The 3D Model of the Digestive System according to Aristotle
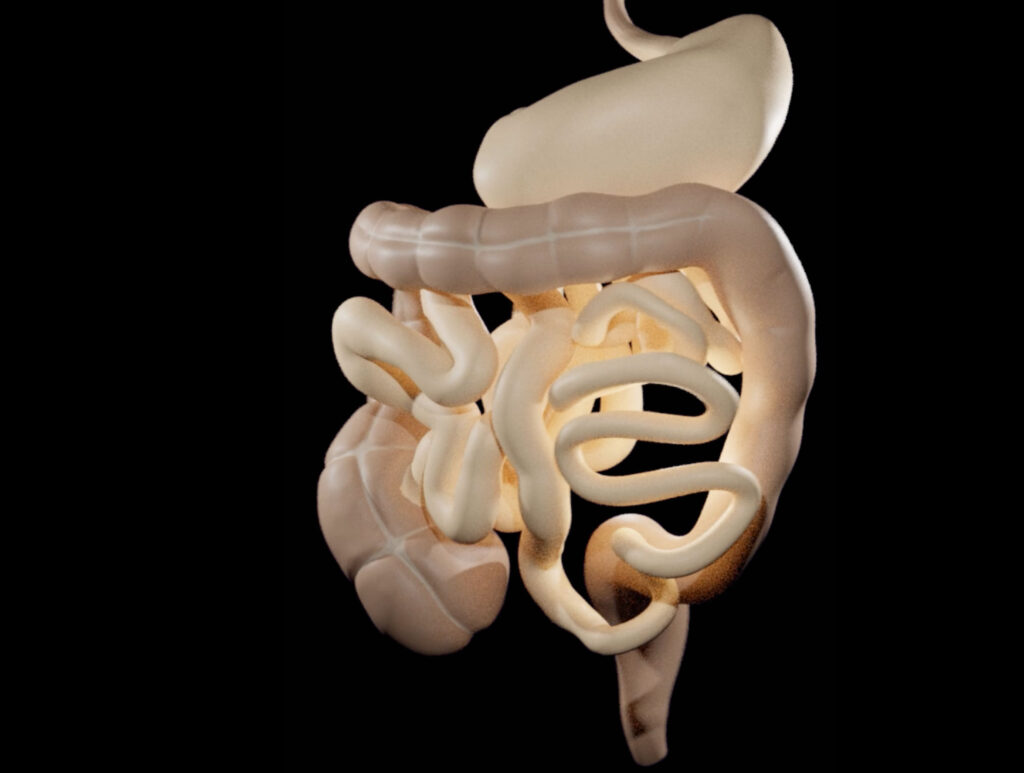
https://comparative-guts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Atlomy-Exhibit-4_2.mp4 The 3D Model of the Digestive System according to Aristotle Copyright: ATLOMY (ERC StG GA 852550) Hebrew University of Jerusalem – This 3-D model of the stomach and the intestines presents ATLOMY’s interpretation of the ancient text. While it might not be evident at first sight, this model differs from contemporary models of the […]
3D Modelling of the Guts according to Aristotle
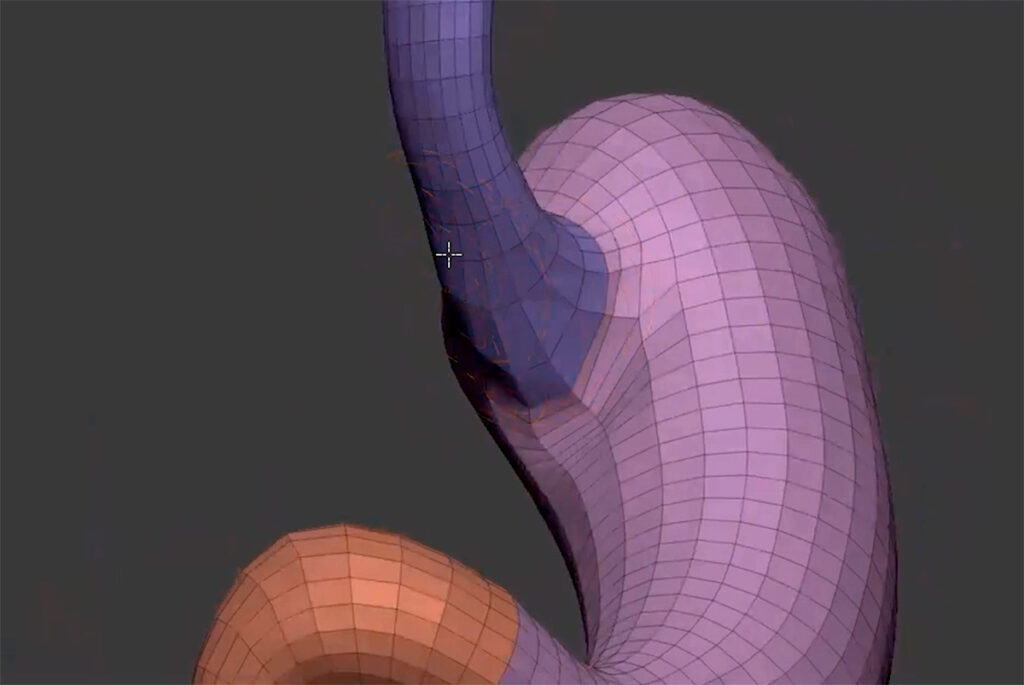
https://comparative-guts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Atlomy-Exhibit-3_1.mp4 3D Modelling of the Guts according to Aristotle Copyright: ATLOMY (ERC StG GA 852550) Hebrew University of Jerusalem – The next stage towards a visual reconstruction of Aristotle’s conception of guts is creating the 3D model. Based on the Table of Instructions the modellers use 3D-modelling software to create the model: from an initial […]
From Text to Model: The Guts according to Aristotle
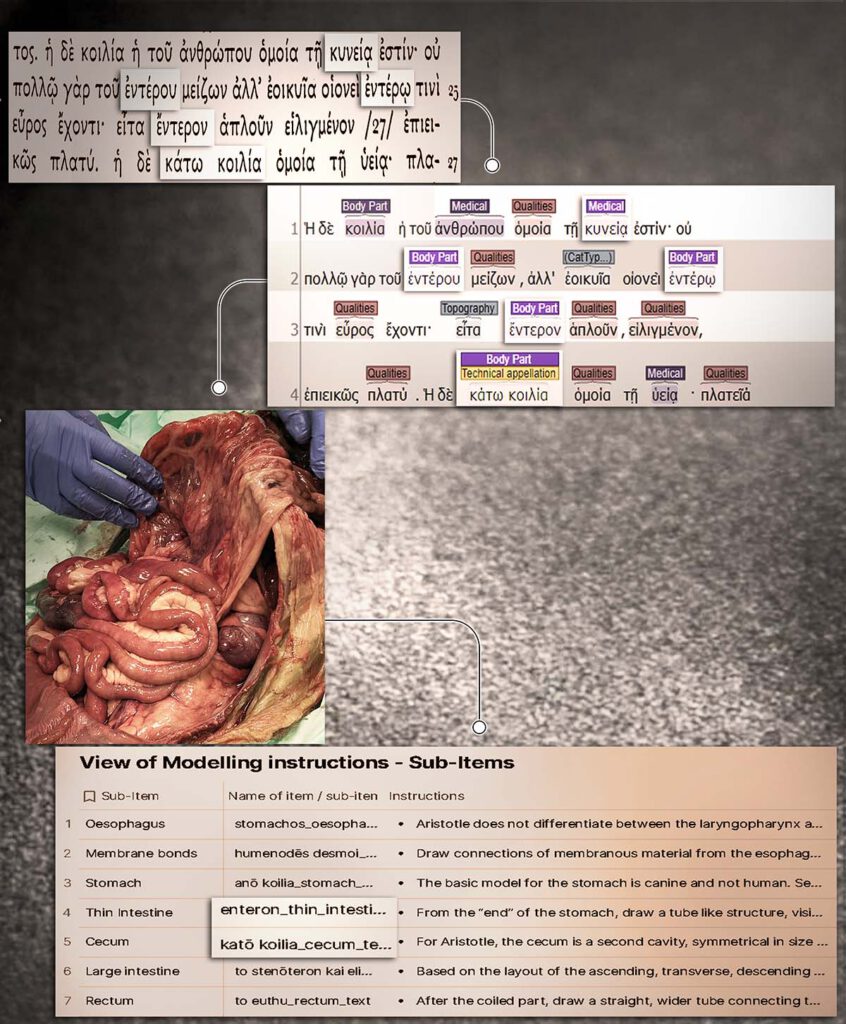
From Text to Model: The Guts according to Aristotle Copyright: ATLOMY (ERC StG GA 852550) Hebrew University of Jerusalem – A depiction of the first stages towards creating a 3D model of the human guts as described in Aristotle’s treatise Inquiries on Animals. The interdisciplinary team facilitates a unique analysis which bridges the gap between […]
From Observation to Text: The Guts according to Aristotle

From Observation to Text: The Guts according to Aristotle Copyright: ATLOMY (ERC StG GA 852550) Hebrew University of Jerusalem Bronze retractor, Roman, 1-100 CE. Science Museum, London. Attribution 4.0. International (CC BY 4.0) http://www.internetculturale.it/ – Sacrificial rituals were a common means to observe and learn about internal anatomy in ancient Greece. Aristotle investigated the body […]
Red-figured terracotta krater
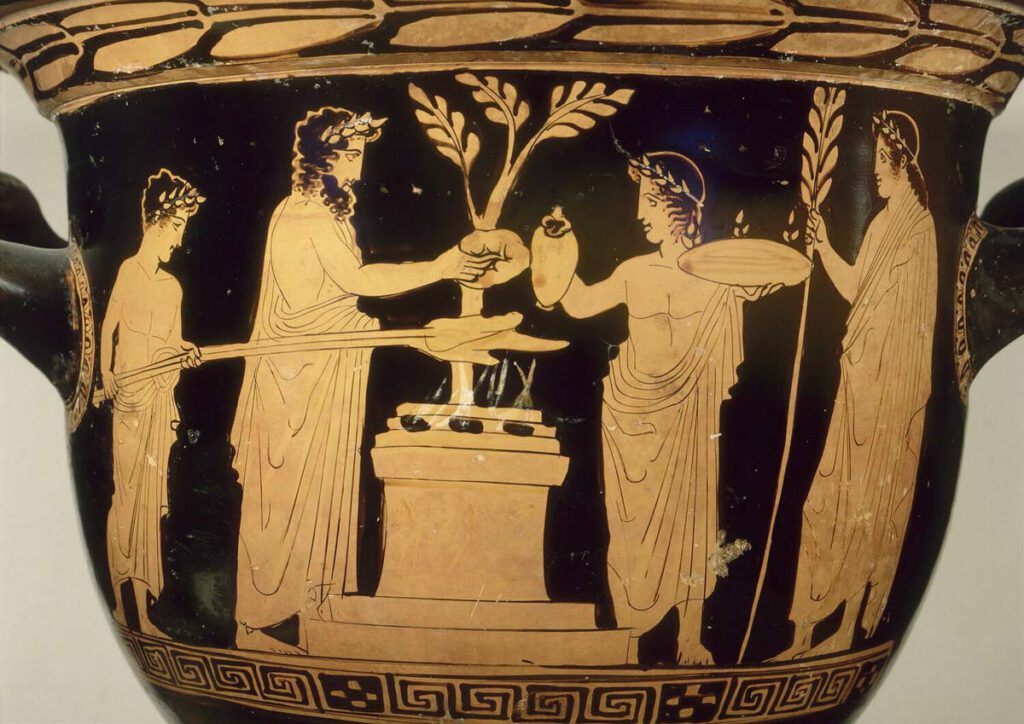

Red-figured terracotta bell-krater – Vessel for mixing wine and water, late 5th century BCE, with four figures and altar smoking with knisa. The boy on the left is holding skewered splanchna and roasting them on the fire. These would produce a complex odour profile including meaty, fatty and smokey odours. A man to the right […]
Red-figured terracotta bell-krater
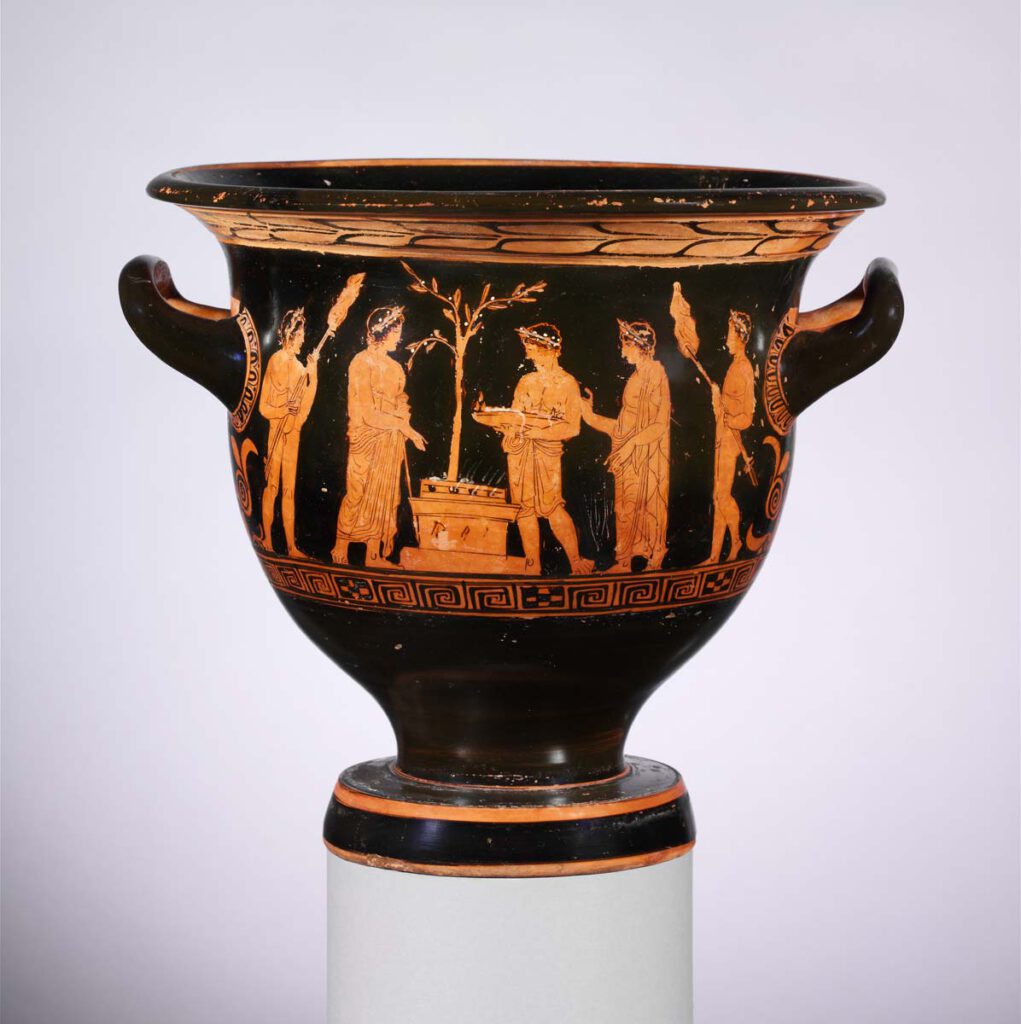

Red-figured terracotta bell-krater – Vessel for mixing wine and water, attributed to the Nikias Painter, late 5th century BCE, with three youths preparing meat offering, altar stacked with burning wood and smoking with knisa. Attendants on either side carry skewers likely holding viscera. The viscera would release putrescine and cadaverine, whose scent is characterised as […]
Red-figured terracotta stamnos
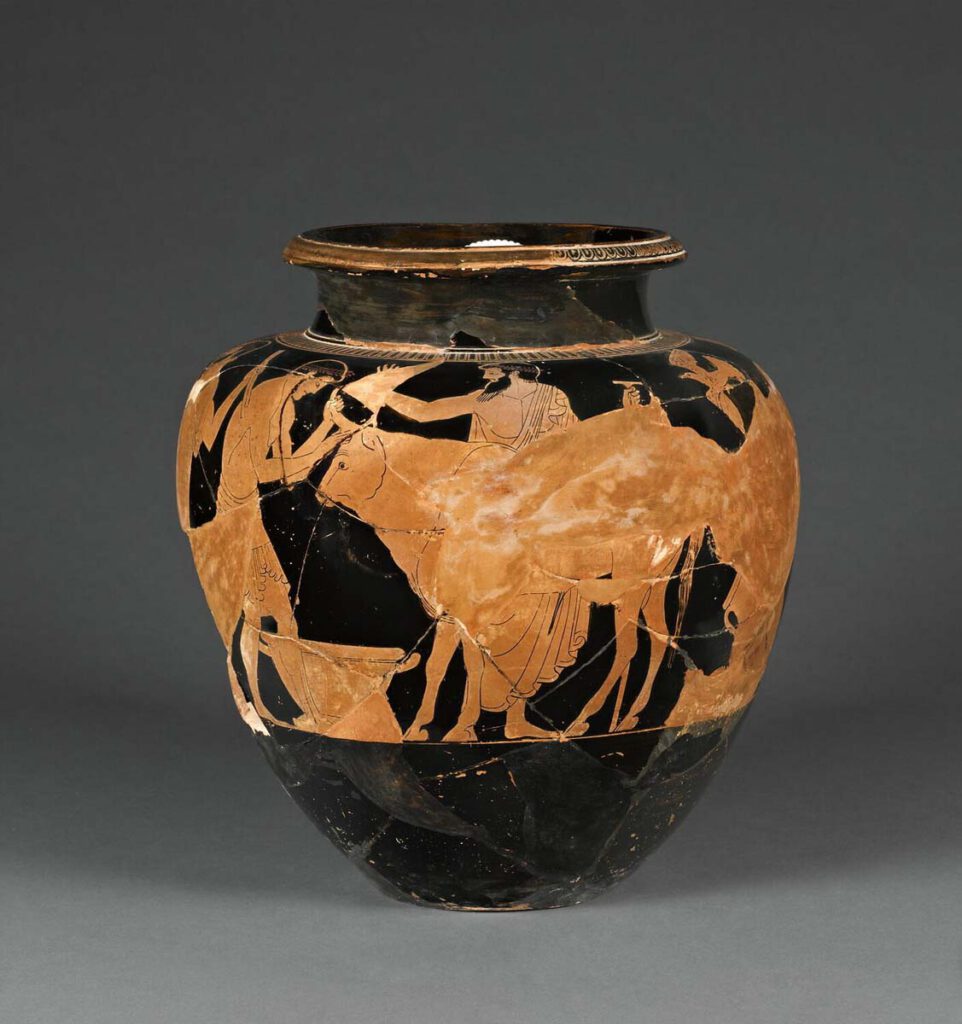

Red-figured terracotta stamnos – Vessel for storing liquids, attributed to the Eucharides Painter, early 5th century BCE, with two figures preparing a bull for sacrifice. When slaughtered, iron ions derived from the haemoglobin in the animal’s blood would interact with fats and oils to form volatile aldehydes and ketones, like Oct-1-en-3-one, typical sources for the […]
Black-figured terracotta column-krater

Black-figured terracotta column-krater – Vessel for mixing wine and water, late 5th century BCE, with men sacrificing a goat to a terminal figure of the god Hermes. The sacrificial victim has been dismembered and a part is being held in the flame on the altar. The entrails resting on the small table would release odorants […]
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist
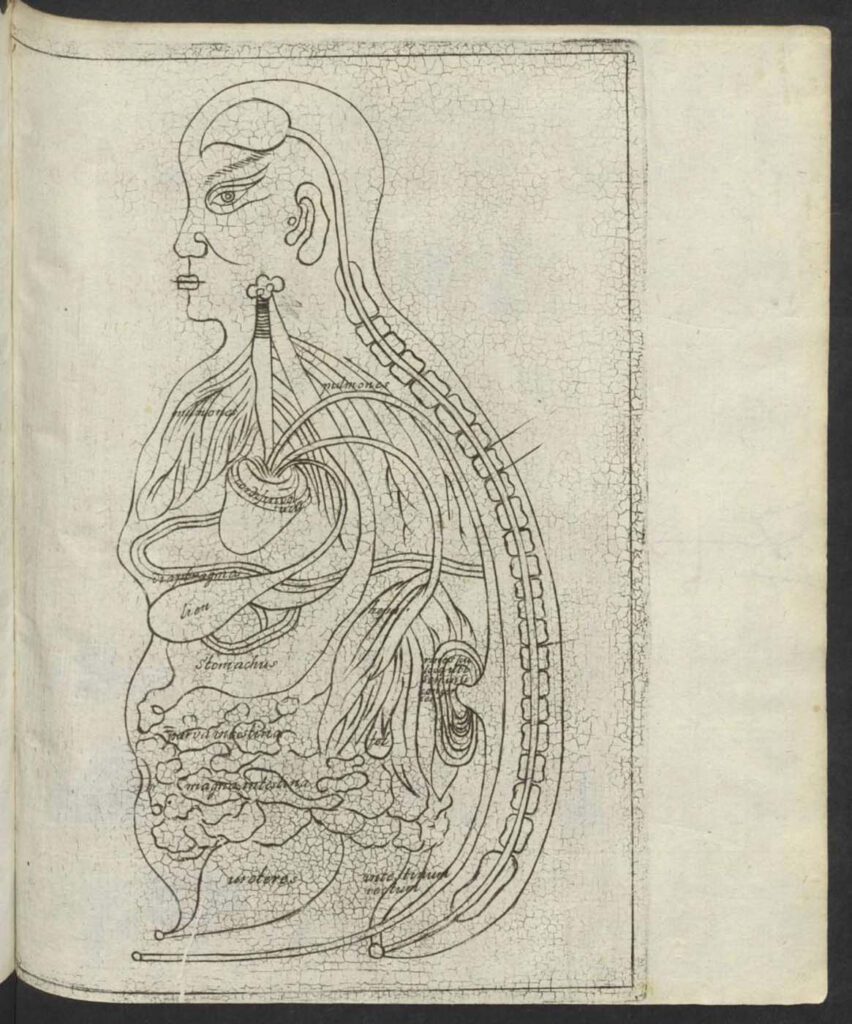
1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae, unknown artist This “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (Image 1) but was printed in the 1682 Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. The anonymous artist retained the Chinese original’s flat rendering (Image 1) rather than the three-dimensional rendering of Christian Mentzel’s sketch (Image 3) and the sketch (Image 4) in […]
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist
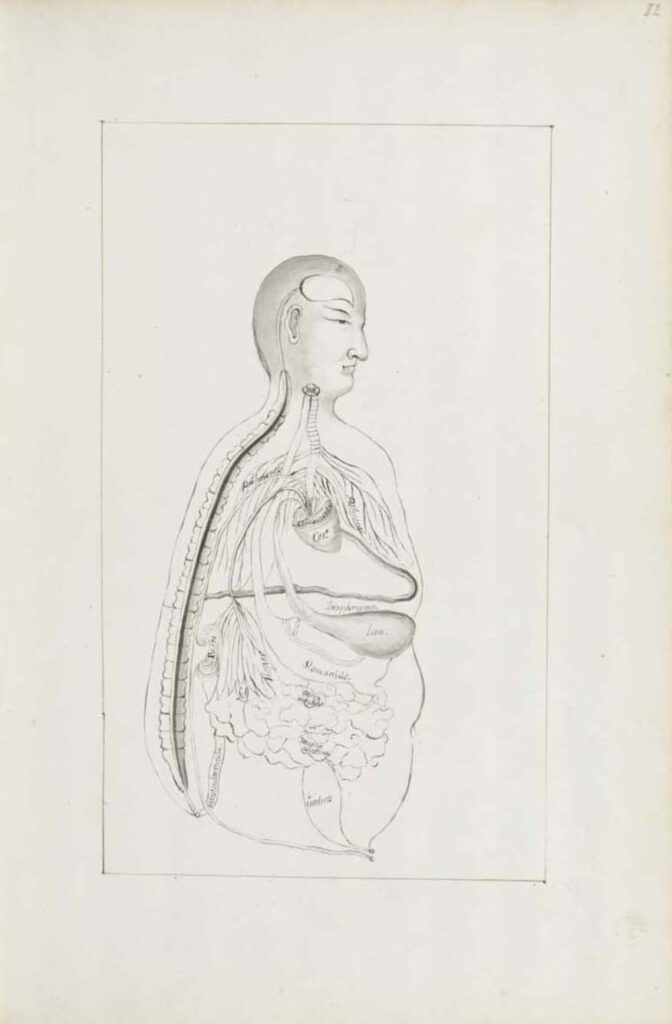
Ca. 1660s-1681c. Lat. Fol. 95, unknown artist This sketch of the “Viscera Man” was also based on a Chinese source (image 1), however, the artist remains anonymous. It was included in the only known extant manuscript (Ms. Lat. Fol. 95 preserved in the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin) of the 1682 printed Specimen Medicinae Sinicae. It illustrates […]
