Rāja Mandhata

Rāja Mandhata Nurpur, Himachal Pradesh, India c. 1690–1700. Source: Cleveland Museum of Art CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) – The yogic body was configured in different ways by various traditions. The abdomen was thought to be the seat of fire in the body, and it could be stimulated by the practice of physical yoga postures, […]
Food’s Course of Movement in the Intestines (engraving)
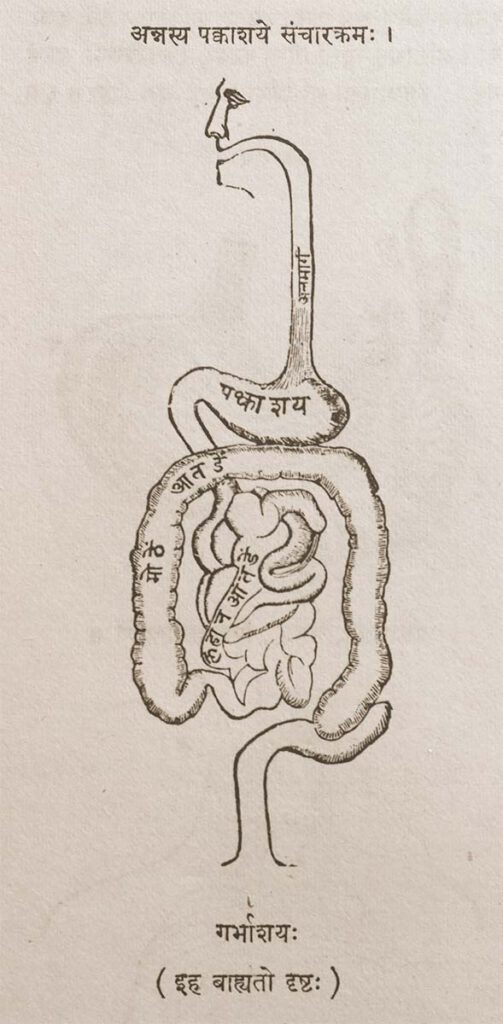
Food’s Course of Movement in the Intestines (engraving) Provenance: Printed Book, page 44. Anglicized Bibliographic data The Śārṅgadhara-saṃhitā by Paṇḍit Śārṅgadharāchārya, son of Paṇḍit Dāmodara with the commentary Aḍhamalla’s Dīpikā and Kāśīrāma’s Gūḍhārtha-Dīpikā. Ed. Paṇḍitaparaśurāmaśāstri. Bombay: Pāndurang Jāwajī, Nirṇaya-Sāgar Press, 1931. Sanskrit Title and Author in Roman font śrīmatpaṇḍitadāmodarasūnu-śārṅgadharācāryaviracitā . śārṅgadharasaṃhitā . bhiṣagvarāḍhamallaviracitadīpikā-paṇḍitakāśirāmavaidyaviracita-gūḍhārthadīpikābhyāṃ ṭīkābhyāṃ saṃvalitā […]
Indian anatomical painting
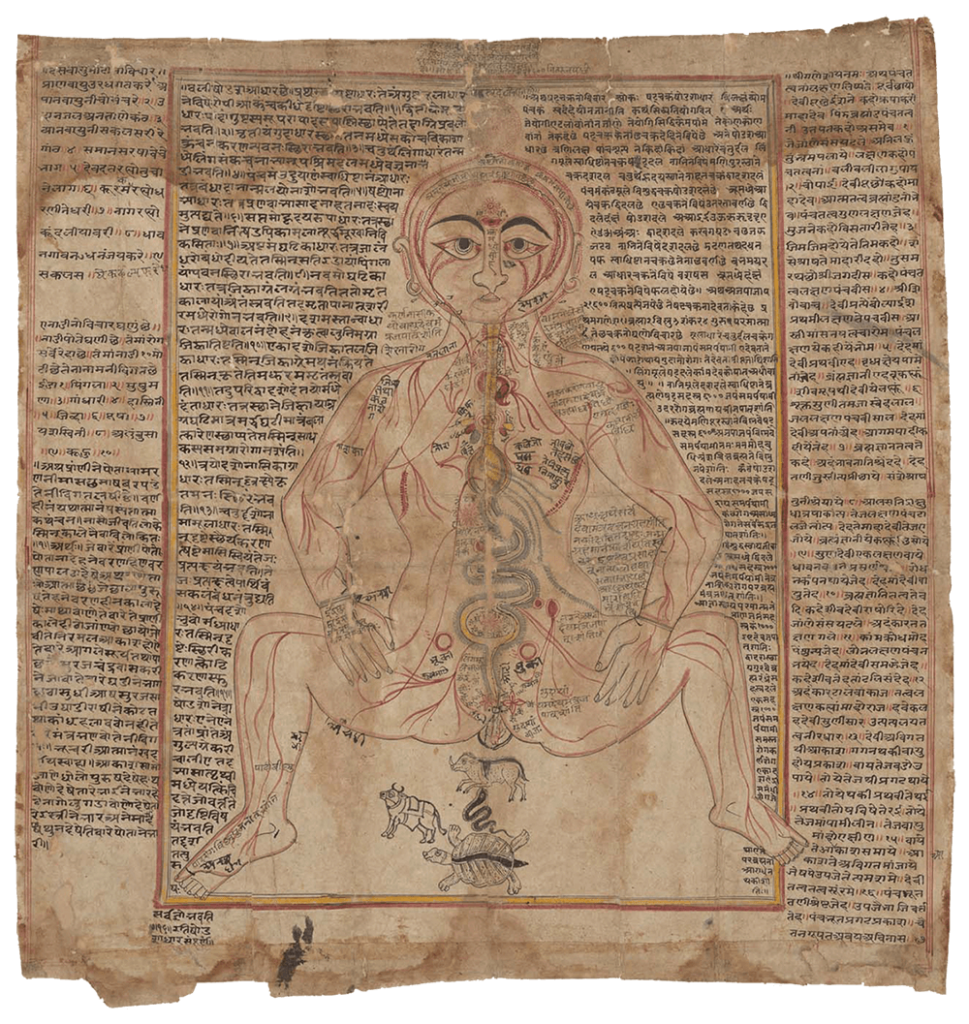
Indian anatomical painting Circa eighteenth century, western India. An old-Gujarati manuscript (circa 1900?). (Wellcome MS Indic d 74. Photo Wellcome Library, London.) Source: Wellcome Collection CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – Premodern anatomical images in India were influenced by Persian drawings on anatomy, particularly during the Mughal dynasty’s reign in north India from the sixteenth to eighteenth […]
A human anatomical figure
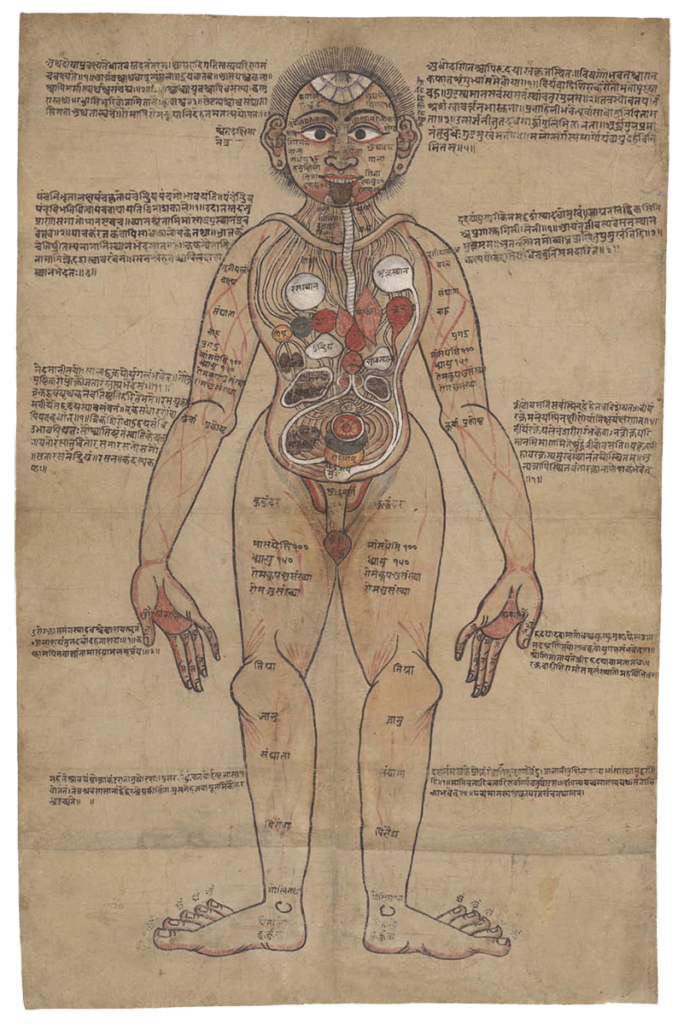
A human anatomical figure Drawing, Nepalese, ca. 1800 (?) Source: Wellcome Library no. 574912iWellcome Collection. Public Domain Mark. – Although India has thousands of manuscripts of premodern medical texts, only a handful contain anatomical illustrations. Text was crucially important for transmitting medical teachings. Figure 1 combines text with an illustration of the body and its […]
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra
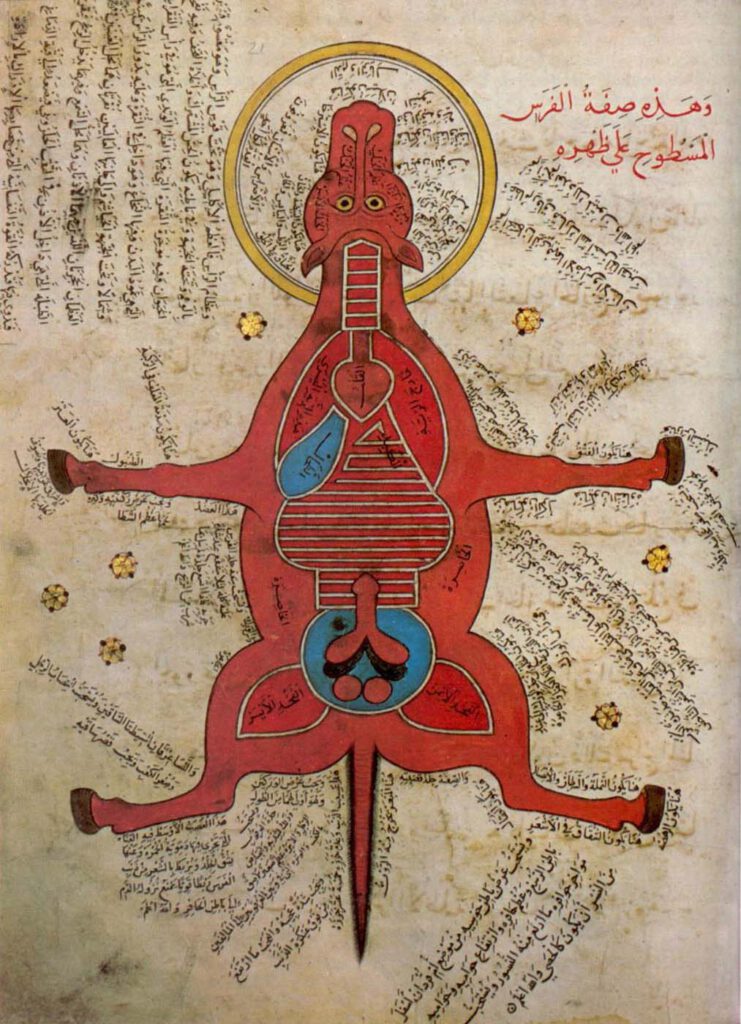
Anonymous, K. Sharḥ al-Maqāma al-Ṣalāḥiyya fī l-Khayl wa-al-Bayṭāra (Commentary on the Maqāma Ṣalāḥiyya on Horses and Venterinary) Istanbul University Library MS 4689 – Egypt, 15th c. – Hyppiatry has a long tradition in Islamic literature. Works dealing with horses may adopt different literary genres and cover a wide range of disciplines, from veterinary sciences to […]
Representation of a woman with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 15v)
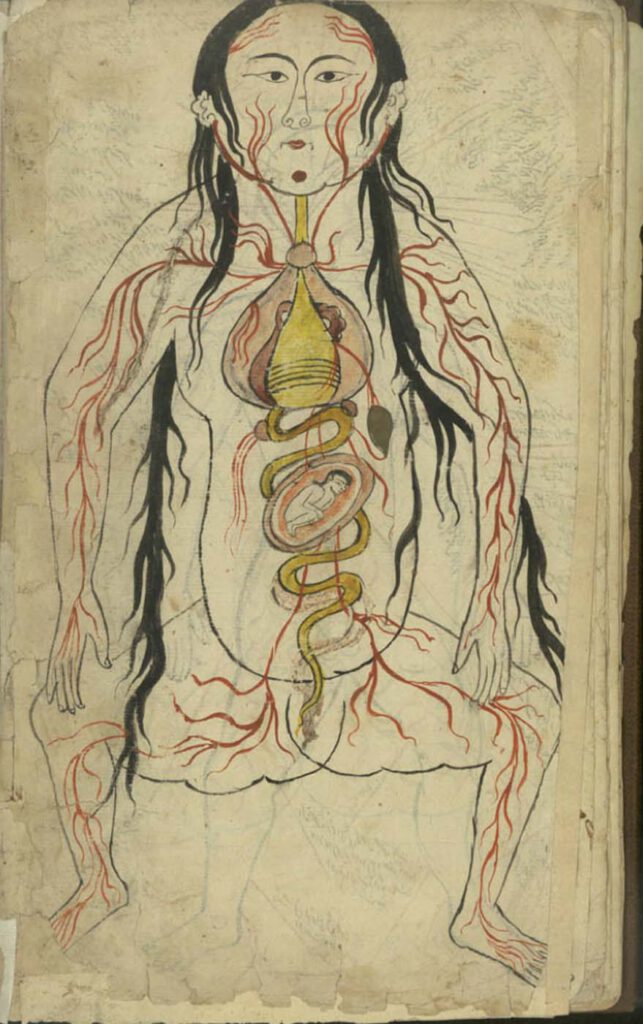
Representation of a woman with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 15v) Manṣūr ibn Ilyās (fl. 14th c.), Tashrīḥ-i badan-i insān. Images from: Teheran MS Majlis 7430. Undated. This image represents the heart, lungs, liver, esophagus/larynx, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and spleen). As in the male representation, the organs involved in […]
Representation of a man with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 13v)
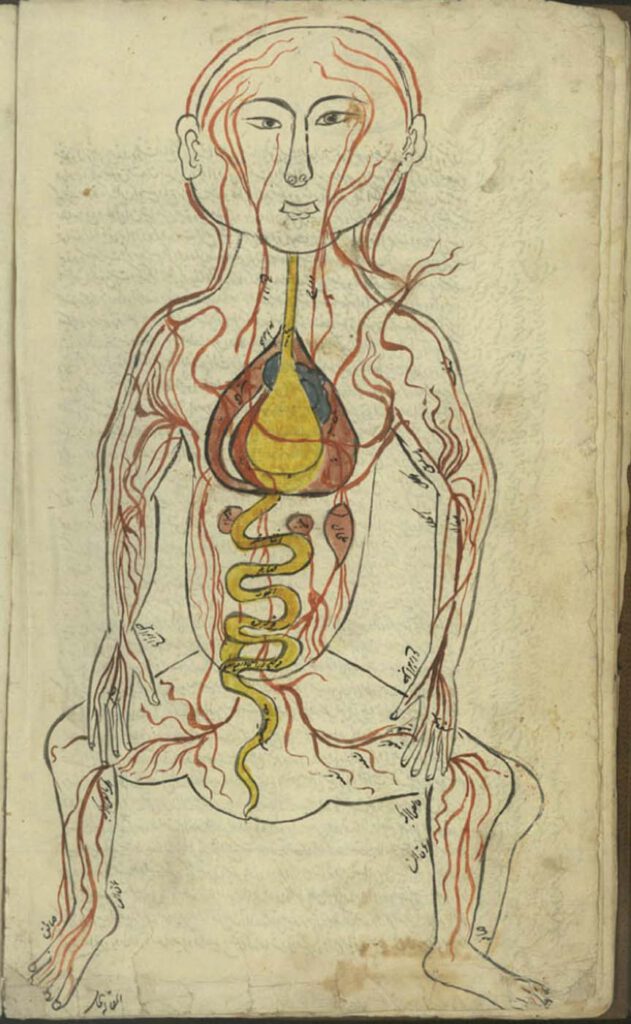
Representation of a man with the distribution of the blood vessels and the internal organs (f. 13v) Manṣūr ibn Ilyās (fl. 14th c.), Tashrīḥ-i badan-i insān. Images from: Teheran MS Majlis 7430. Undated. The illustration depicts the heart, lungs, liver, esophagus/larynx, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and spleen. The organs involved in digestion are coloured in yellow. […]
Illustration depicting a right lateral view of the body (f. 72r)
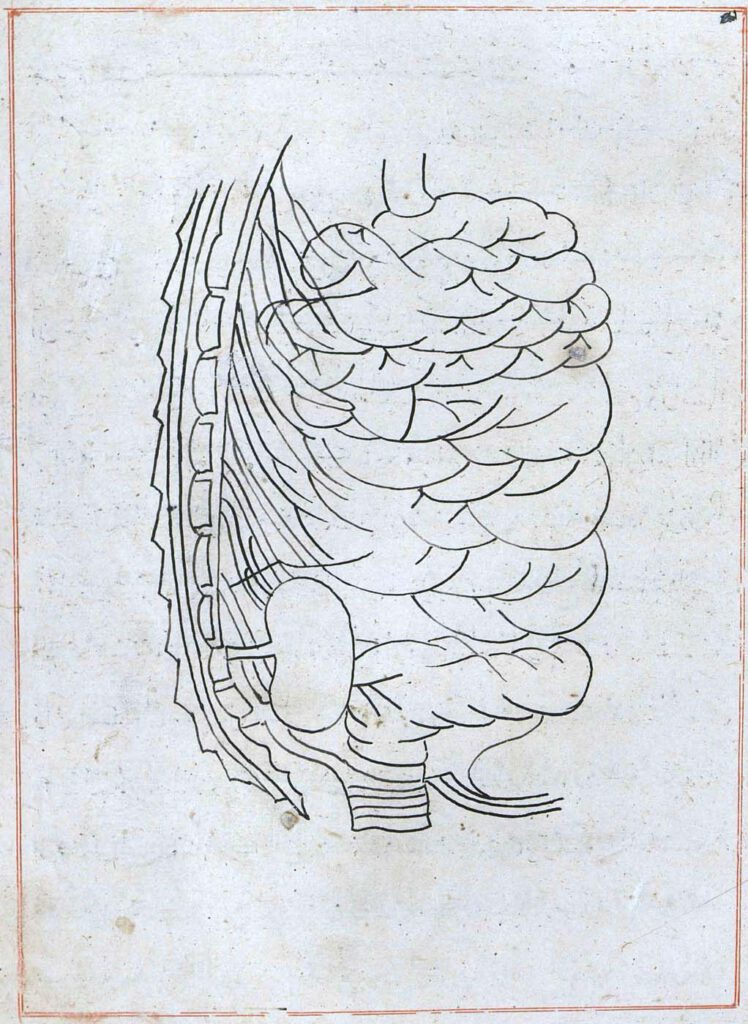
Illustration depicting a right lateral view of the body (f. 72r) Tansūqnāmah-i Īlkhān dar funūn-i ʿulūm-i Khatāʾī (Ilkhan’s Treasure Book on the Branches of the Chinese Sciences). Istanbul MS Aya Sofya 3596. Tabriz, 1313. The image closes the sixth section. It shows the spine, the right kidney, the intestines, and the bladder. – Read the […]
Frontal illustration of the small and large intestines and the bladder (f. 69v)
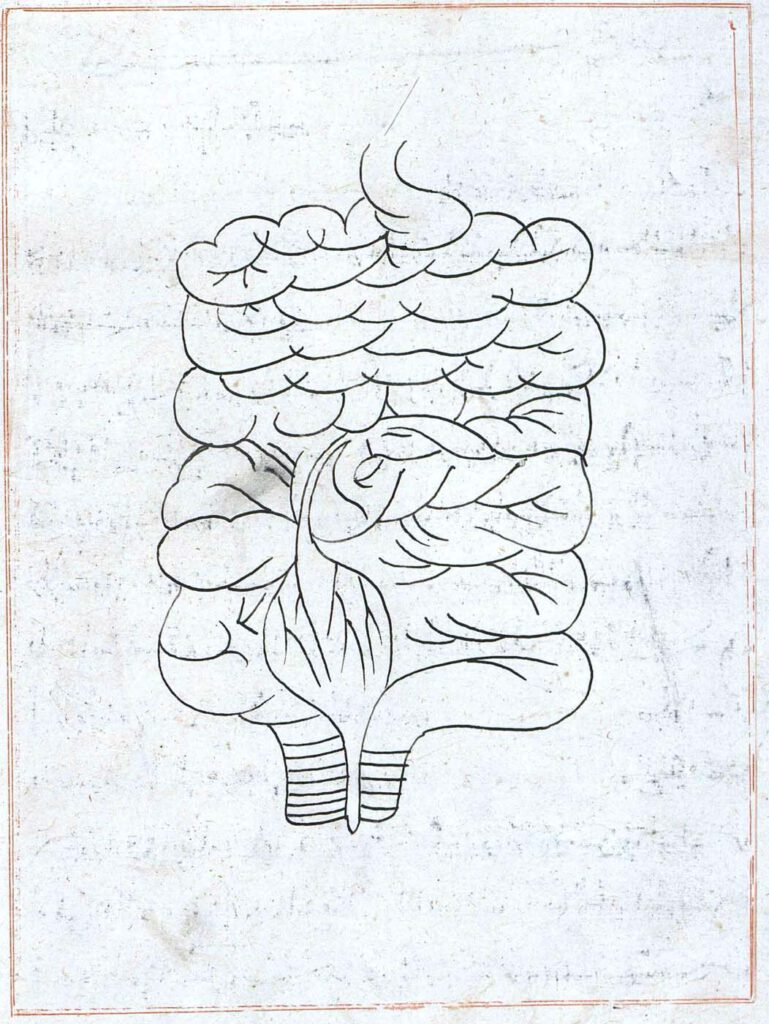
Frontal illustration of the small and large intestines and the bladder (f. 69v) Tansūqnāmah-i Īlkhān dar funūn-i ʿulūm-i Khatāʾī (Ilkhan’s Treasure Book on the Branches of the Chinese Sciences). Istanbul MS Aya Sofya 3596. Tabriz, 1313. This illustration occurs right before the beginning of the sixth section of the book (f. 70r) describing the connection […]
A Brave Warrior with Guts
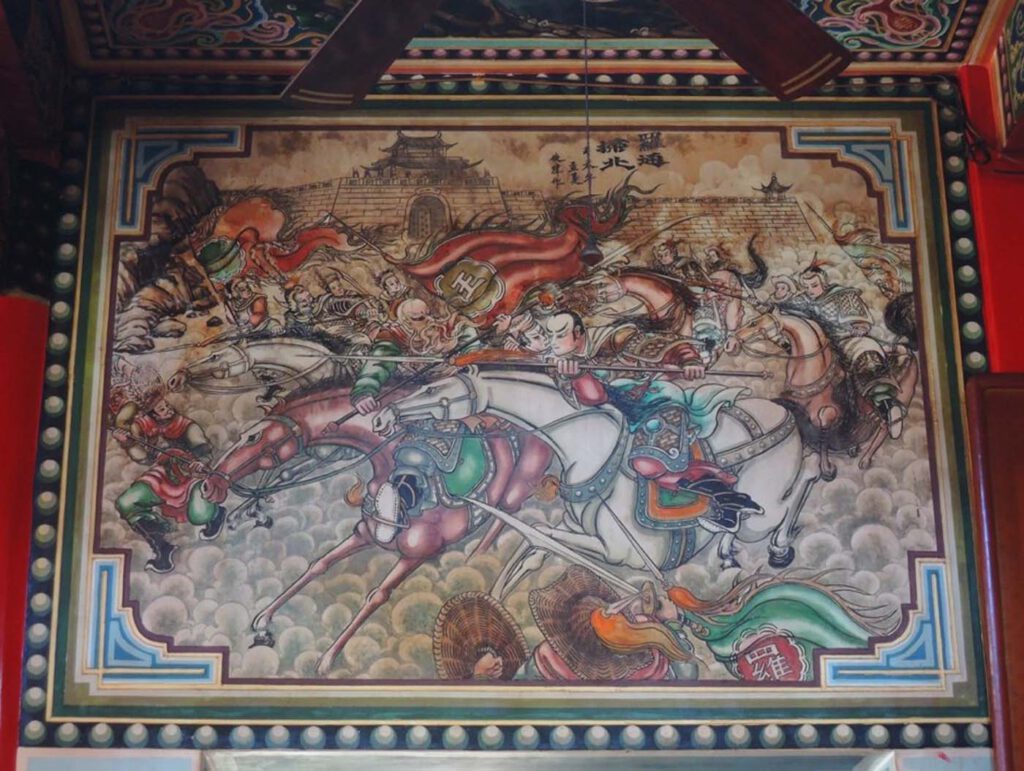

A Brave Warrior with Guts (1991)”Luo Tong Sweeps the North”, Caiyuan dong’an’gong Temple, Magong CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 – Wall painting is an adequate to transmit the religion’s value. This painting in a Taoist temple depicts a scene before the heroic sacrifice of a fictional warrior. When General Luo Tong joined Emperor Tang Taizong’s (reign 626-649) expeditionary […]
