A female ‘open torso’ figurine

A female ‘open torso’ figurine Nottingham Castle Museum – This female figurine was discovered at the sanctuary of the Graeco-Roman goddess Artemis/Diana Nemorensis at Lake Nemi in Italy in 1885. It was excavated and recovered from a sacred pit where it had been ritually disposed of sometime in antiquity after it had ceased to be […]
A polyvisceral plaque
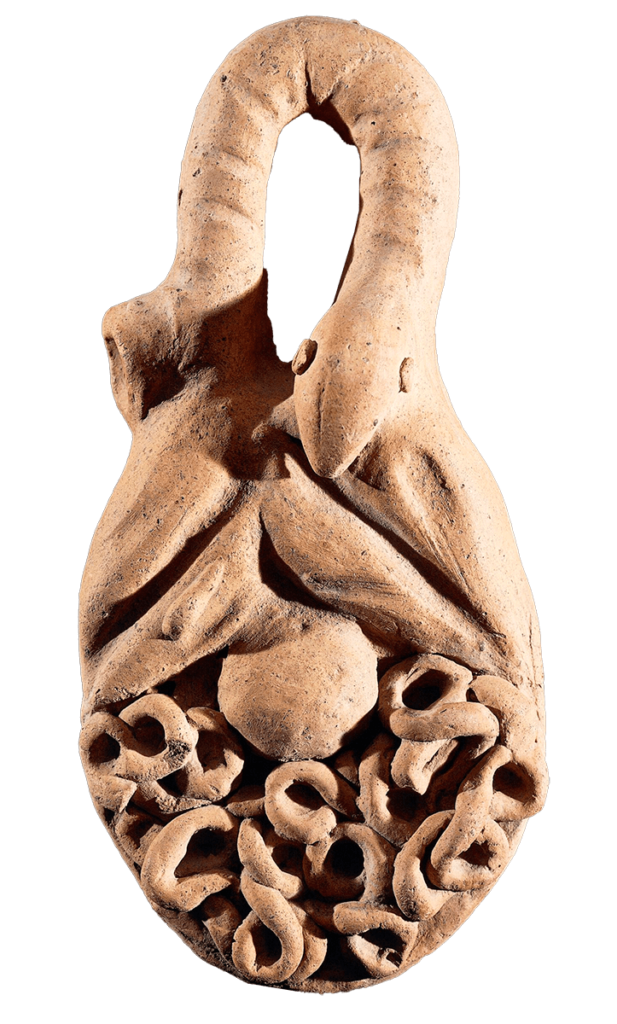

A polyvisceral plaque Museo Nazionale Etrusco Di Villa Giulia – This Etruscan polyvisceral plaque from Tessennano in Latium in Italy is thought to date from around 400 BCE. Anatomical votives like these were deposited in sanctuaries and temples as offerings to the gods, generally interpreted as a gesture of gratitude for some manner of divine […]
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra
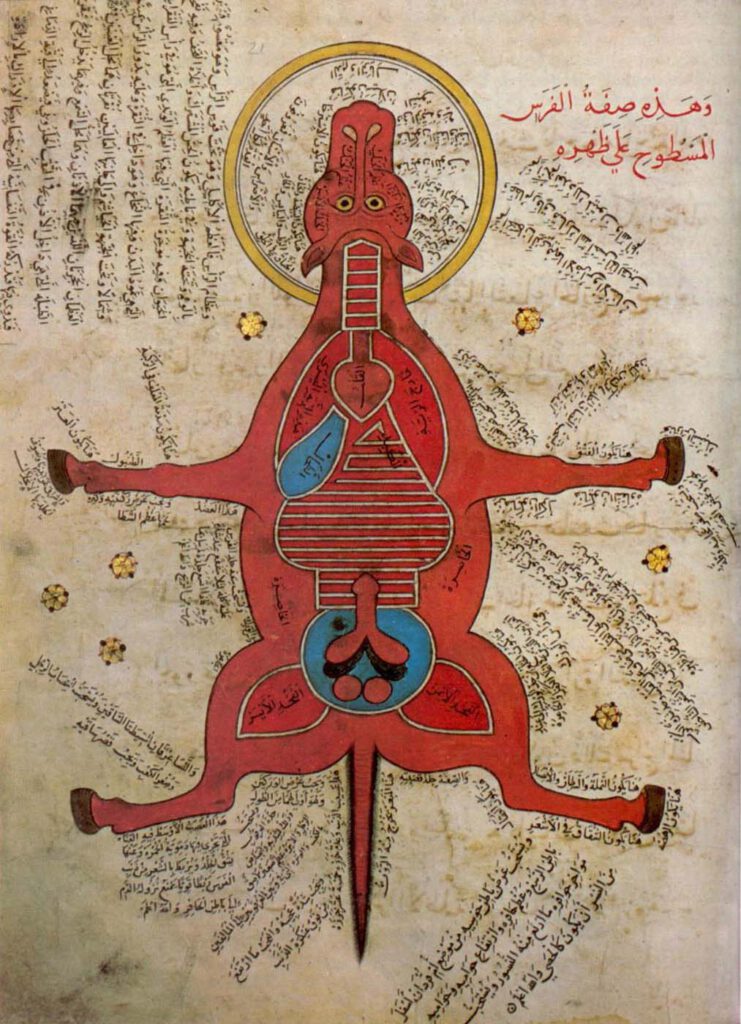
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra (Commentary on the Maqāma Ṣalāḥiyya on Horses and Venterinary) Istanbul University Library MS 4689 – Egypt, 15th c. – Hyppiatry has a long tradition in Islamic literature. Works dealing with horses may adopt different literary genres and cover a wide range of disciplines, from veterinary sciences to […]
Representation of a woman with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 15v)
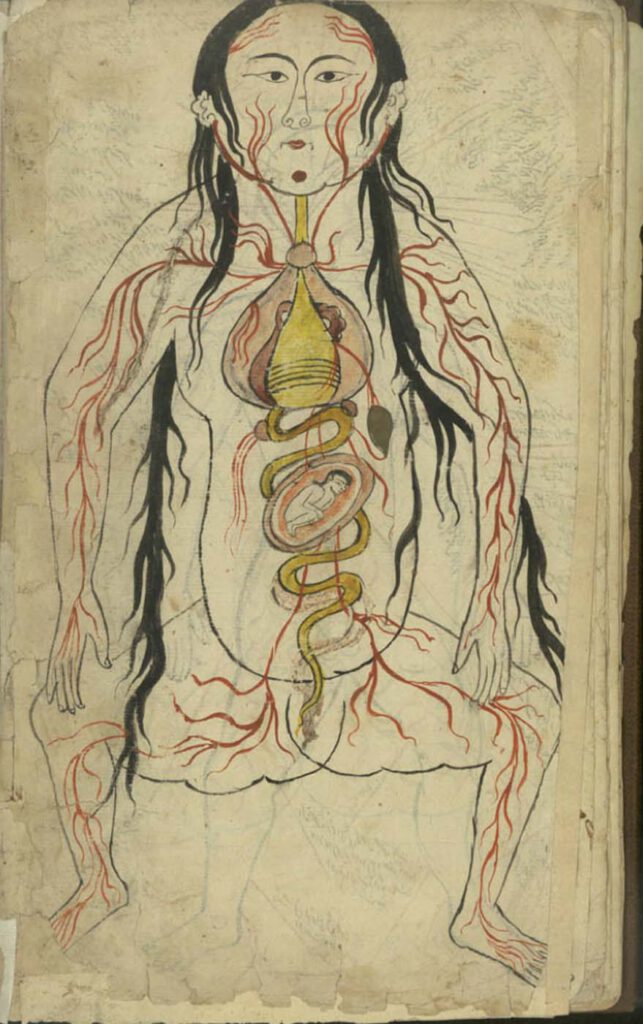
Representation of a woman with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 15v) Manṣūr ibn Ilyās (fl. 14th c.), Tashrīḥ-i badan-i insān. Images from: Teheran MS Majlis 7430. Undated. This image represents the heart, lungs, liver, esophagus/larynx, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and spleen). As in the male representation, the organs involved in […]
Representation of a man with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 13v)
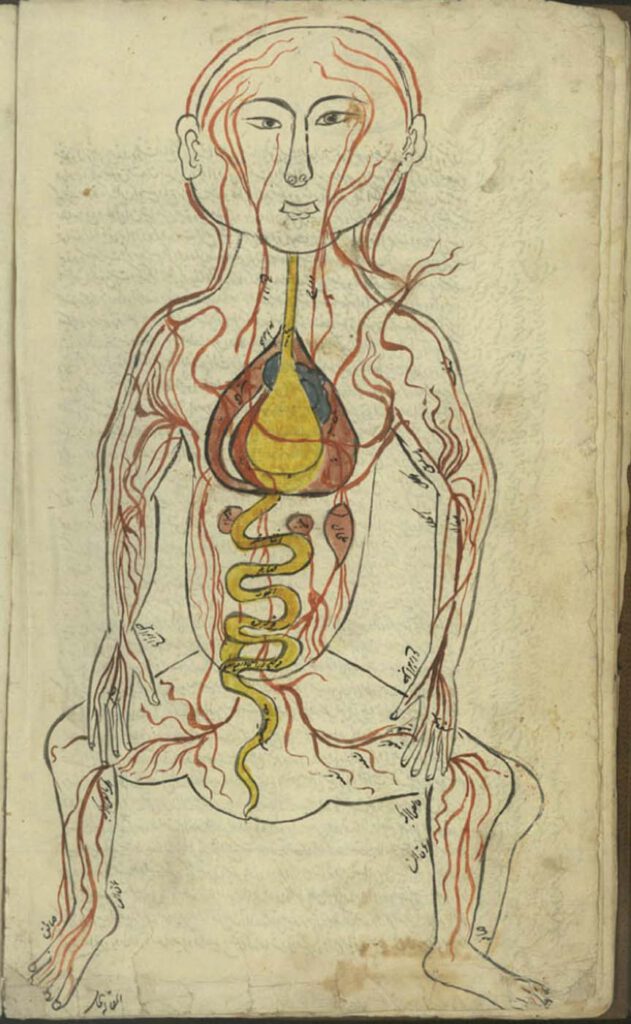
Representation of a man with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 13v) Manṣūr ibn Ilyās (fl. 14th c.), Tashrīḥ-i badan-i insān. Images from: Teheran MS Majlis 7430. Undated. The illustration depicts the heart, lungs, liver, esophagus/larynx, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and spleen. The organs involved in digestion are coloured in yellow. […]
Illustration depicting a right lateral view of the body (f. 72r)
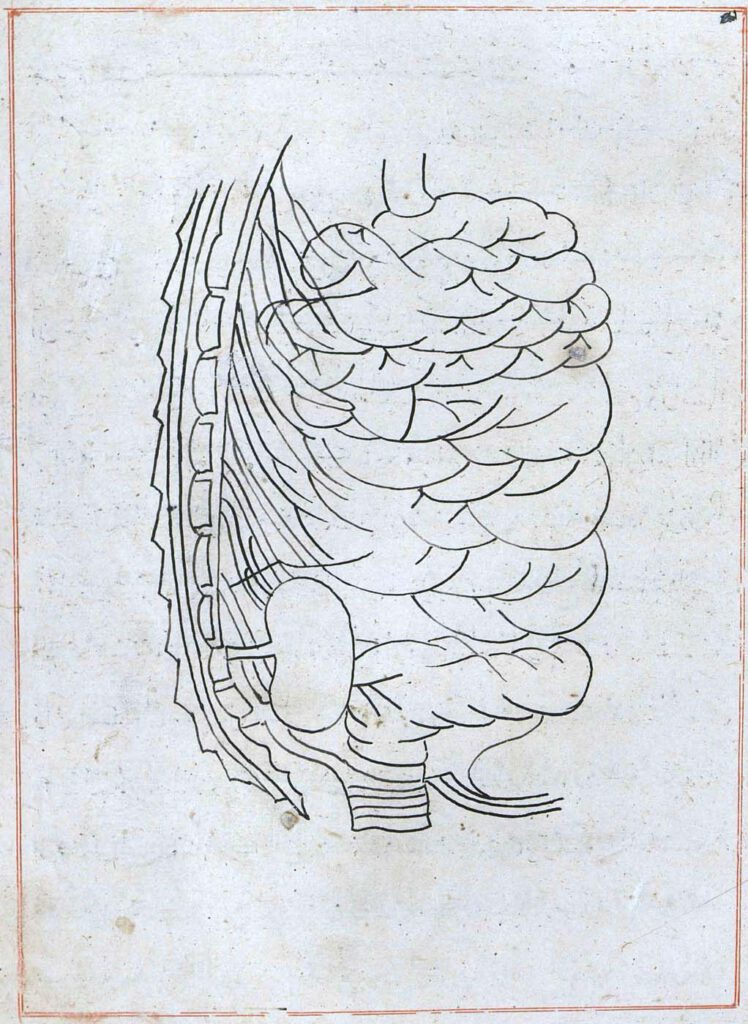
Illustration depicting a right lateral view of the body (f. 72r) Tansūqnāmah-i Īlkhān dar funūn-i ʿulūm-i Khatāʾī (Ilkhan’s Treasure Book on the Branches of the Chinese Sciences). Istanbul MS Aya Sofya 3596. Tabriz, 1313. The image closes the sixth section. It shows the spine, the right kidney, the intestines, and the bladder. – Read the […]
Frontal illustration of the small and large intestines and the bladder (f. 69v)
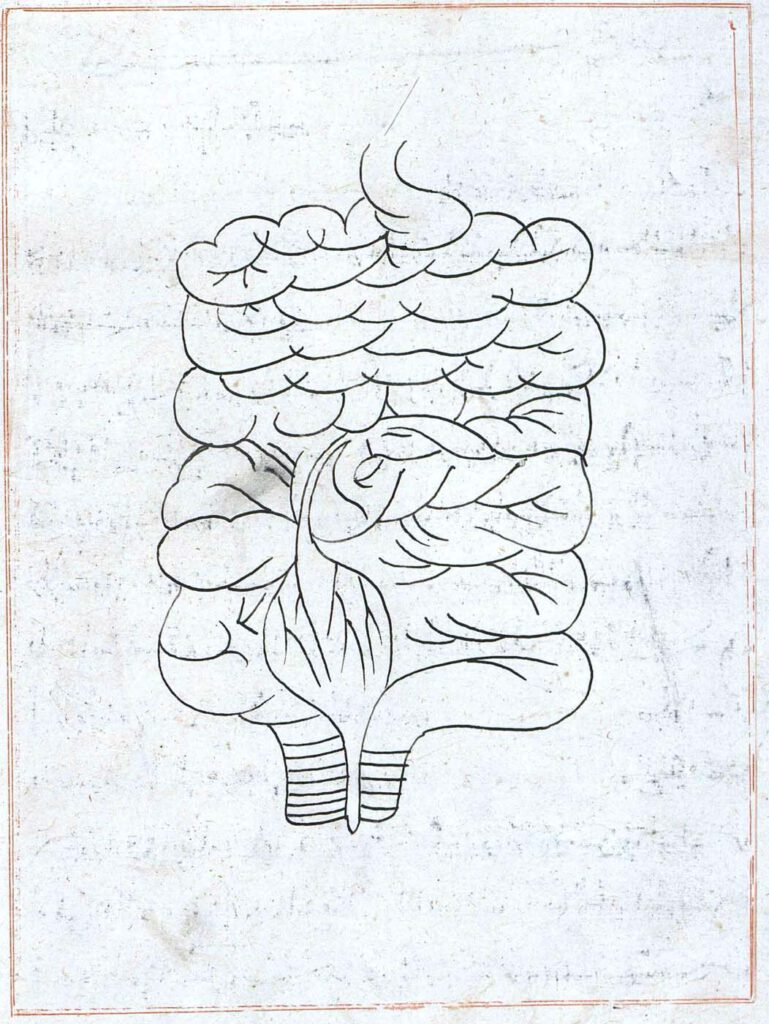
Frontal illustration of the small and large intestines and the bladder (f. 69v) Tansūqnāmah-i Īlkhān dar funūn-i ʿulūm-i Khatāʾī (Ilkhan’s Treasure Book on the Branches of the Chinese Sciences). Istanbul MS Aya Sofya 3596. Tabriz, 1313. This illustration occurs right before the beginning of the sixth section of the book (f. 70r) describing the connection […]
Illustration accompanying De Arte Physicali et de Cirurgia
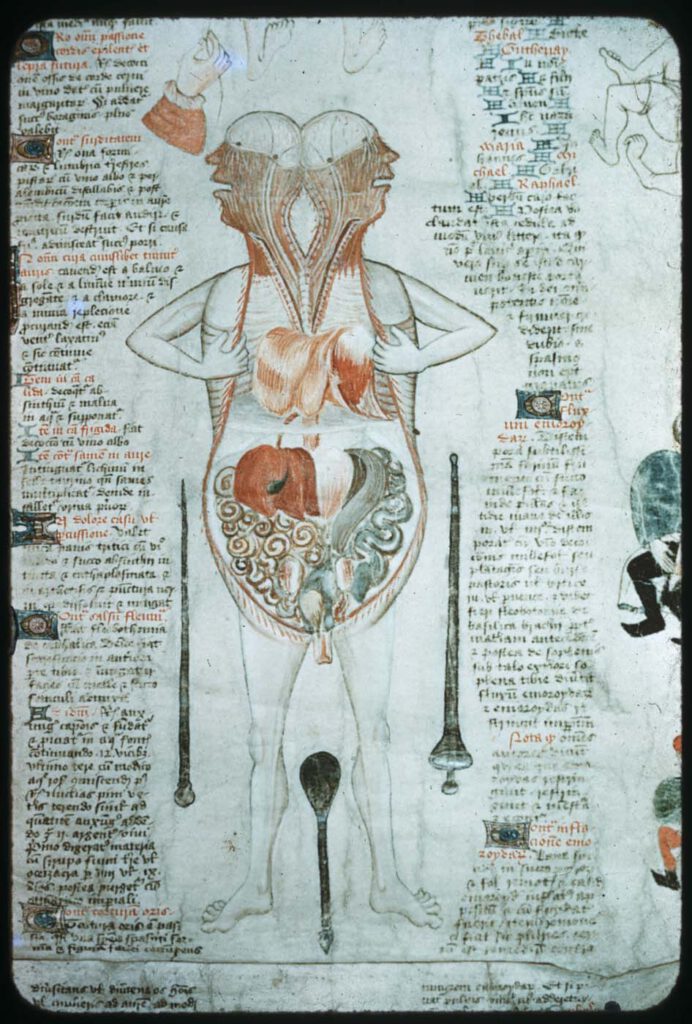
Illustration accompanying De Arte Physicali et de Cirurgia, attributed to John Arderne Stockholm, Kungliga Biblioteket X.118, fol. 6v/6r; c. 1430 – While the frontal approach to anatomical illustration exhibited in the Five/Nine-Figure Series and Guido da Vigevano’s work is most dominant, an alternative, sagittal approach emerged in the medieval period and survives in a few […]
Guido da Vigevano’s Anathomia, Figure 8
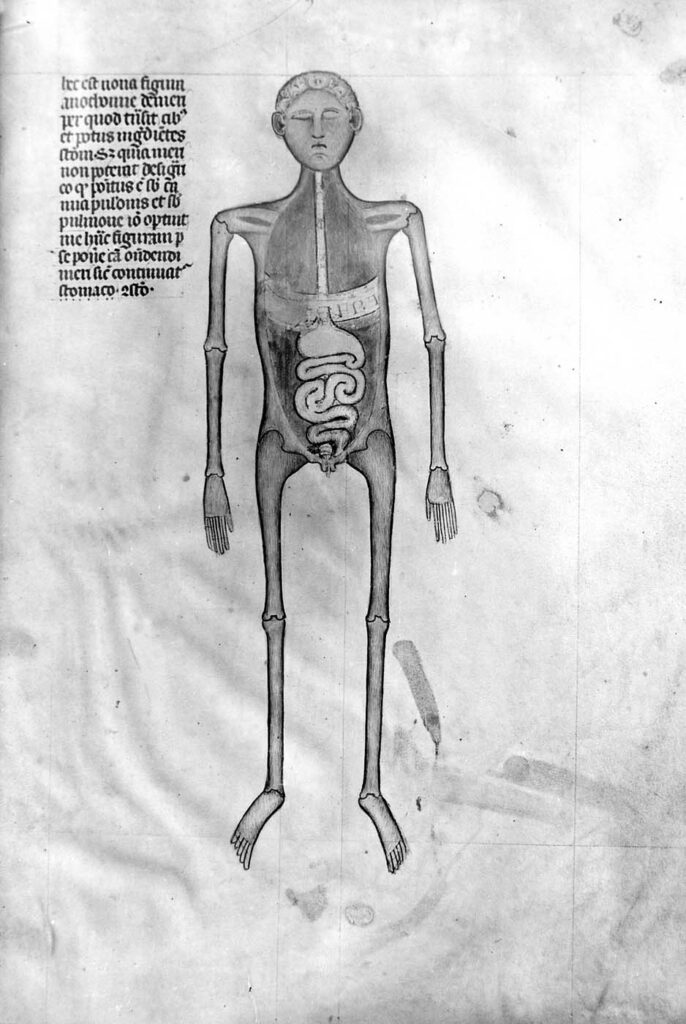
Guido da Vigevano’s Anathomia, Figure 9 (1345) Guido da Vigevano, Anathomia, 1345CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – Although human dissection began to be systematically practiced in Italy in the early 14th century, it was not immediately embraced across Europe. This prompted Guido da Vigevano to produce a series of seventeen illustrations included in his Book of Notable […]
Terracotta anatomical votive; spiral coil ending in trefoil
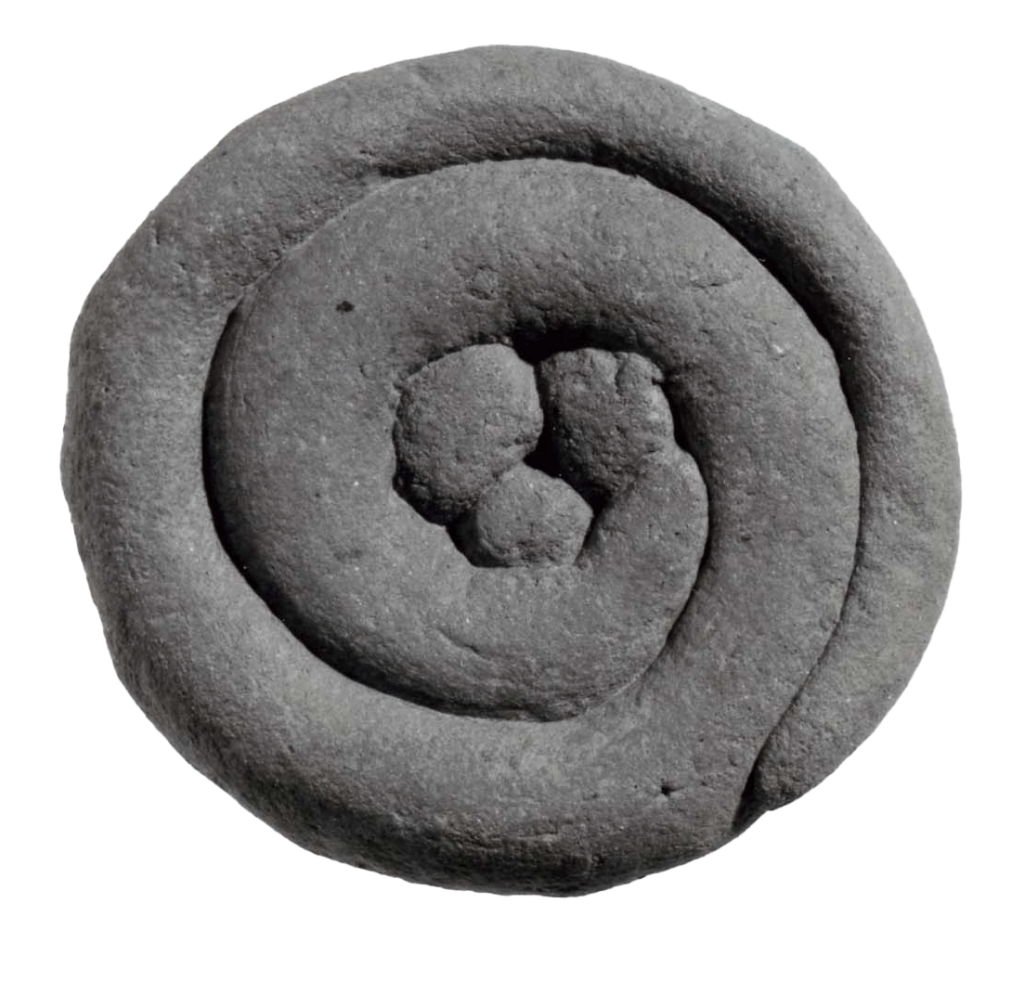

Terracotta anatomical votive; spiral coil ending in trefoil. Tivoli/Lazio, 3rdC BC-1stC BC © The Trustees of the British Museum Museum Number 1899,0720.13 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – This terracotta votive nicely combines the clean volumetric rotundity of the belly with the coiled shape of the imagined innards (intestines? the uterus? the spiral image as an abstract […]
