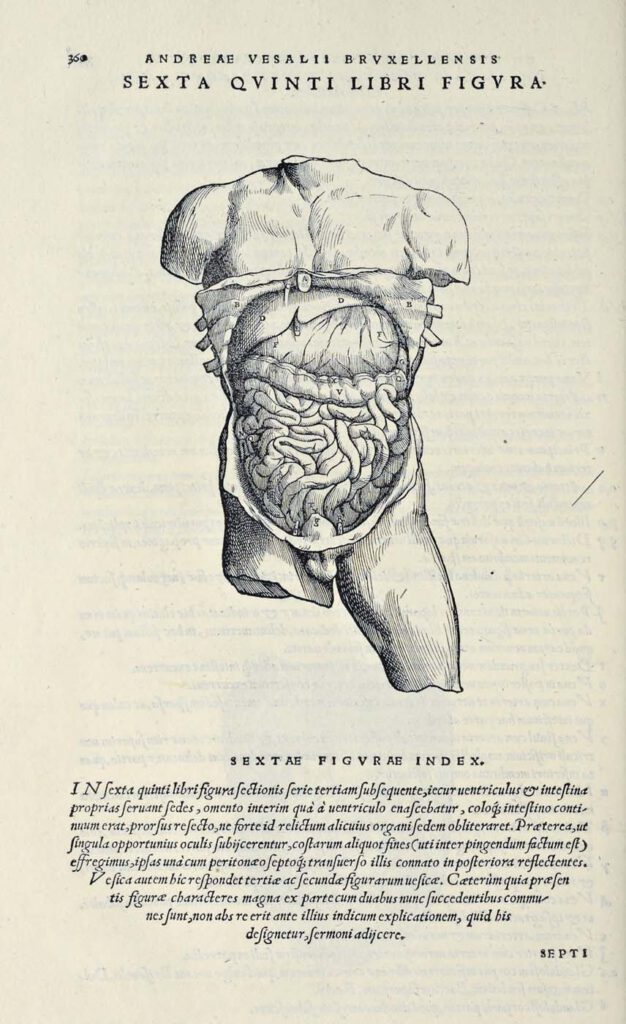
Abdominal Dissection woodcut after Jan Steven van Calcar (North Netherlandish, ca. 1515– ca. 1546). From Andreas Vesalius, De humani corporis fabrica libri septem (Basel: J. Oporinus, 1543), bk. 5, p. 360 [460], fig. 6. Getty Research Institute, Los Angeles, 84-B27611 – Ribs have been broken and the skin peeled back to display the liver, stomach, […]
