Manase Dōsan 曲直瀬道三, Hyakufuku zusetsu
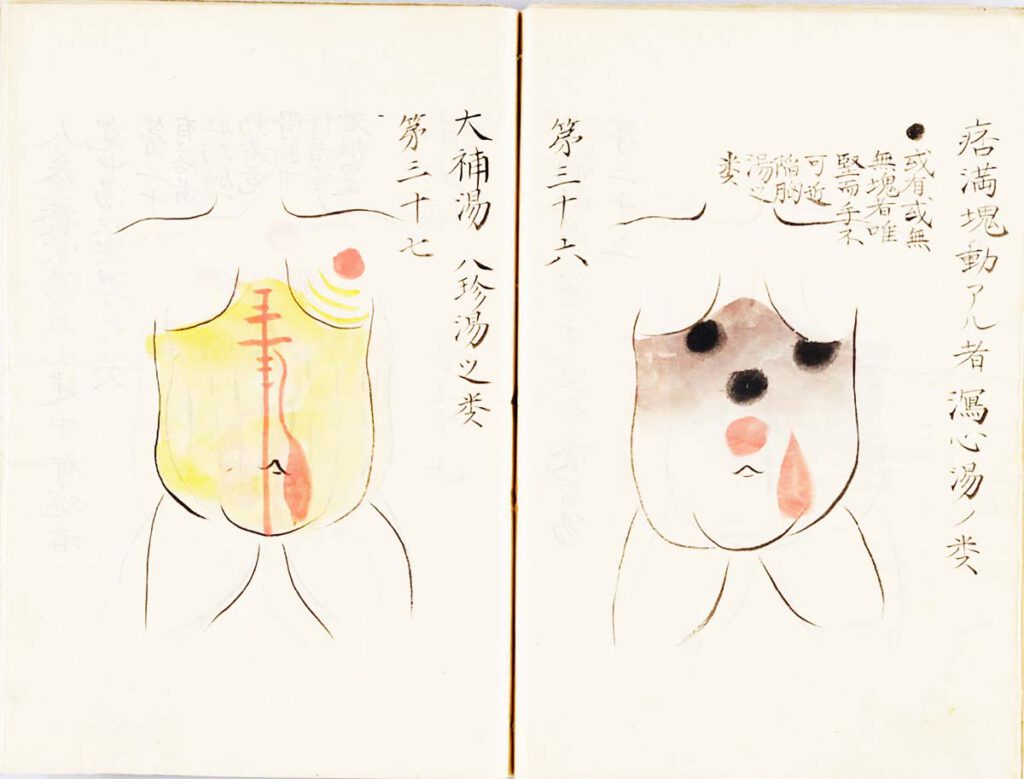
Manase Dōsan 曲直瀬道三, Hyakufuku zusetsu (百腹図説, “Illustrated Explanations of a Hundred Bellies”; n.d.) – Nothing more directly translated the early modern stress on practical, tangible realities than the Japanese innovation known as fukushin 腹診 (abdominal inspection). Whereas Chinese doctors had relied chiefly on feeling the pulse at the wrist to diagnose diseases, Japanese advocates of […]
Sugita Gempaku’s Kaitai shinsho
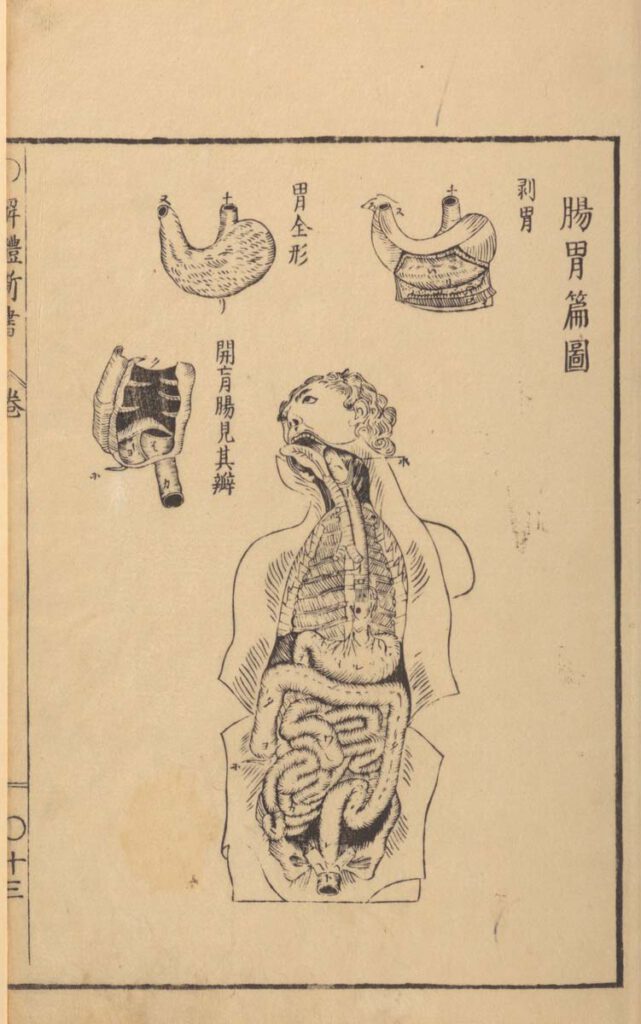
Sugita Gempaku’s Kaitai shinsho (解体新書, “New Book of Anatomy”; 1774) – Sugita Gempaku undertook his epoch-making translation of a Dutch anatomical manual before he could read Dutch. This point is key: What persuaded him of the manual’s truth was not its text, which he initially couldn’t comprehend, but rather, its images, and more specifically their […]
Moxibustion points according to Medical Arts of the Lunar King, Sowa Rigpa intersections with Chinese and Indian medical canons
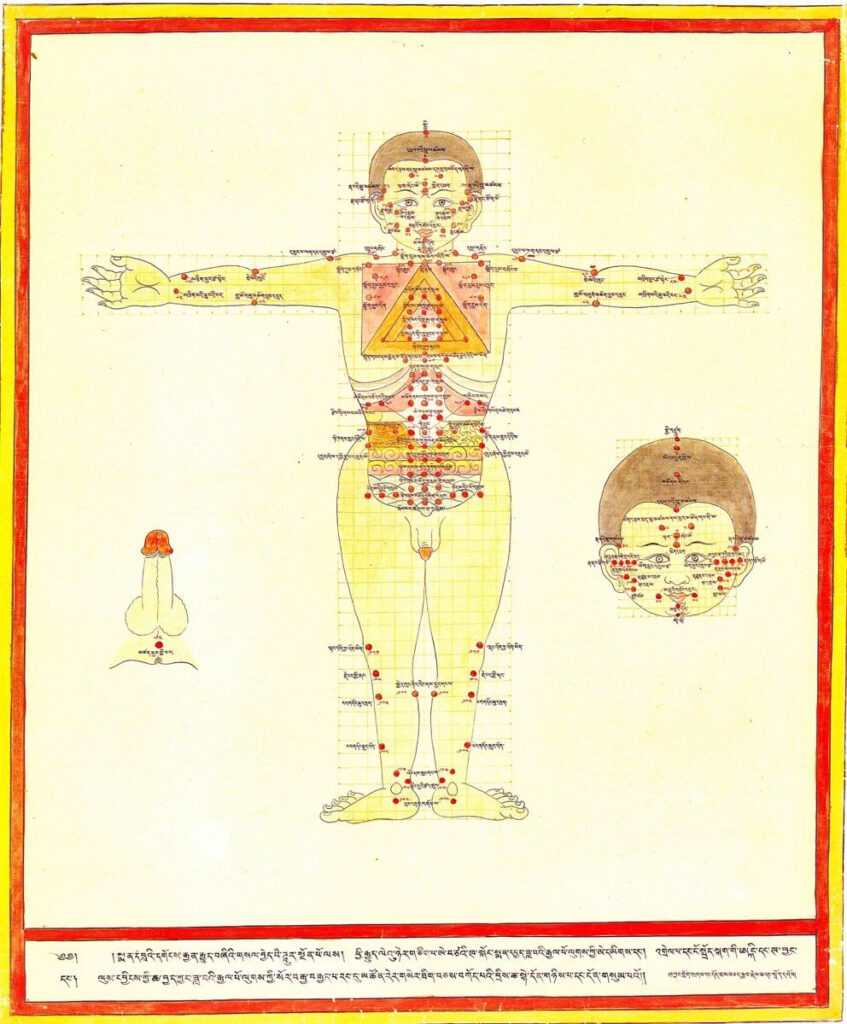
Moxibustion points according to Medical Arts of the Lunar King, Sowa Rigpa intersections with Chinese and Indian medical canons 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – Moxibustion is a treatment particularly indicated for metabolic conditions (ma zhu ba) and weak digestive fire (me drod nyams pa) […]
Treatment points for moxibustion, venesection, and surgery
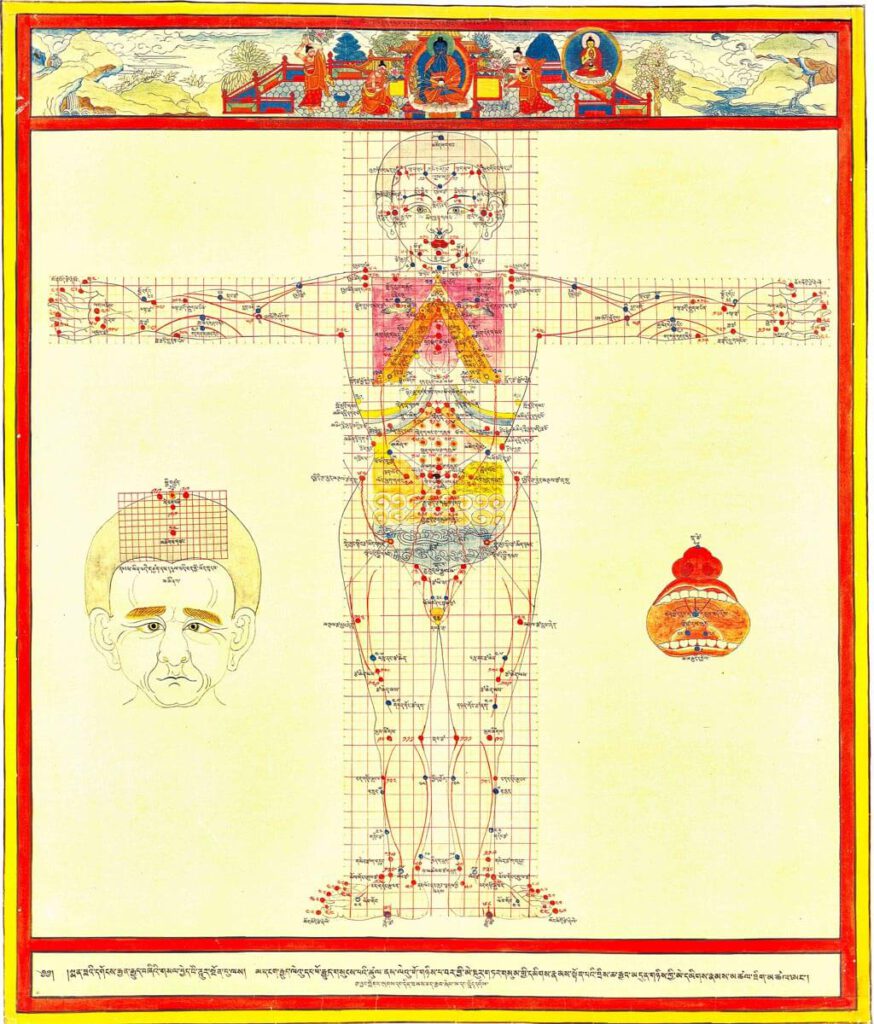
Treatment points for moxibustion, venesection, and surgery 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – This painting depicts the anterior view for the three types of external therapy treatment points: moxibustion, venesection, and surgical puncture. Moxibustion points are vermillion numbers and lines, venesection points are blue lines […]
Guts depicted as vulnerable part of the body
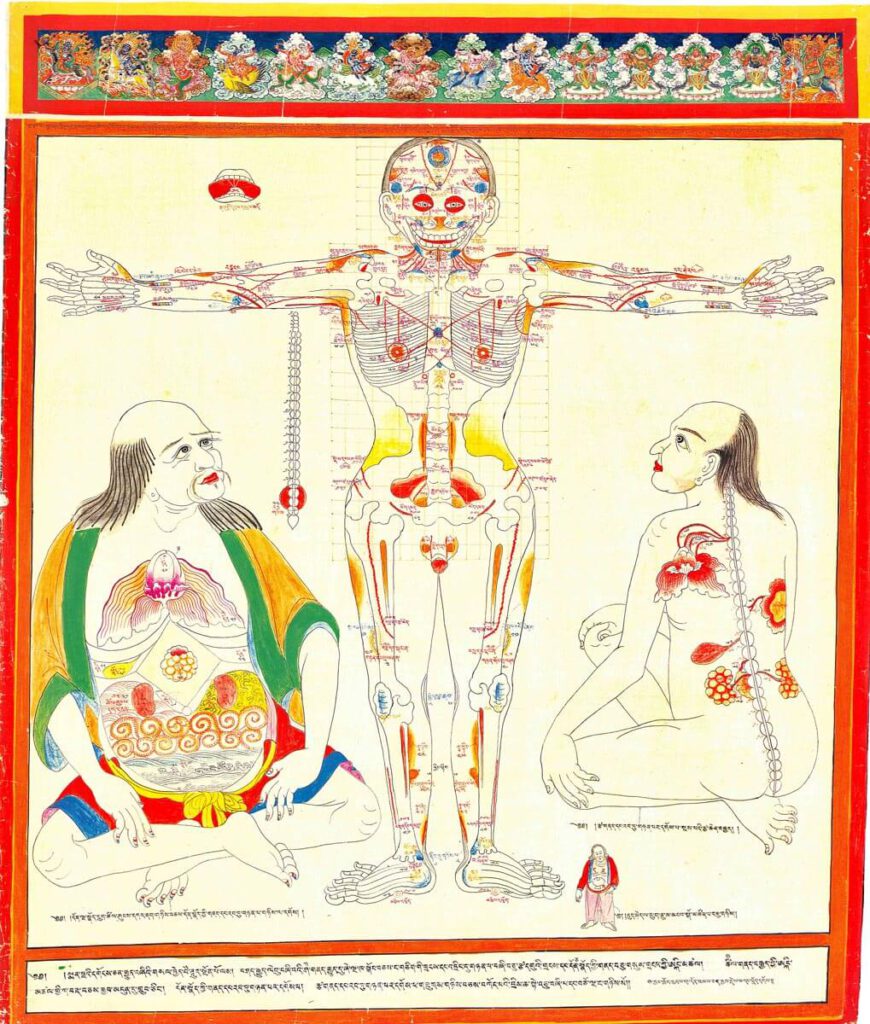
Guts depicted as vulnerable part of the body 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – Tibetan medicine recognizes specific vulnerable body parts to which trauma is described to be terminal or at least treated with difficulty. All critical internal organs are defined as vulnerable, the left […]
Minor connecting blood vasculature of the body including gut
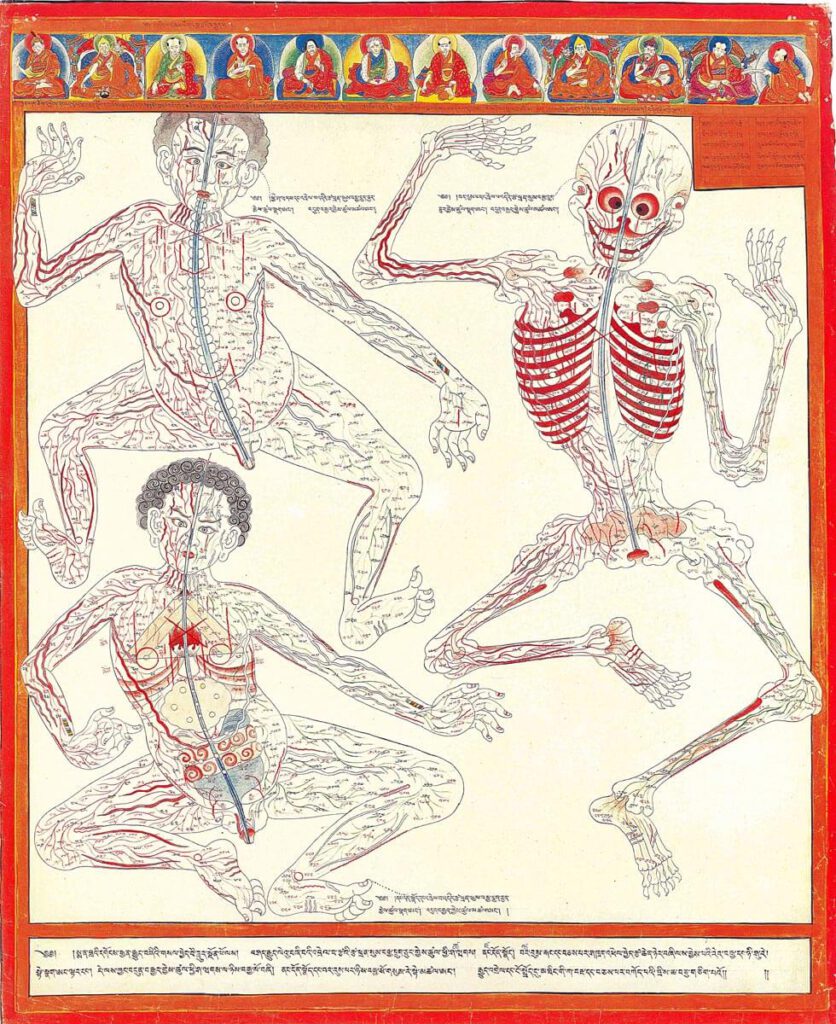
Minor connecting blood vasculature of body including gut 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia – The Four Tantras details specific enumerations of minor channels illustrated here in anatomical layout with important physiological functions. There are 360 interconnecting channels as they relate to skin and muscle tissue, […]
Major connecting blood vasculature of the body including gut with related vulnerable points
Major connecting blood vasculature of body including gut with related vulnerable points 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – Explicated in high detail in the traumatology section of the Four Tantras as developed from early military medical manuals, this painting depicts major blood vessels of the […]
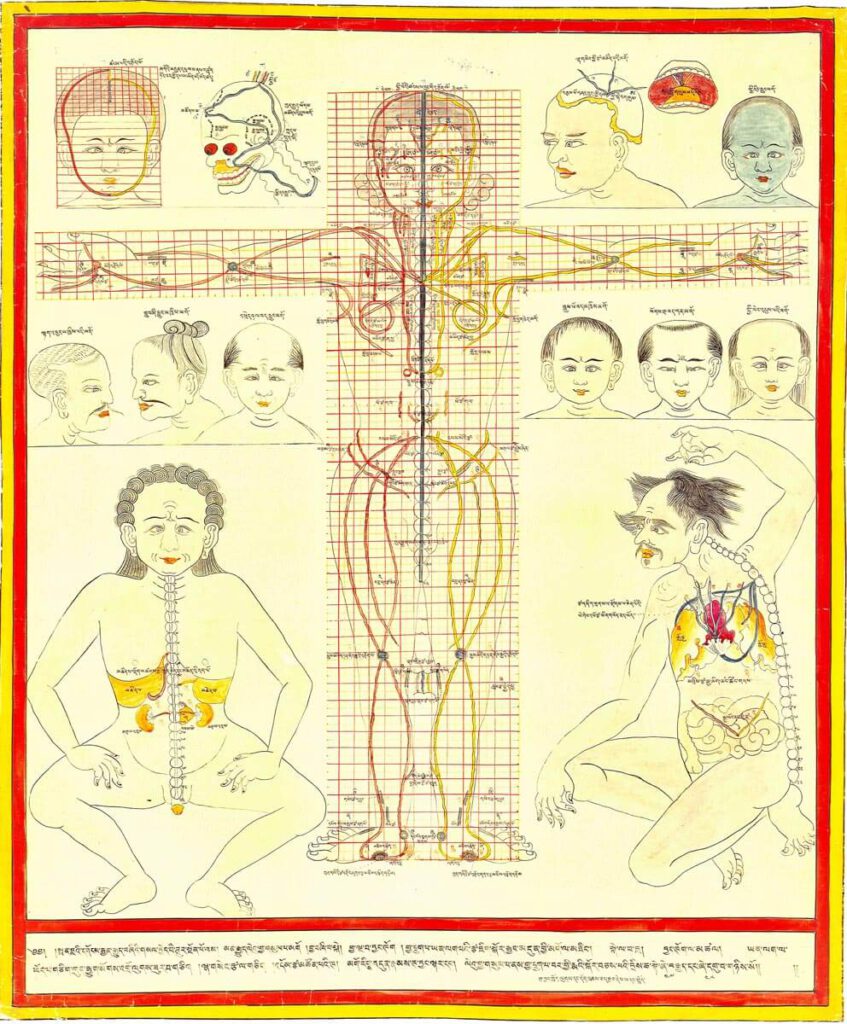
Body metaphors including guts

Body metaphors including guts 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia – The musculoskeletal system is likened to the architecture of a Tibetan temple, while internal organs, differentiated as solid (vital) and hollow (vessel) types, use different illustrative metaphors. The group of solid viscera include the heart, […]
Location of internal organs on modular grid
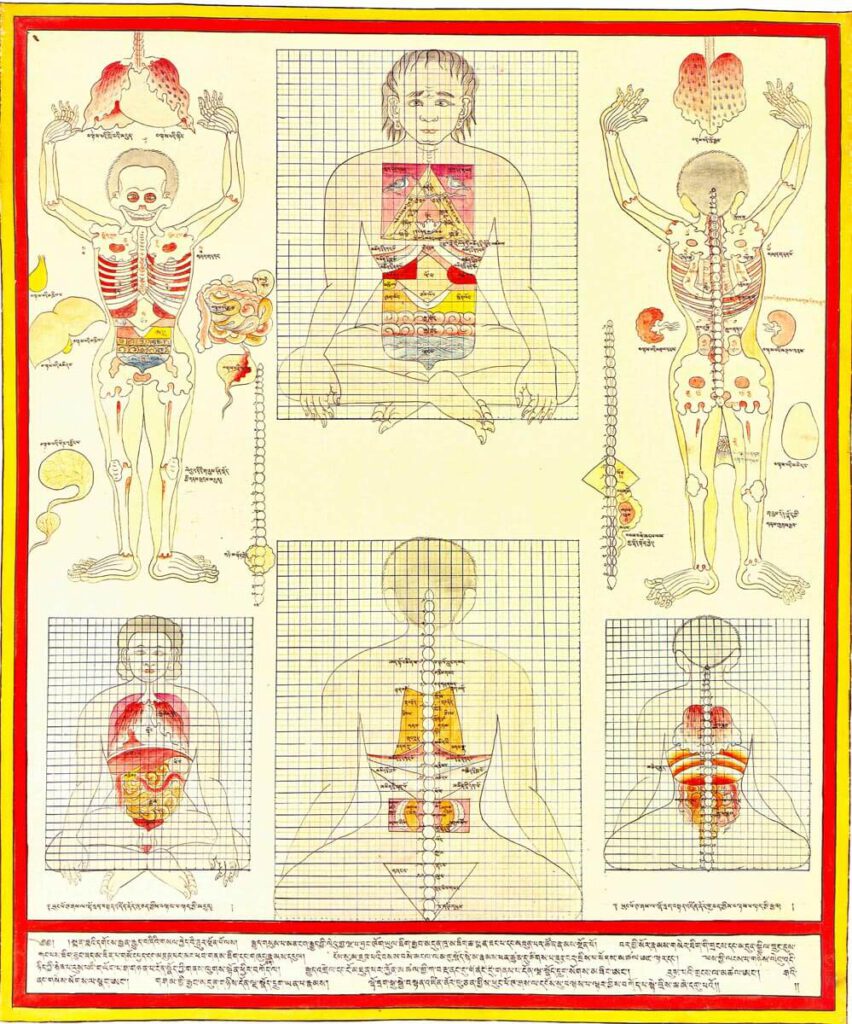
Location of internal organs on modular grid 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – The central figures present the anterior and posterior views of the proper positions and proportions of anatomical structures from a theoretical perspective in relation to the spine by means of the Tibetan […]
Anatomy of the gut, anterior view
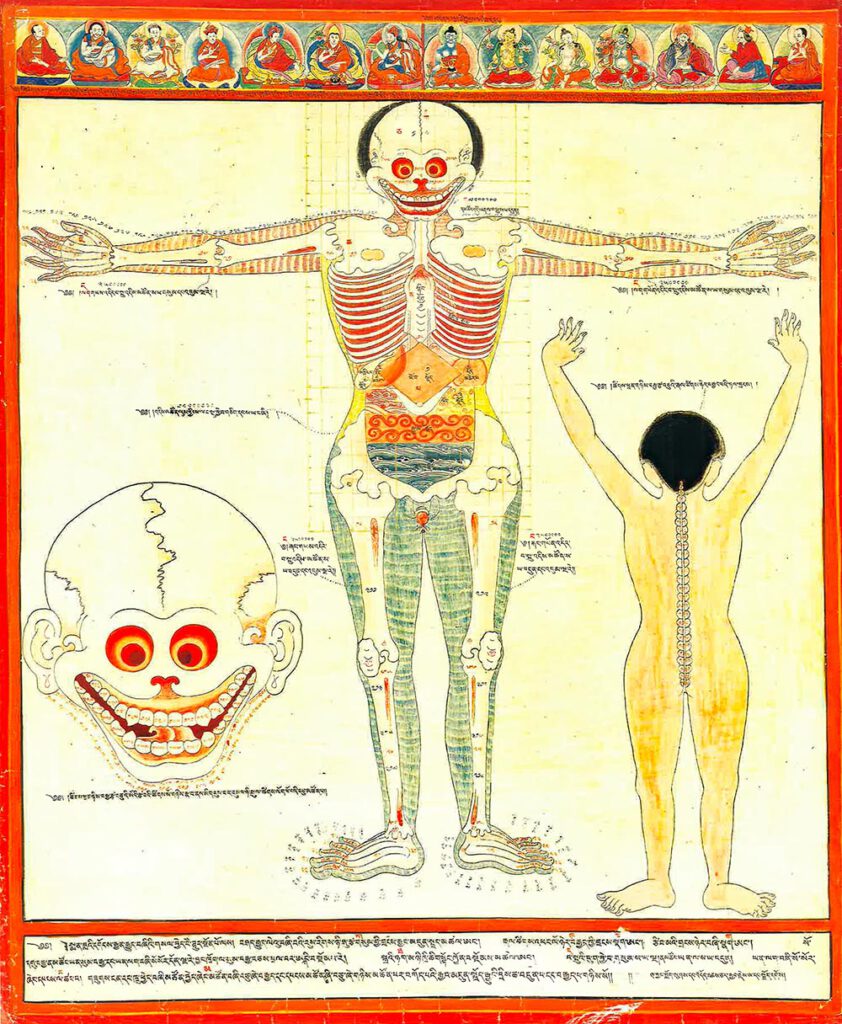
Anatomy of the gut, anterior view 20th century reproduction of 17th century CE painting. Held in Ulan-Ude, Republic of Buryatia, Russia. – This painting displays an enumeration of body part components (e.g., bones, vertebrae, joints, etc.) and diagrams the proper associated relational measures in anterior view using a quadrant grid. The abdominal quadrant covers 12×8 […]
